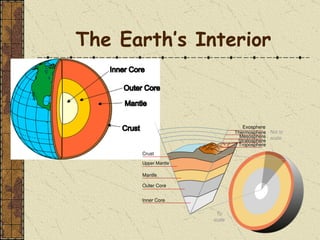
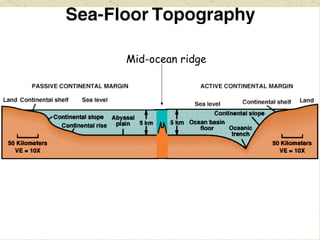
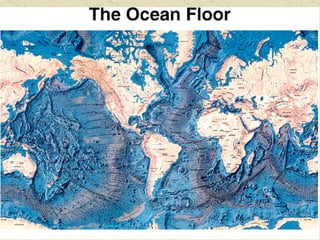
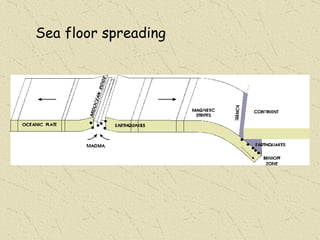
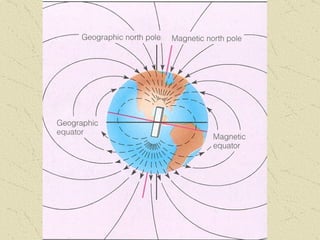
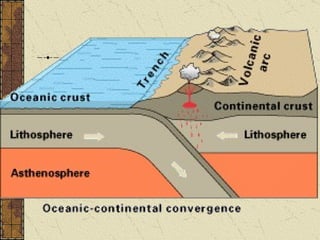
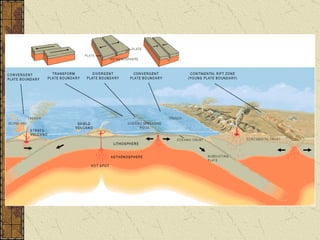
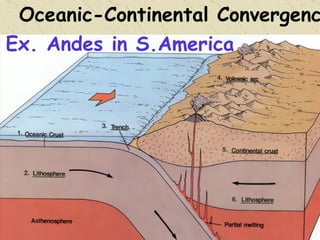
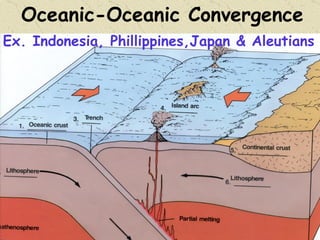
The document summarizes the structure and composition of Earth's interior. It has four main layers from innermost to outermost - the solid inner core made of iron and nickel, the liquid outer core also made of iron and nickel, the solid mantle made of iron, silicon and magnesium minerals, and the rigid outer crust made of lighter rock. Temperature and pressure increase from the crust towards the core. The crust is thinnest under oceans and thickest under mountains.