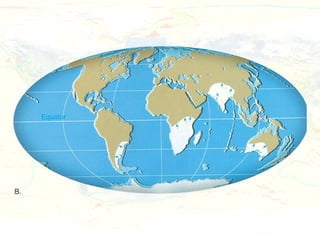
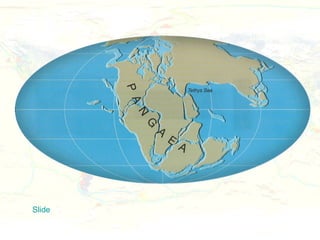
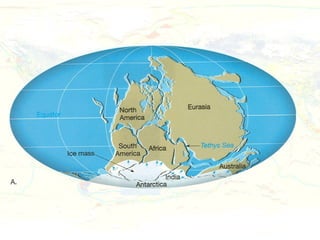
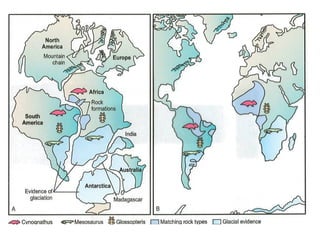
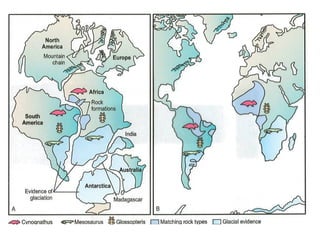
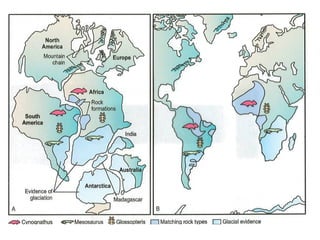
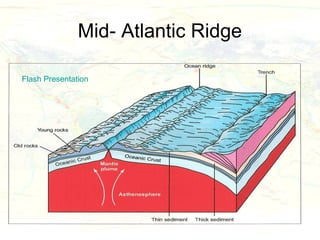
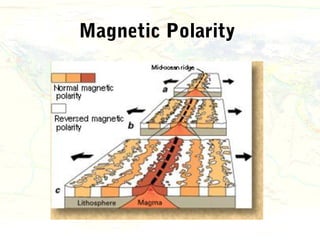
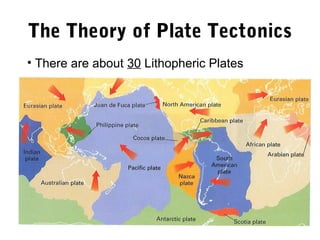
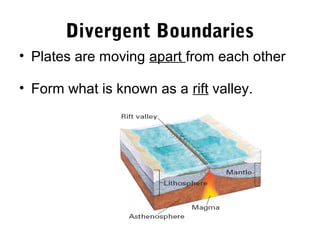
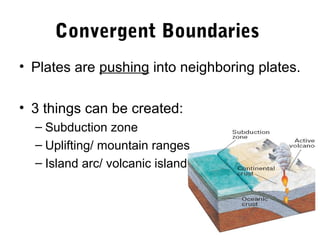
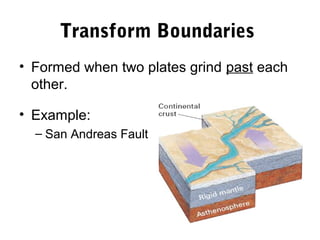
The document discusses plate tectonics and the evidence that supports the theory. It describes how Alfred Wegener first proposed continental drift in 1912 and how scientists later discovered seafloor spreading at mid-ocean ridges. The theory of plate tectonics emerged, stating that the Earth's lithosphere is broken into plates that move over the asthenosphere. The boundaries between plates can be divergent, convergent, or transform. Plate motions are driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle.