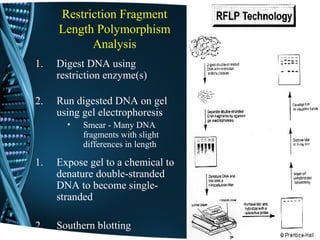
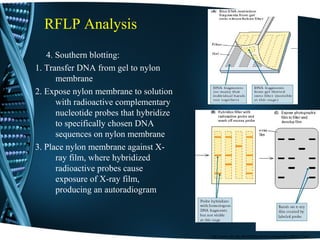
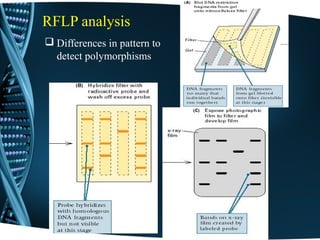
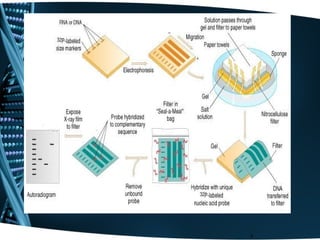
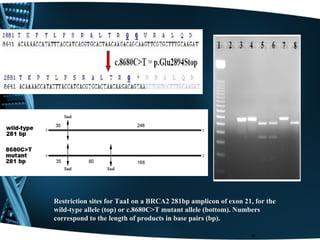
This document discusses Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, which is a technique used to differentiate organisms by analyzing patterns in their DNA after digestion with restriction enzymes. RFLP analysis can be used for various applications like determining paternity, detecting mutations, and genetic mapping. The process involves digesting DNA with restriction enzymes, running the fragments on a gel, transferring the DNA to a membrane, and using probes to detect polymorphisms and produce an autoradiogram showing differences in fragment patterns. As an example, the document describes using PCR-RFLP to rapidly screen for a BRCA2 mutation by taking advantage of a restriction site change caused by the mutation.