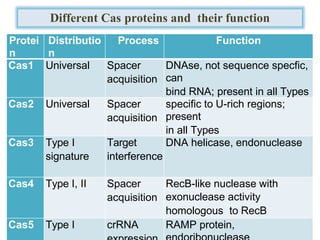
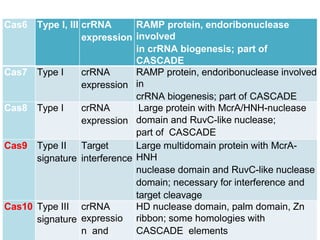
CRISPR is a new genome editing tool that uses the bacterial immune system to detect and cut foreign DNA. It contains repeating DNA sequences that allow bacteria to recognize and cut invading viruses. There are three main types of CRISPR systems that vary in their targeting mechanisms and effects. The CRISPR-Cas9 system involves a Cas9 enzyme that can be guided by CRISPR RNA to cut specific locations in the genome. This tool is revolutionizing biotechnology and holds promise for applications in medicine, but more research is still needed to fully characterize its activity and address ethical considerations before human applications.