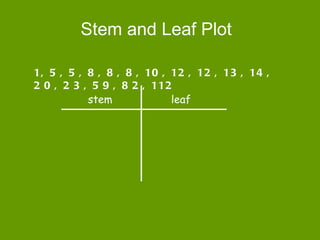
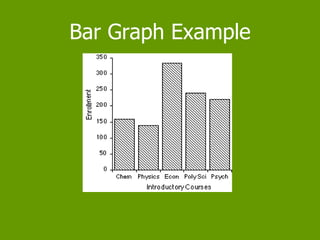
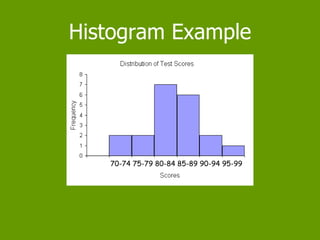
This document defines and provides examples of three different types of plots used to represent data distributions: stem and leaf plots, bar graphs, and histograms. It explains that stem and leaf plots organize large data sets by separating values into "stems" and "leaves", bar graphs represent frequencies using bars of equal or varying widths, and histograms use intervals to group continuous data and display frequencies. The document also lists advantages and disadvantages of each type of plot.