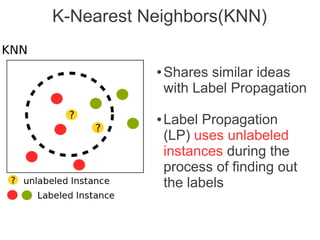
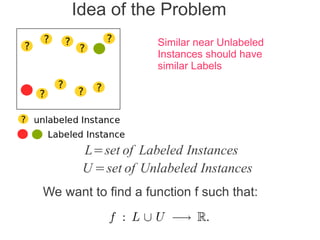
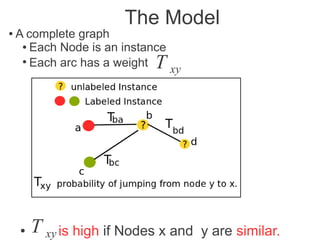
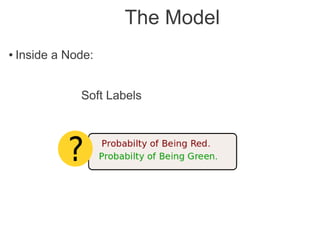
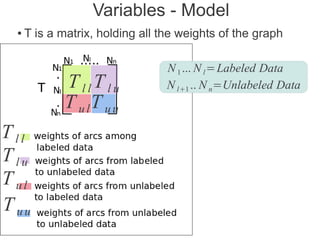
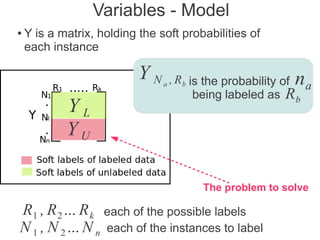
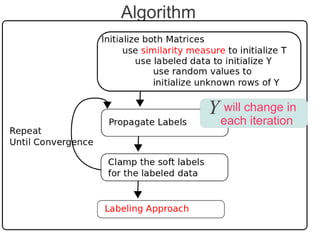
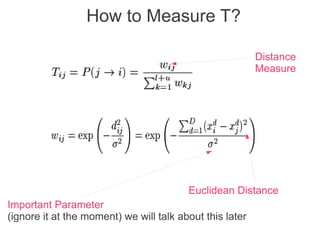
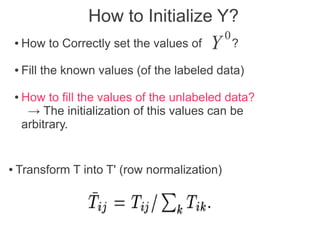
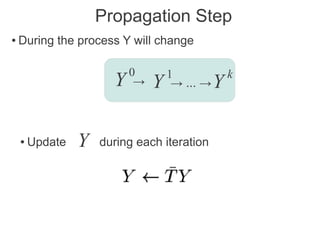
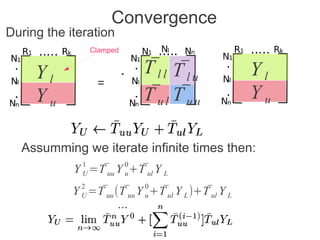
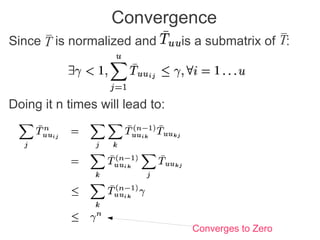
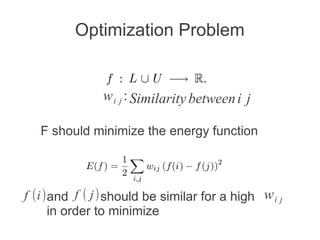
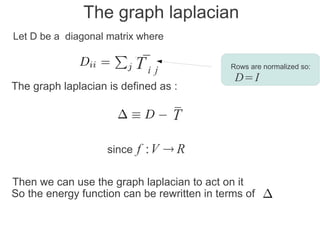
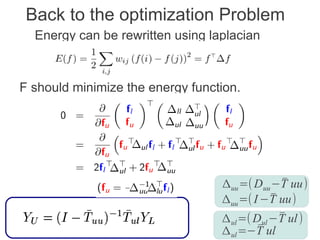
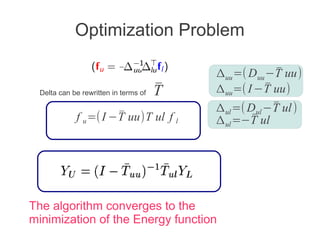
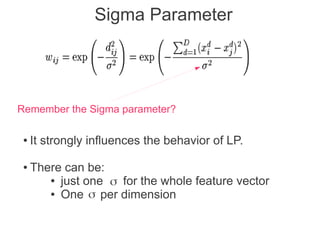
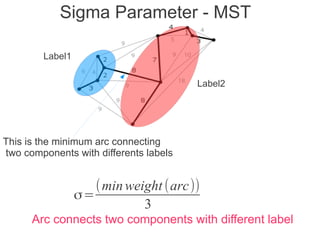
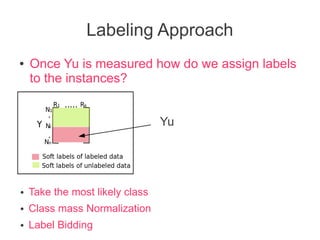
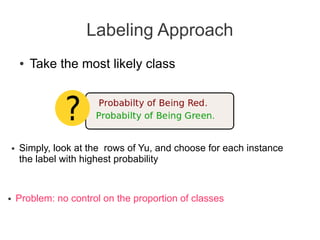
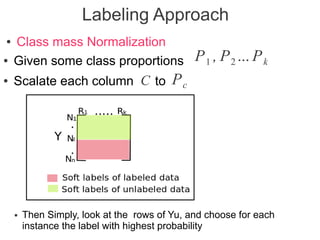
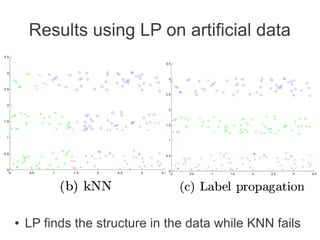
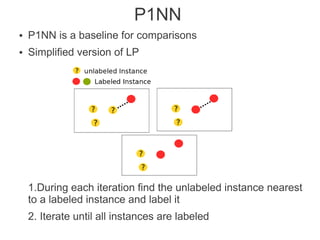
