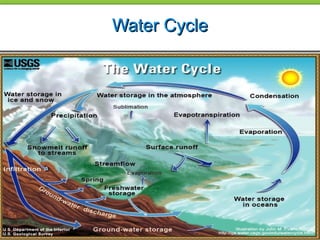
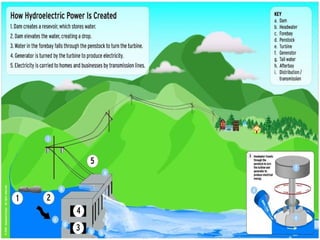
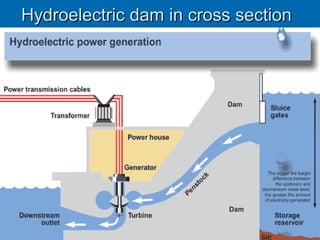
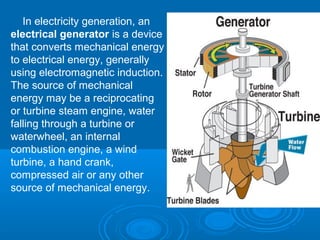
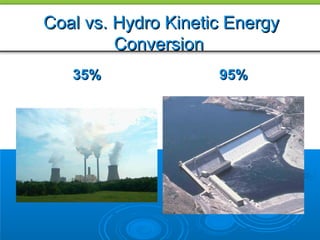
Water power has been used for centuries to power mills and other tasks, but is now mainly used to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power involves creating dams on streams and rivers to direct the kinetic energy of flowing water towards turbines that spin generators to produce electricity. Large dams like Hoover Dam can generate significant amounts of hydroelectric power. While hydro is a renewable source that avoids greenhouse gas emissions, dams can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and require population relocation. Future advances aim to make hydro power more environmentally sustainable.