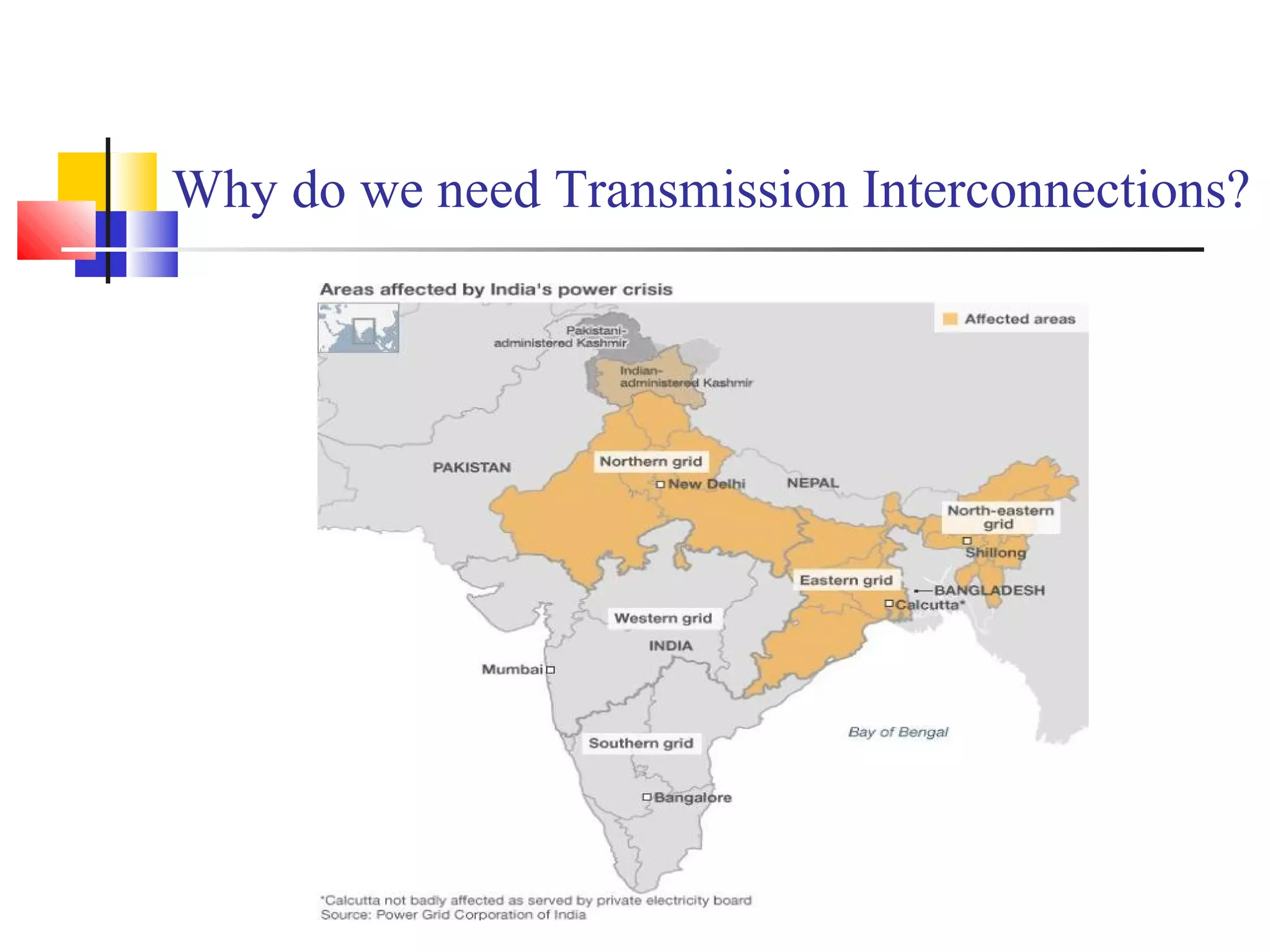
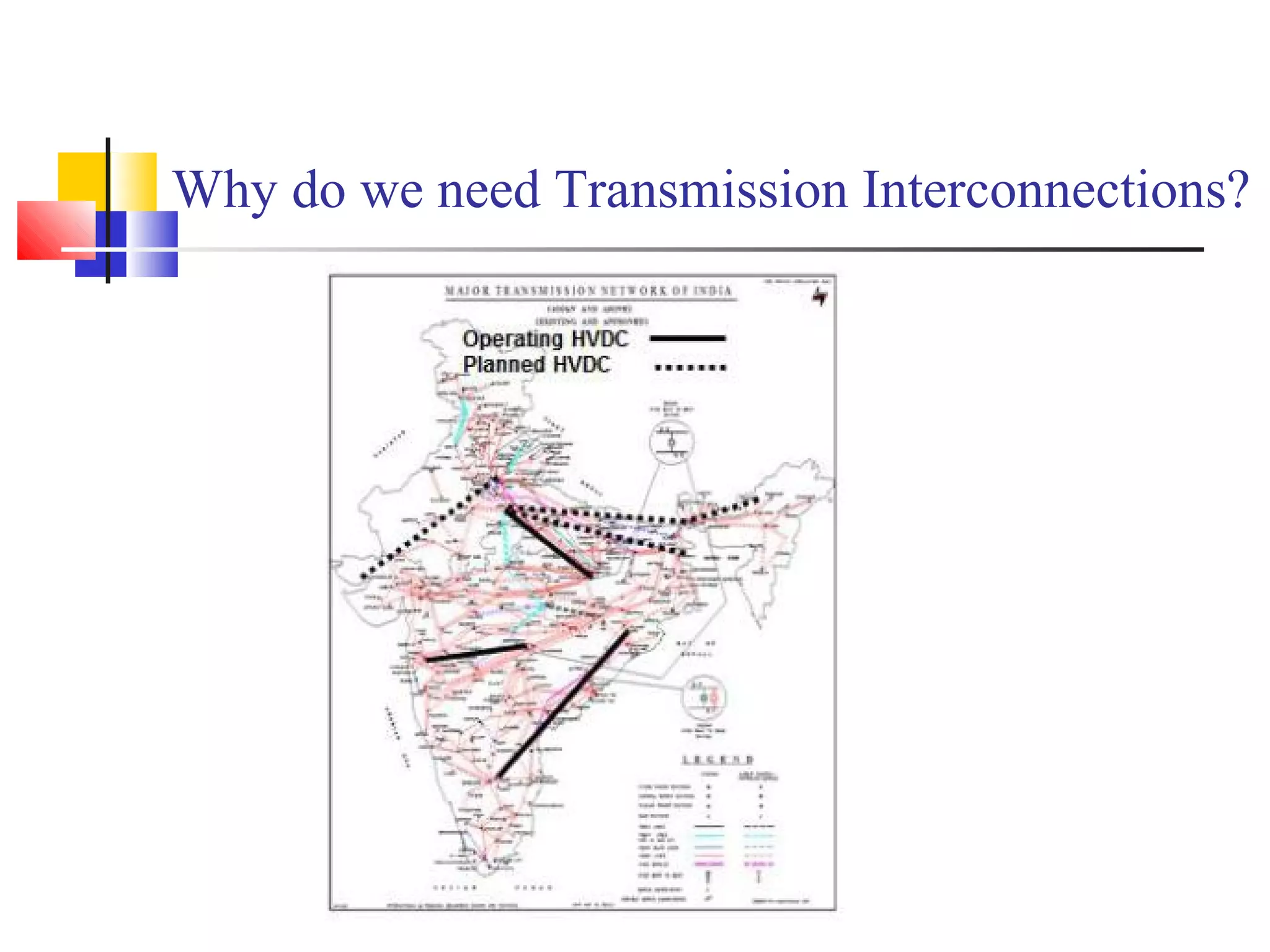
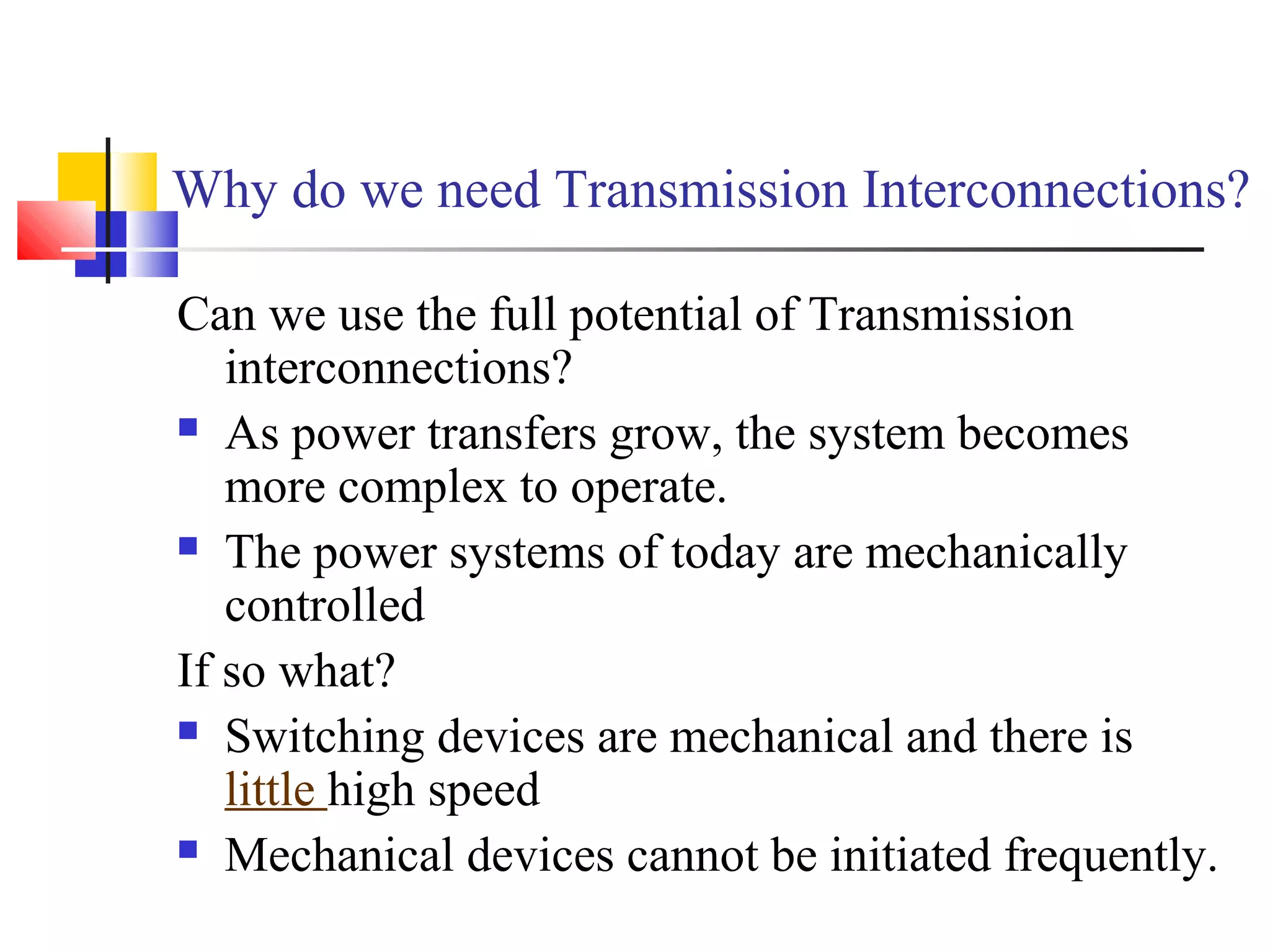
