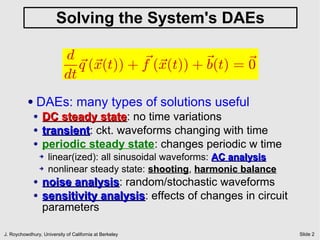
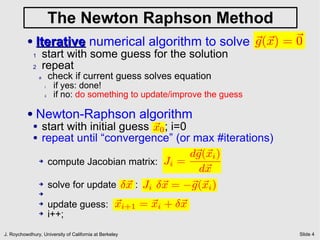
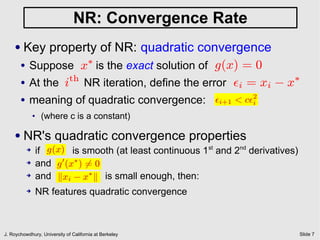
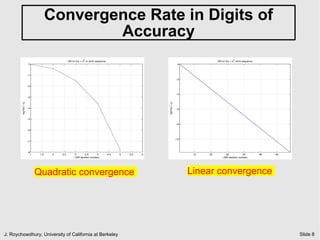
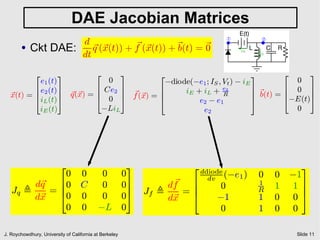
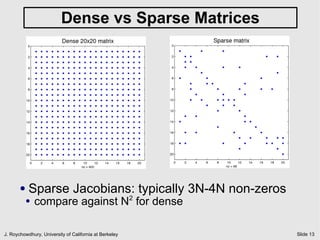
The document discusses quiescent steady state (DC) analysis using the Newton-Raphson method. It begins by introducing DC analysis and defining the goal as solving the system's differential algebraic equations (DAEs) under the assumption of no time variation. It then describes the Newton-Raphson method as an iterative numerical technique for solving nonlinear systems of equations. The method computes the Jacobian matrix at each iteration to determine the update to the state vector that will converge to a solution.