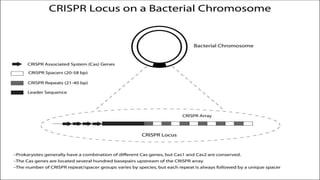
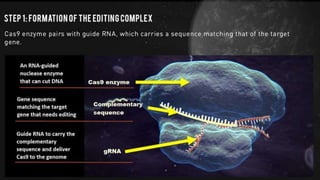
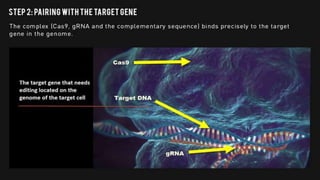
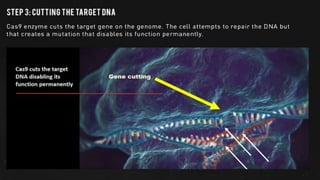
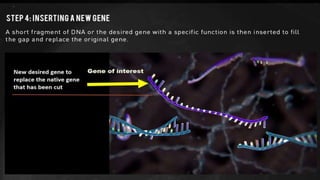
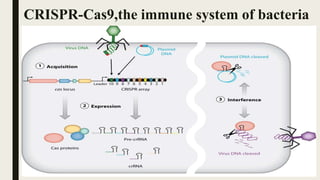
Genome engineering uses programmable nucleases like CRISPR-Cas9 to make targeted modifications to DNA. CRISPR-Cas9 is an adaptive immune system in bacteria that uses Cas9, an RNA-guided DNA endonuclease, to cleave DNA when guided by CRISPR RNA (crRNA). The Cas9 protein uses crRNA and trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA) to induce double-strand breaks in DNA matching the crRNA sequence. CRISPR-Cas9 allows for efficient, precise genome editing and has applications in gene therapy, agriculture, and research.