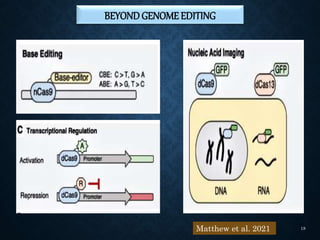
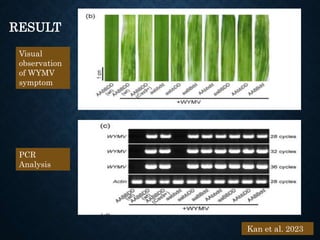
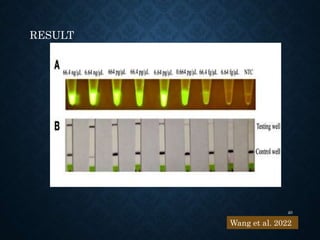
This document provides an overview of the CRISPR-Cas system including its history, mechanisms, types, applications in plant pathology, and use for genome editing. Some key points covered include:
- CRISPR-Cas is an adaptive immune system found in bacteria that provides resistance to viruses. It was discovered in 1987 and its mechanism of targeting invading DNA was determined in 2005.
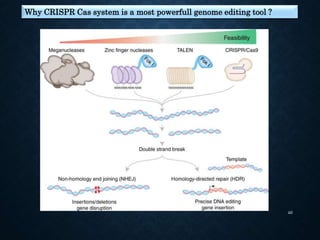
- There are six types of CRISPR-Cas systems classified by their effector proteins. Type II uses Cas9 protein and is commonly used for genome editing.
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system involves crRNA guiding Cas9 to cleave invading DNA at specific locations. This has enabled powerful applications like knocking out genes