Embed presentation


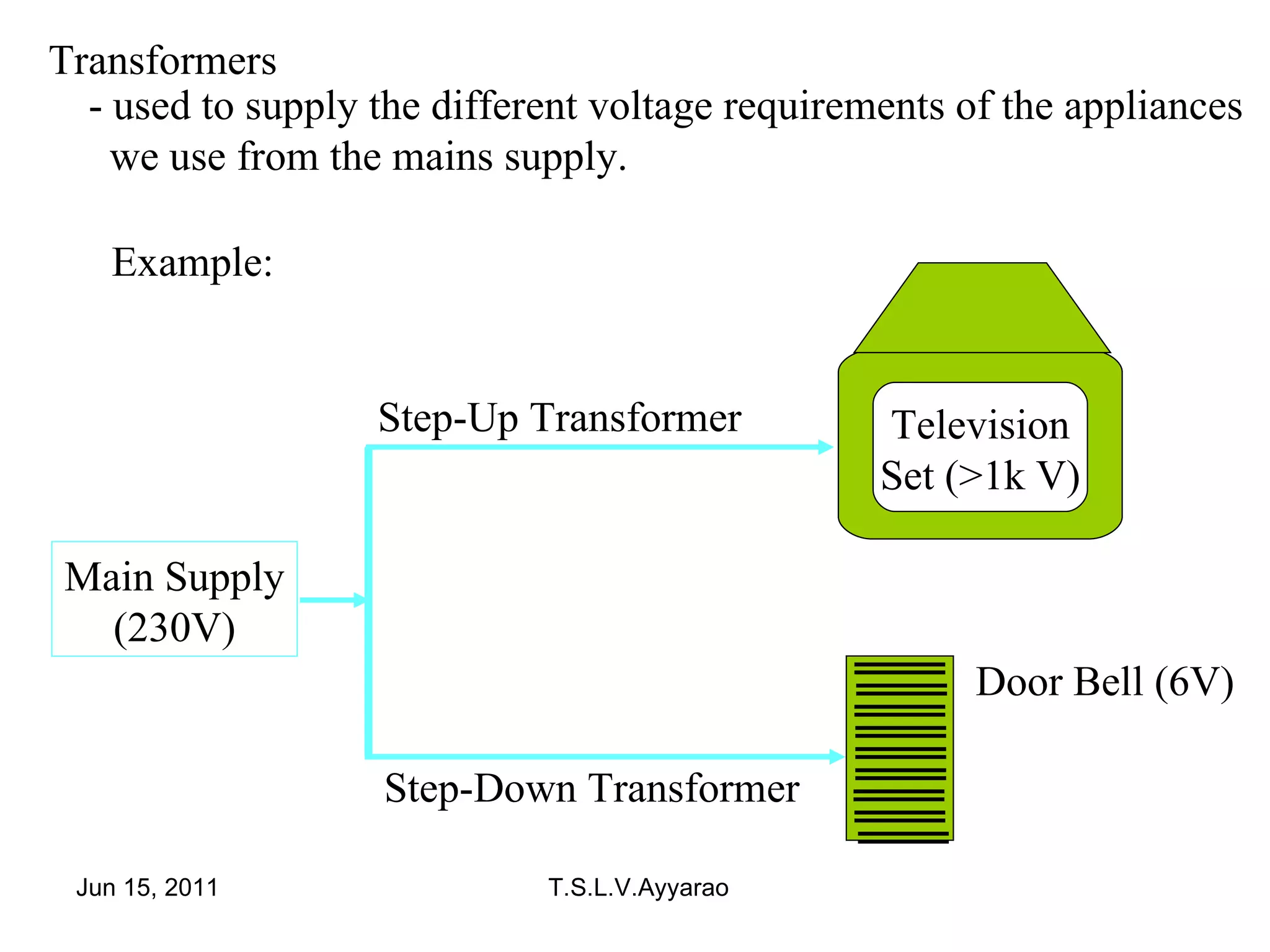
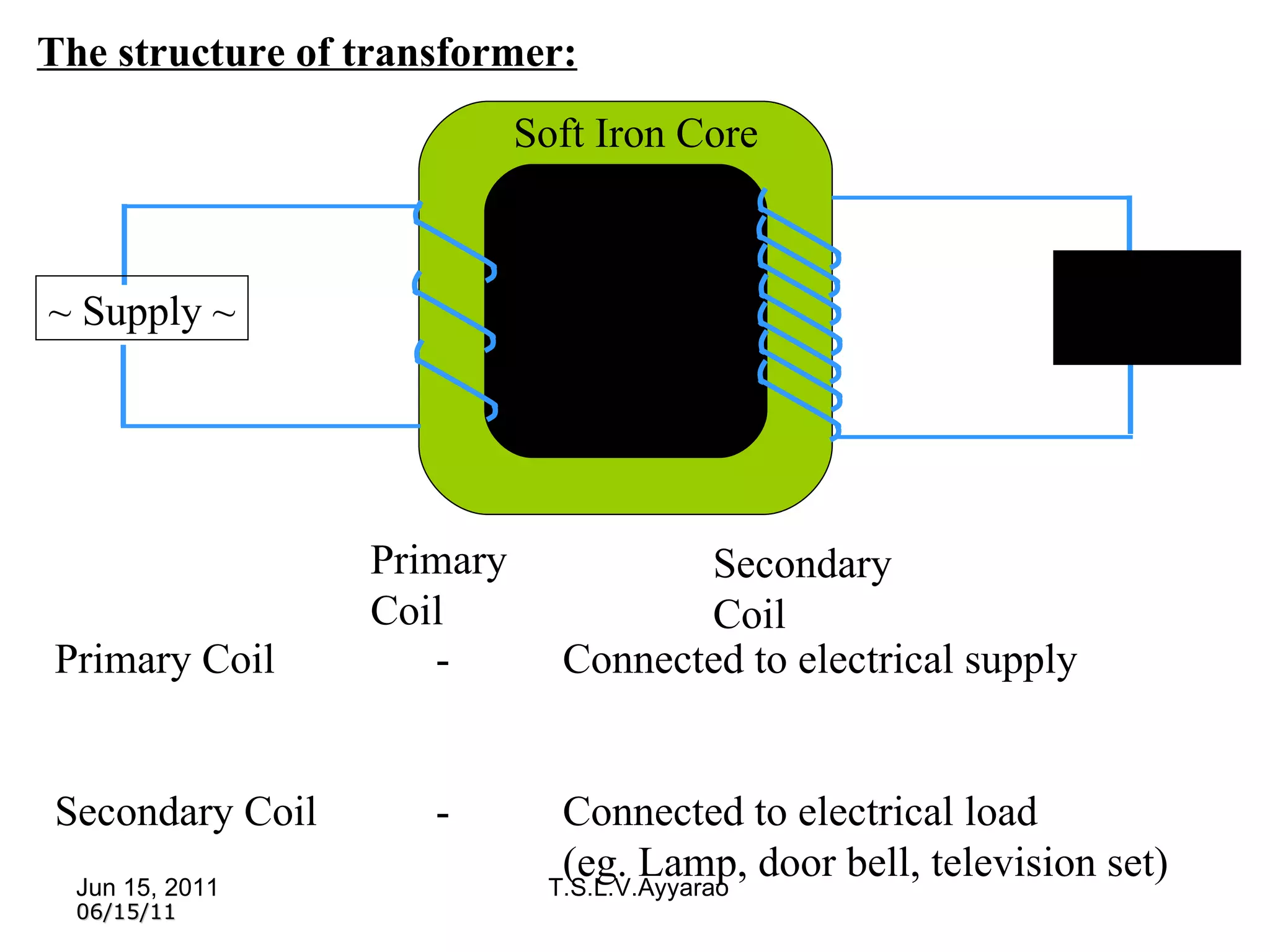
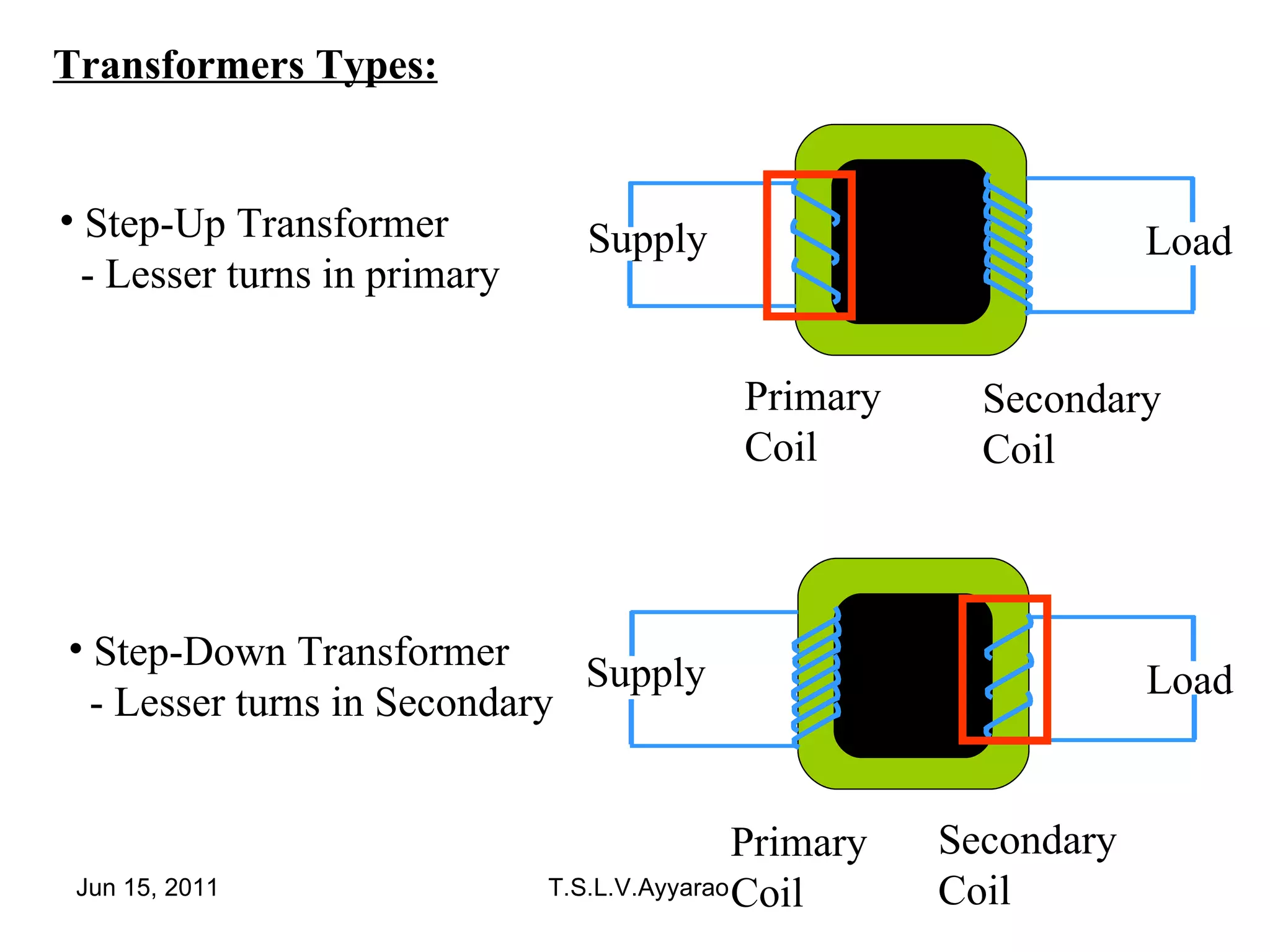