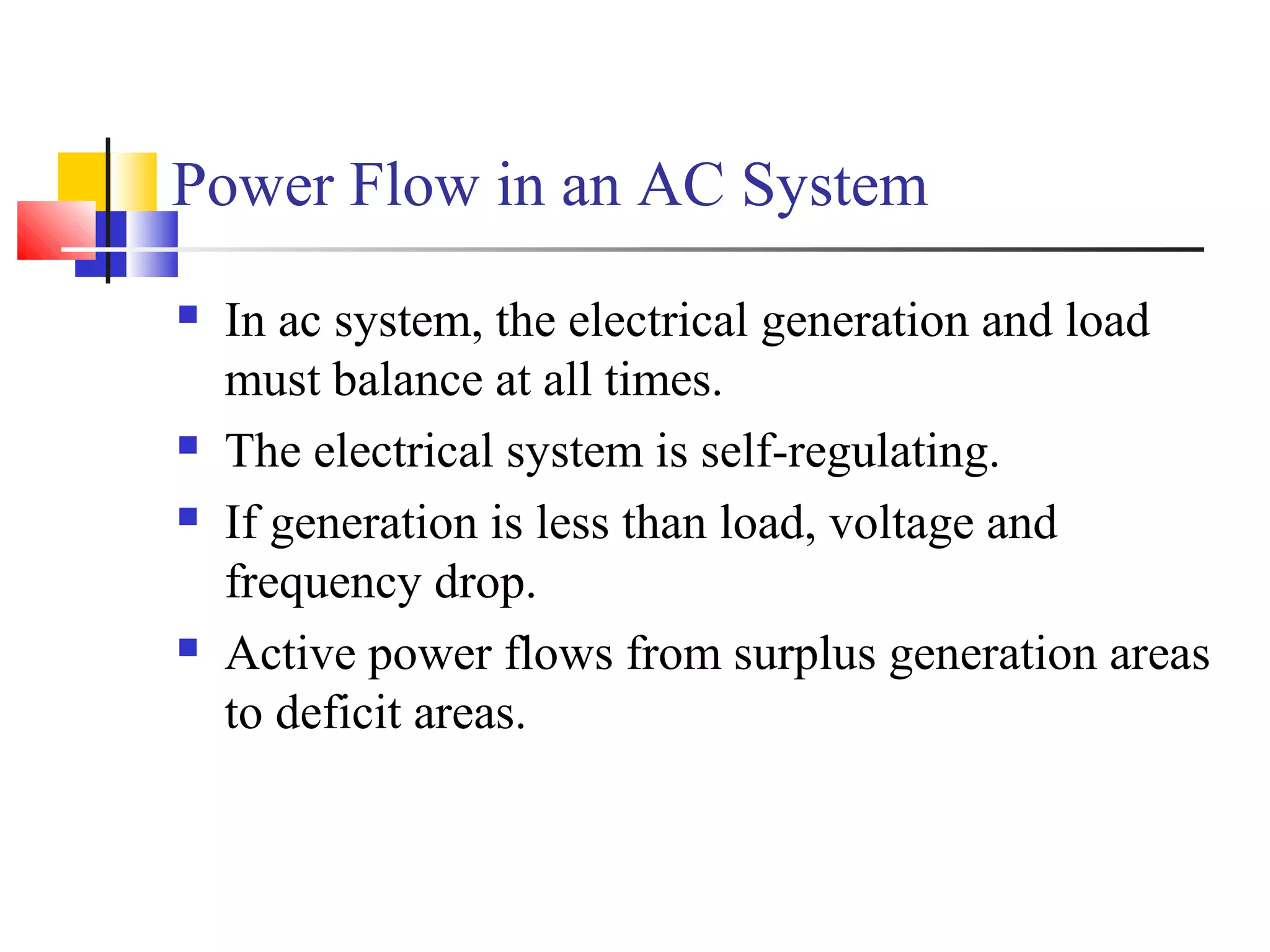
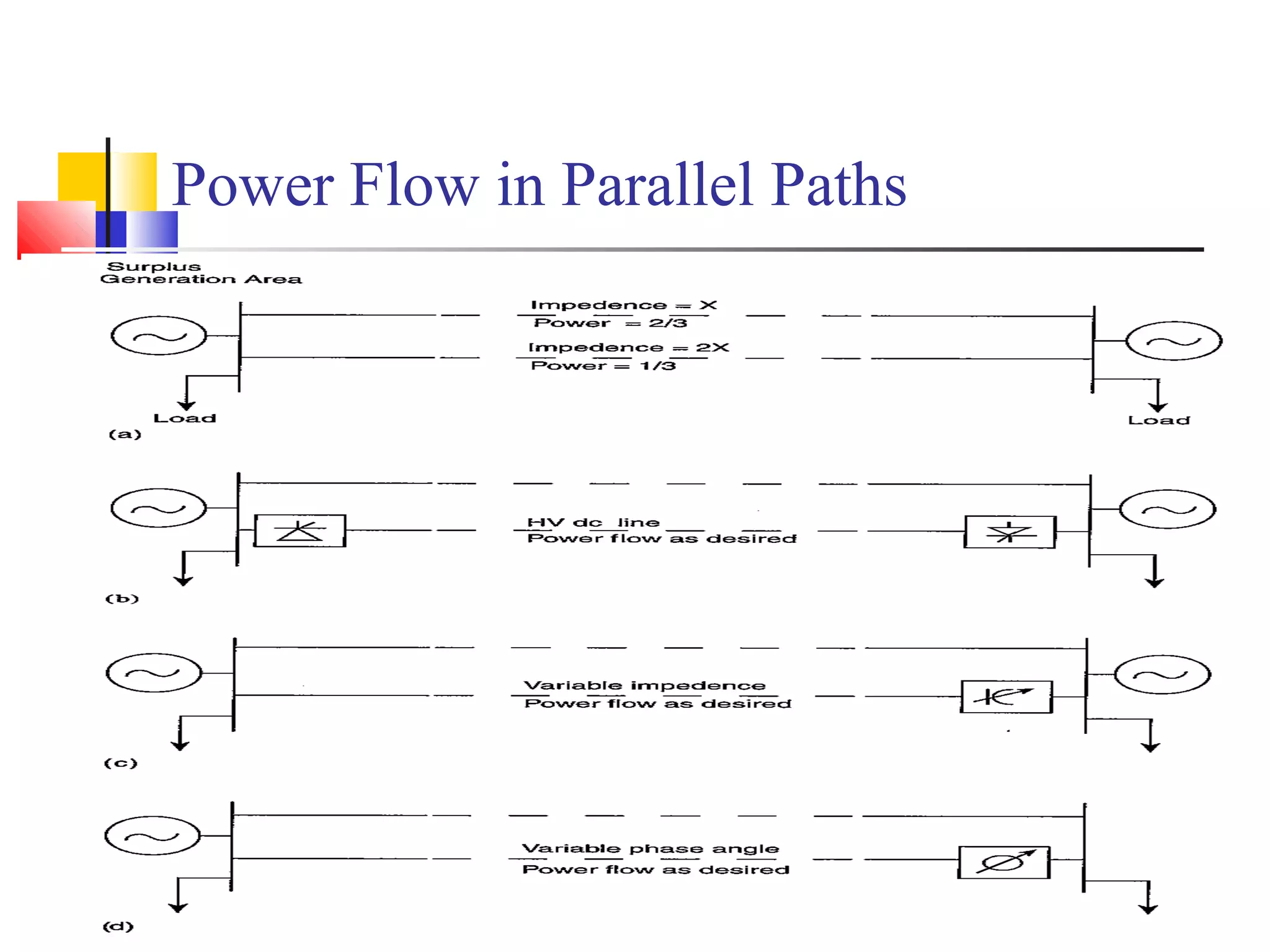
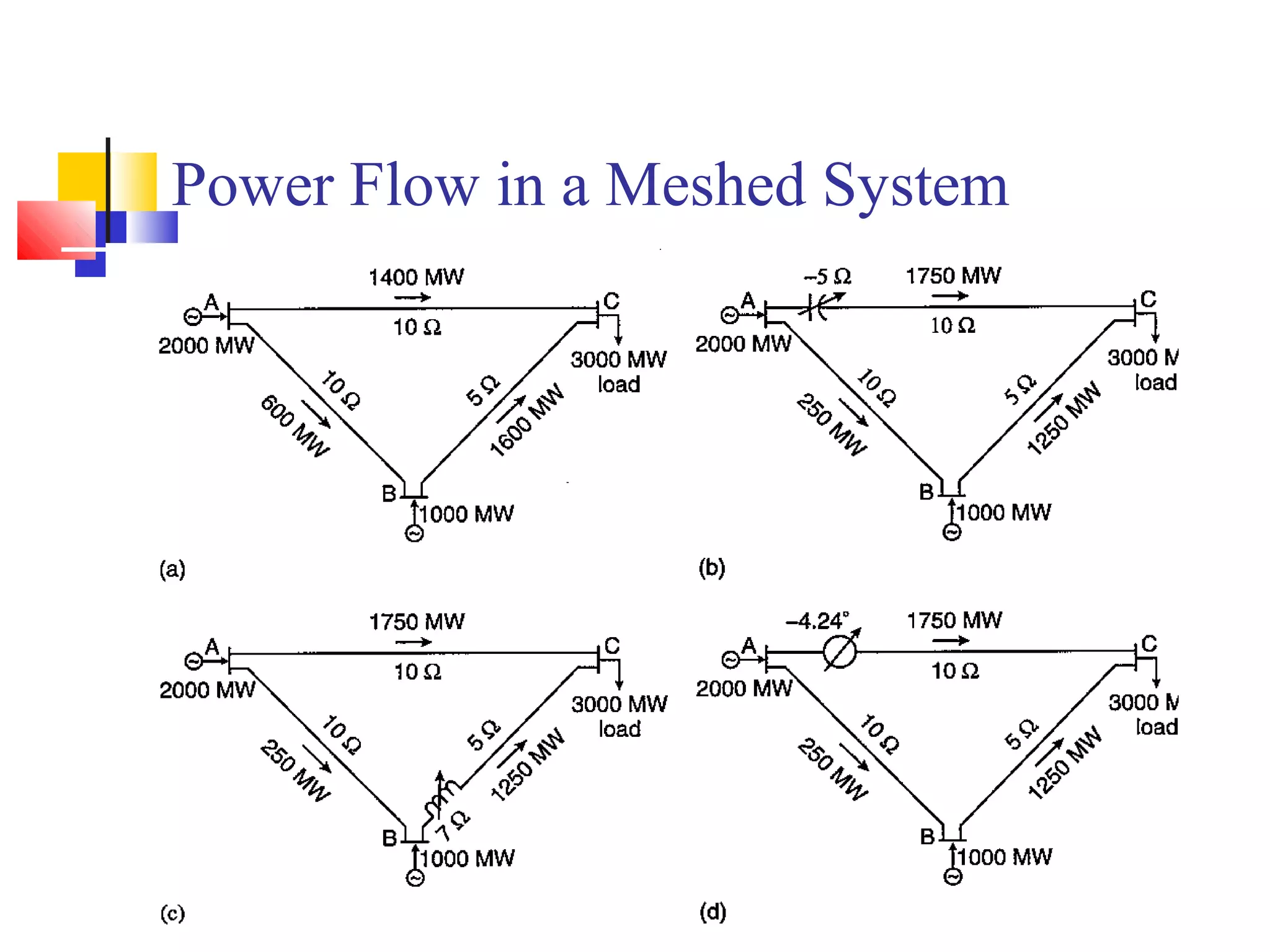
