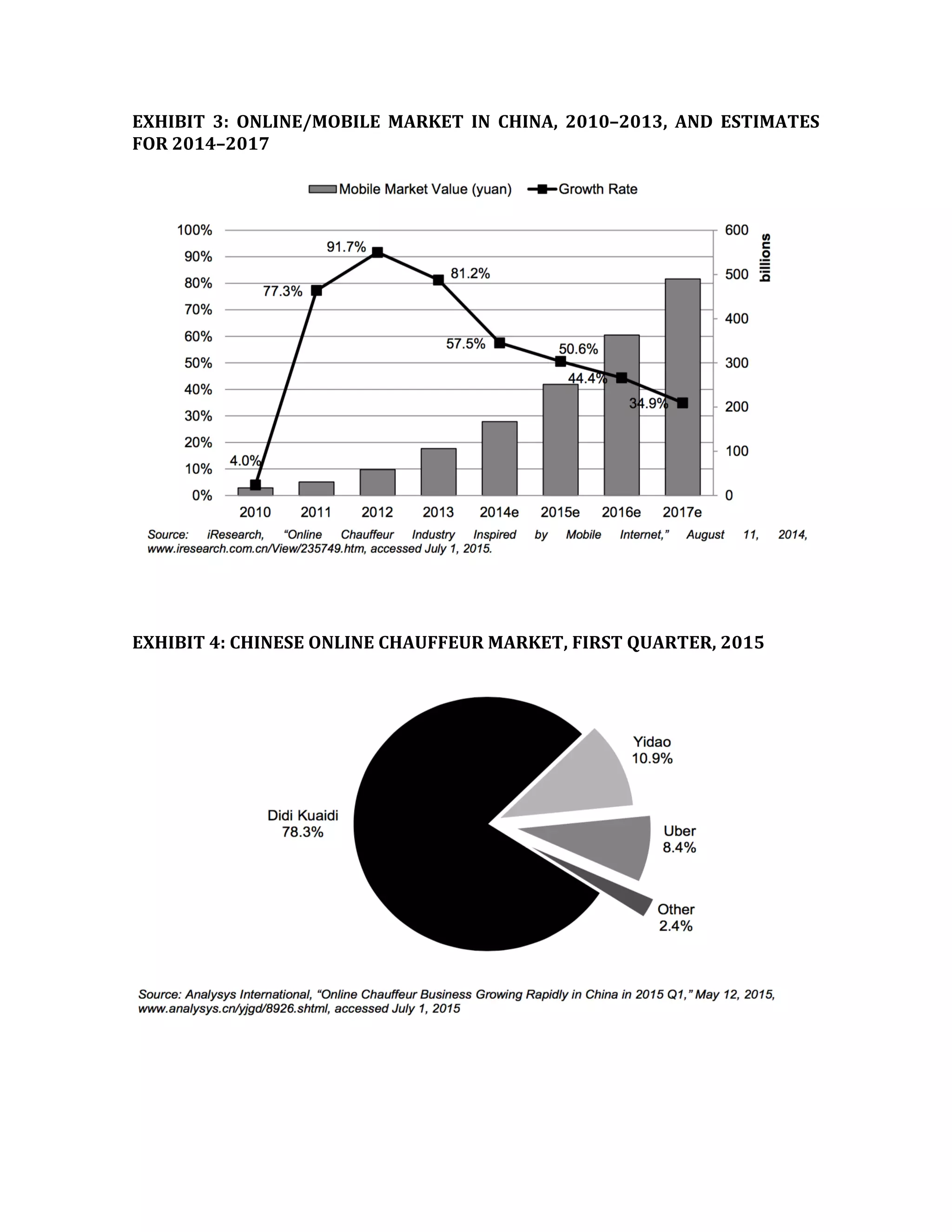
Uber is expanding globally and considering entering the Chinese market. The document provides background on Uber's founding in 2009 as a mobile app for ridesharing. It has grown rapidly to operate in over 68 countries and 300 cities worldwide. Uber faces challenges expanding into new markets from opposition by taxi unions and regulators, as well as some safety and ethical concerns regarding surge pricing. The company aims to disrupt the taxi industry with its business model of using independent contractor drivers without owning vehicles itself.