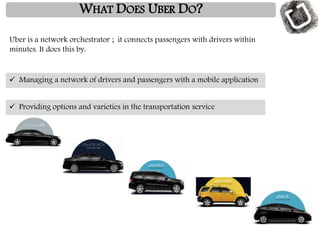
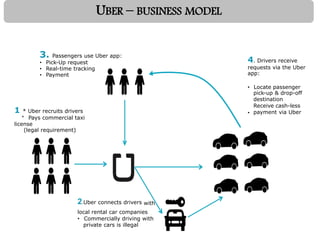
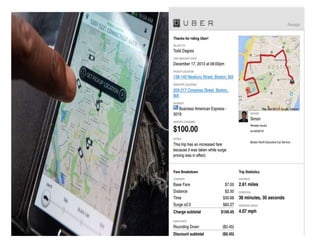
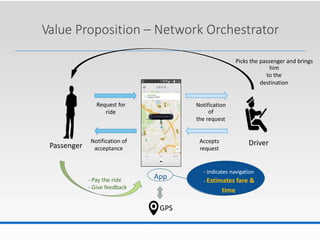
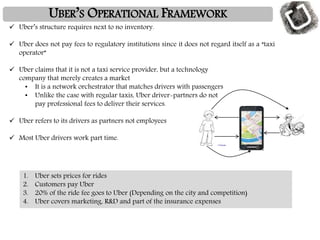
Uber was founded in 2009 and has expanded rapidly to operate in over 60 countries. It connects riders to drivers through a mobile app, allowing riders to request trips that are routed to nearby drivers. Uber argues it is a technology company, not a transportation provider, as it does not own vehicles or directly employ drivers. The business model relies on recruiting partner drivers who use their personal vehicles. Surge pricing increases fares during high demand to incentivize more drivers to work. While competitors have emerged, Uber's large network gives it an advantage over potential alternatives.