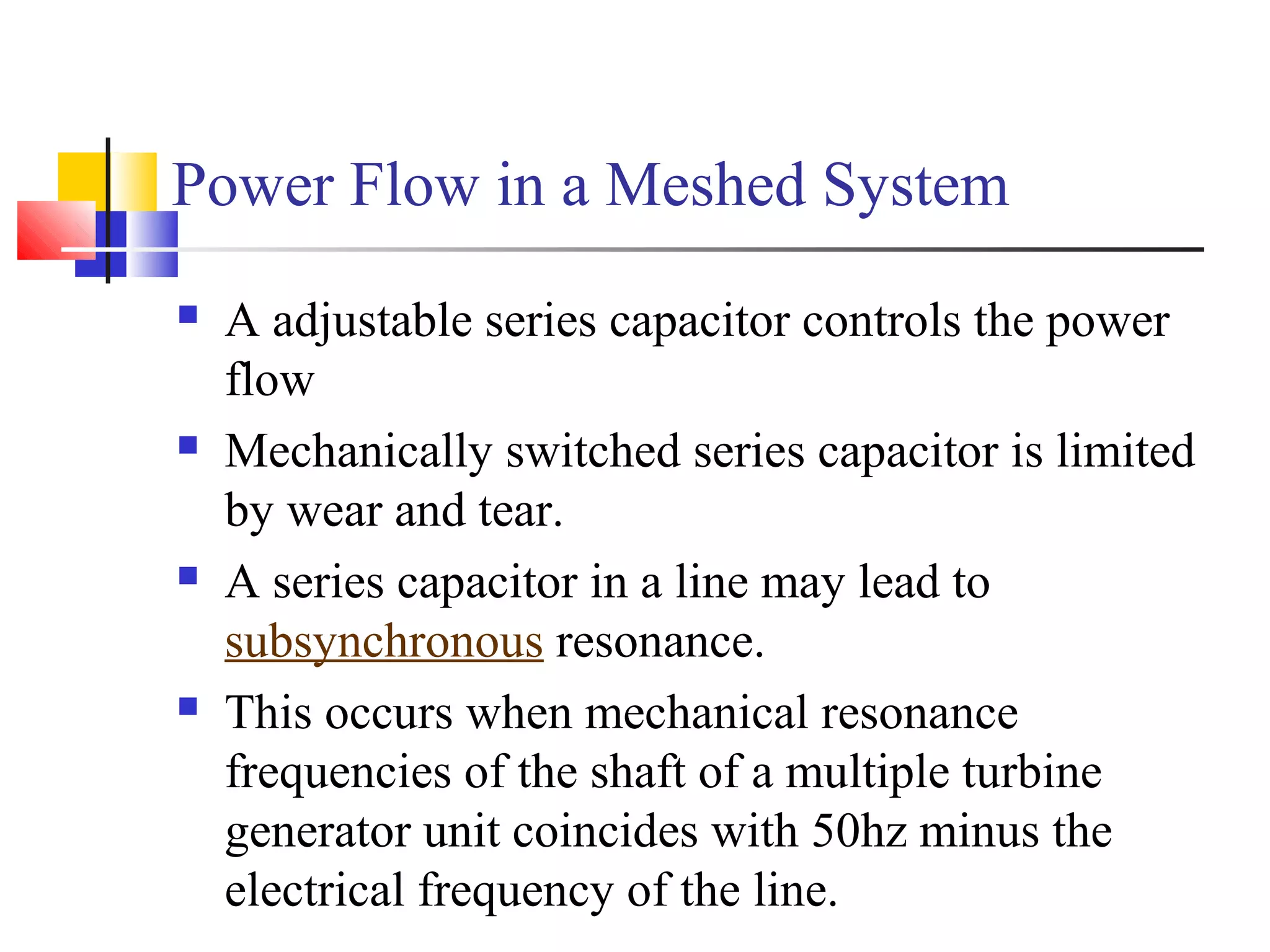
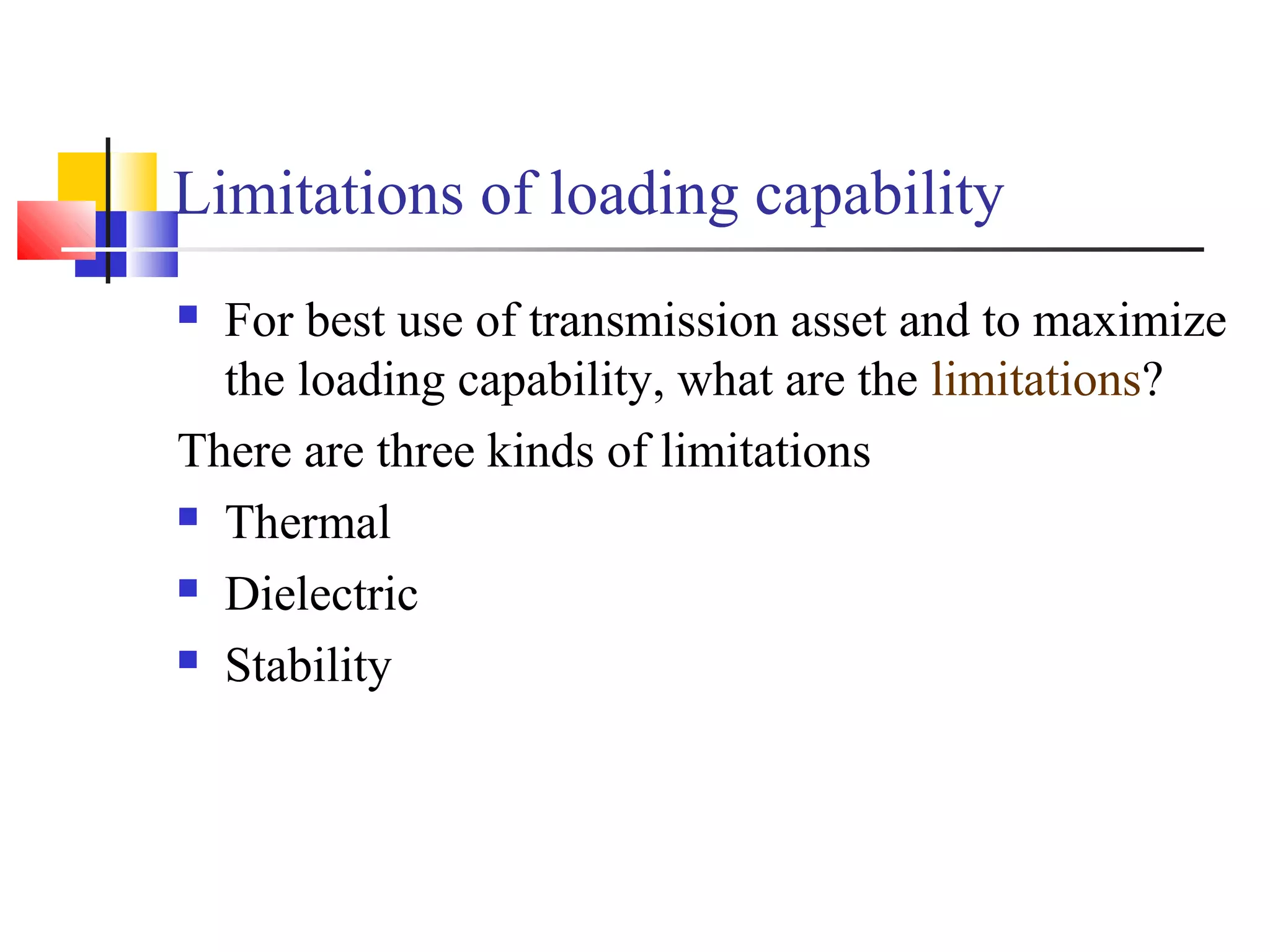
This document discusses the need for transmission interconnections and opportunities provided by FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) technology. It notes that India has generation surpluses in some grids but deficits in others, and interconnections allow sharing of power to reduce costs. FACTS devices can control power flows and enhance line capacity, enabling more economic energy transfers. They offer advantages over mechanical switching like reduced wear and ability to damp oscillations. FACTS technology opens opportunities to better utilize transmission assets by overcoming thermal, dielectric and stability limitations on line loadings.