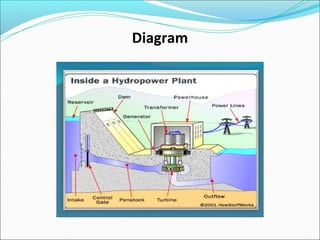
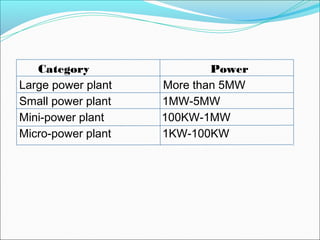
Hydroelectric energy is produced by converting the gravitational potential energy of stored water into electrical energy in power plants. While it provides a clean and renewable energy source, the construction of plants has significant drawbacks including high costs and environmental impacts such as flooding and disruption of natural water flows. The document also distinguishes between different types of hydraulic power plants and emphasizes the need for increased adoption of hydroelectric energy over fossil fuels.