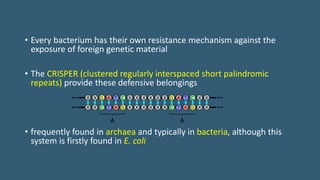
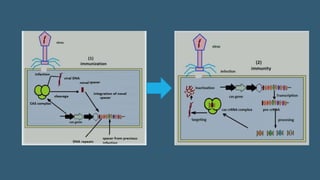
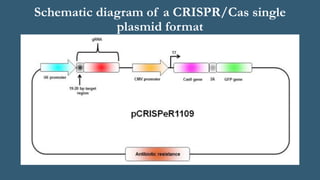
This document provides an overview of CRISPR-Cas as an advanced and efficient tool for genome modification. It describes how CRISPR-Cas systems incorporate DNA from invading viruses or plasmids and use RNA-guided Cas nucleases to cleave matching sequences in foreign DNA. The two main components required for genome editing are Cas9 nuclease and a guide RNA. By altering the guide RNA sequence, Cas9 can be directed to cleave any desired DNA target. The document discusses applications of CRISPR-Cas in genome editing, gene regulation, molecular barcoding, and potential future uses in medicine and biotechnology.