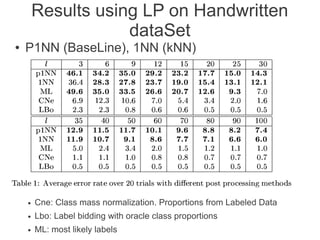
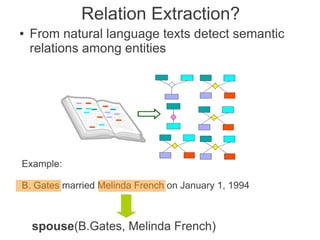
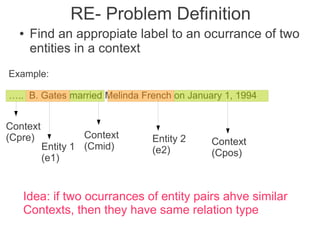
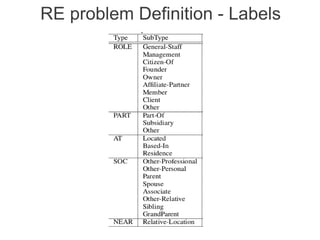
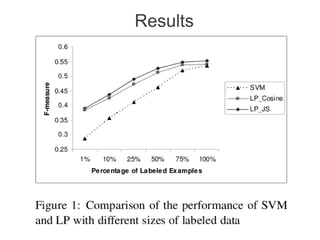
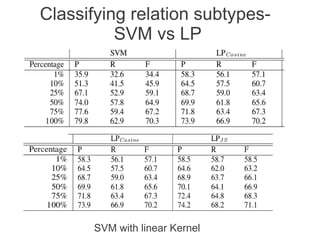
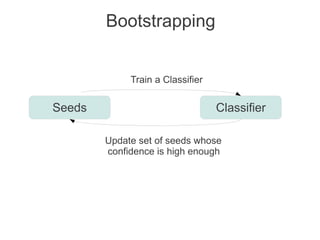
Label propagation is a semi-supervised learning algorithm that propagates labels from a small set of labeled data points to unlabeled data points. The algorithm constructs a graph with nodes for each data point and weighted edges representing similarity between points. It then iteratively propagates the labels across the graph from labeled to unlabeled points until convergence, resulting in "soft" probabilistic labels for all points. The algorithm aims to minimize an energy function that encourages points connected by strong edges to receive similar labels. It performs well with limited labeled data by leveraging the graph structure to make predictions for unlabeled points.