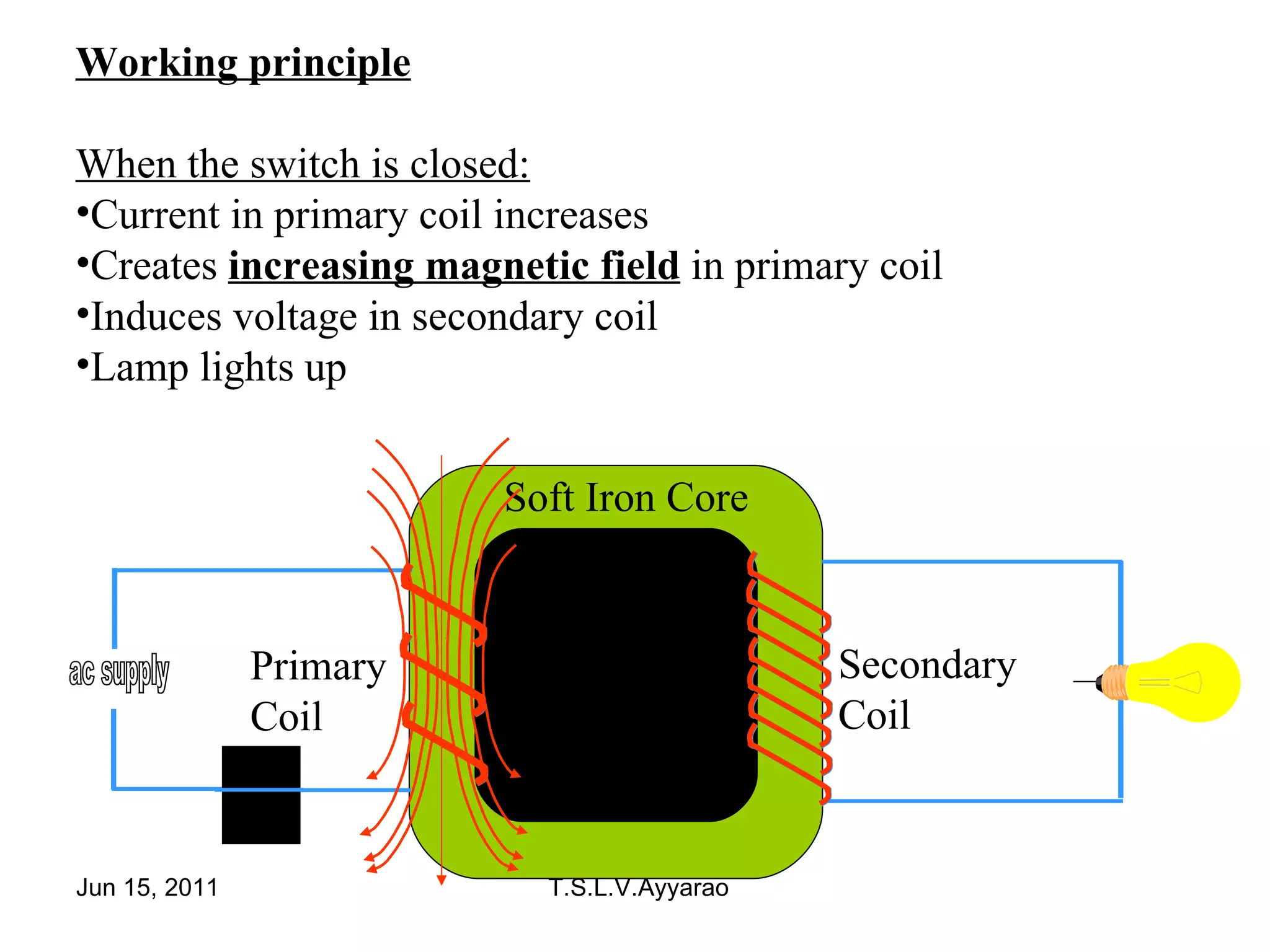

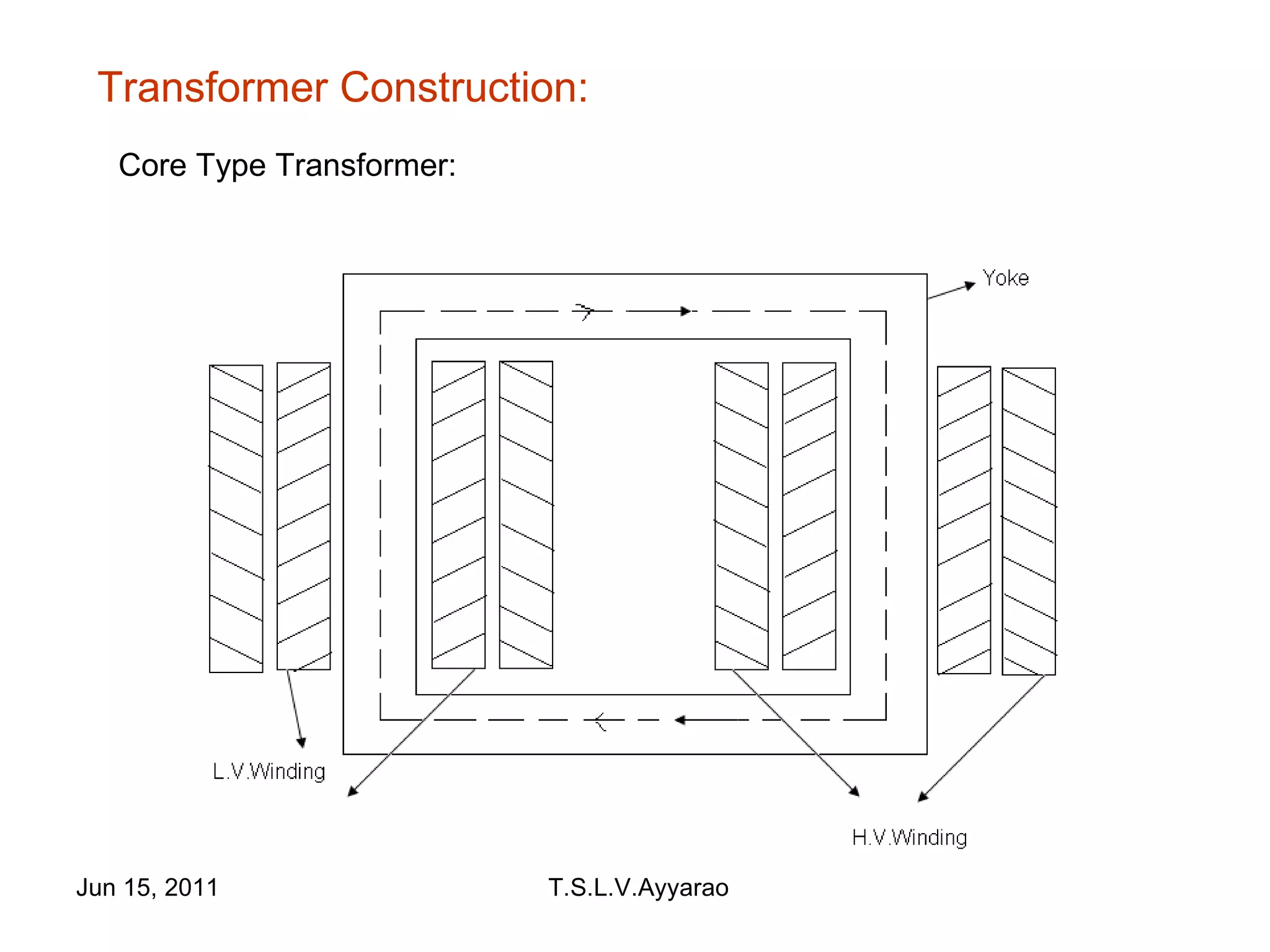
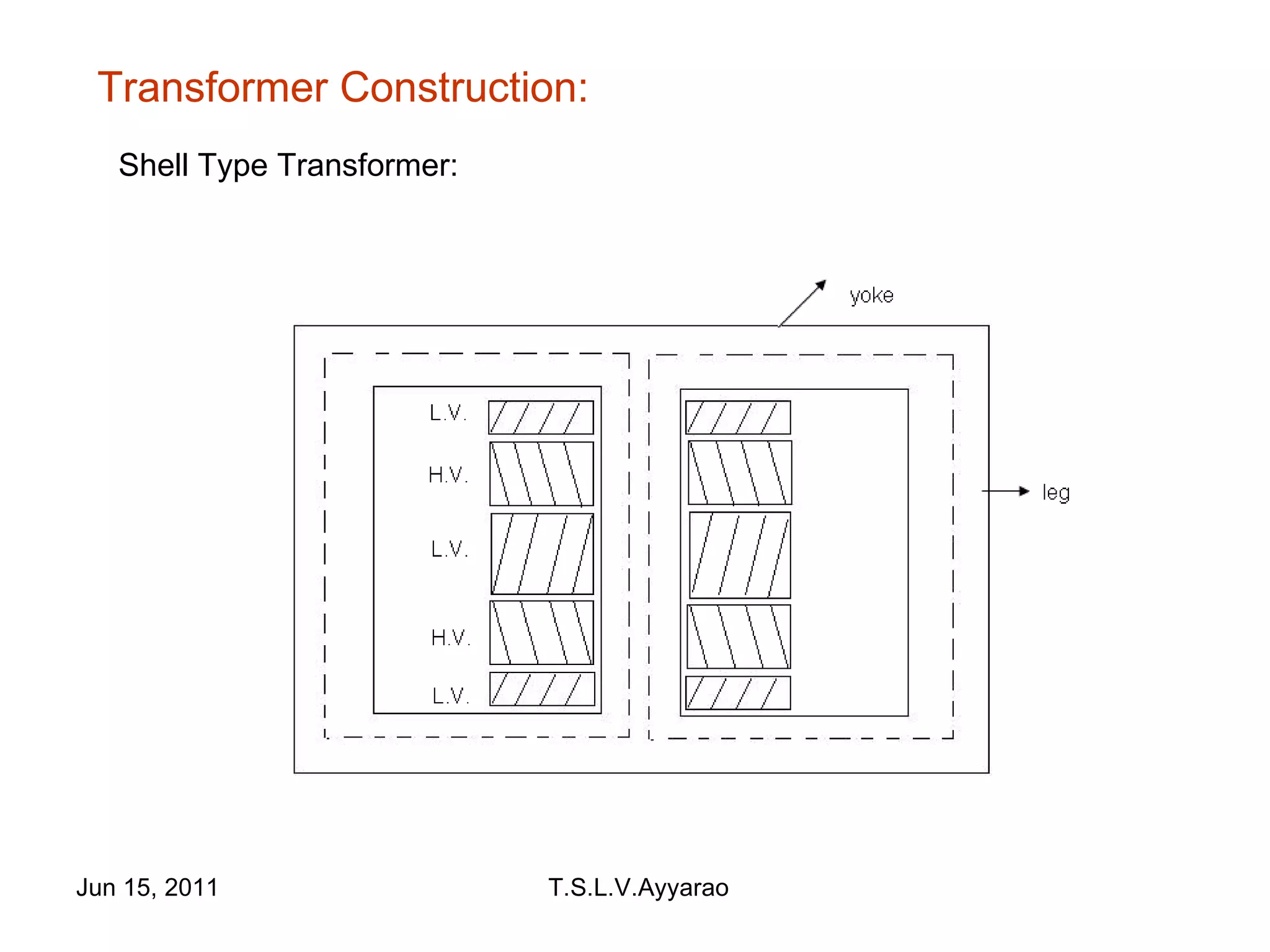


A transformer is a static device that transforms power from one circuit to another without changing the frequency. It uses a primary coil connected to a power supply and a secondary coil connected to a load to induce a voltage in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction from the primary coil. There are two main types of transformers: step-up transformers which have fewer turns in the primary coil to increase voltage, and step-down transformers which have fewer turns in the secondary coil to decrease voltage.









