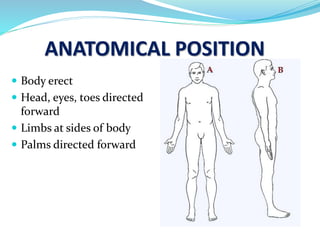
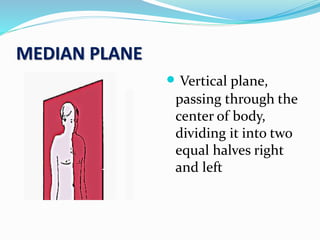
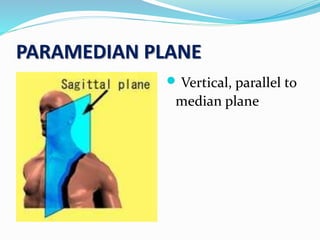
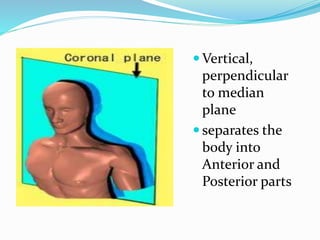
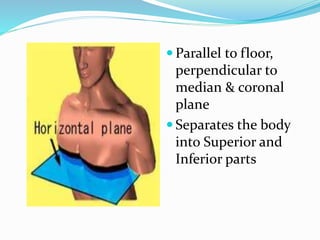
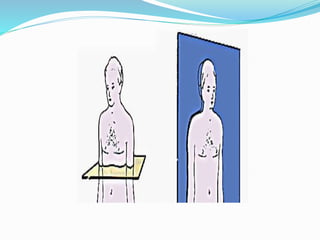
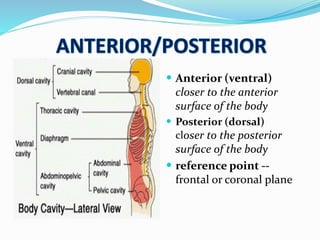
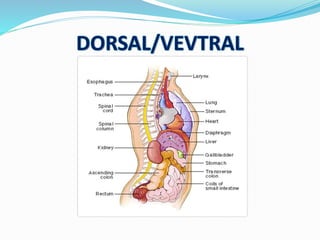
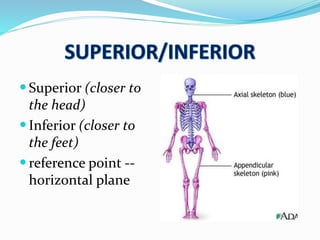
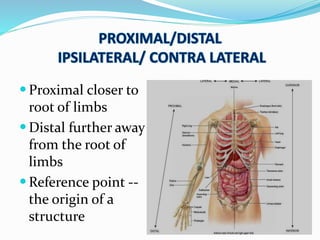
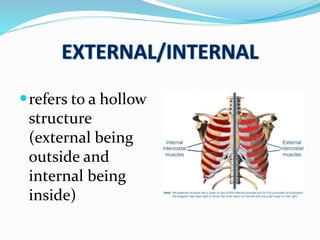
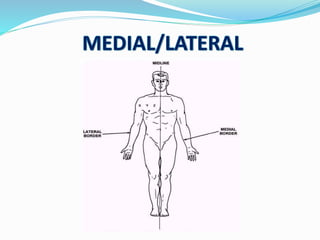
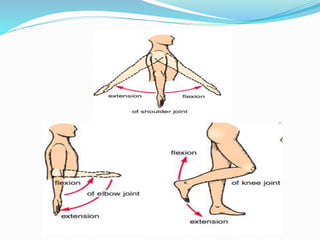
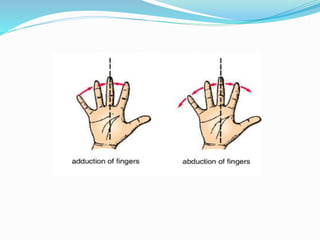
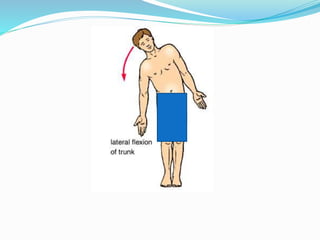
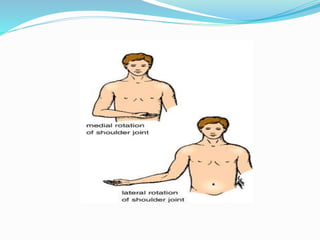
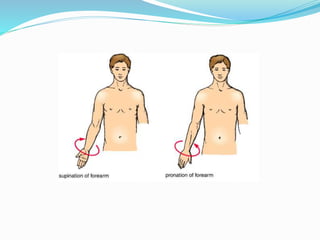
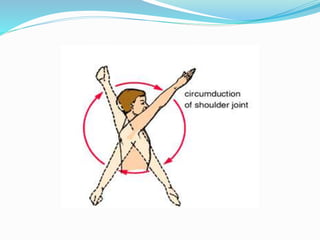
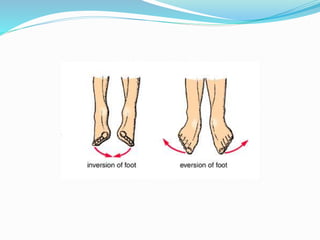
This document provides an overview of human anatomy, including its main disciplines, definitions, basic organization, and key terminology. It discusses the microscopic, macroscopic, developmental, and neuroanatomical approaches. Key terms are defined, such as anatomical position, planes (median, sagittal, frontal, horizontal), and directional language (anterior, posterior, proximal, distal). Diagrams illustrate anatomical planes and examples of movements. The purpose is to introduce foundational concepts in human anatomy.