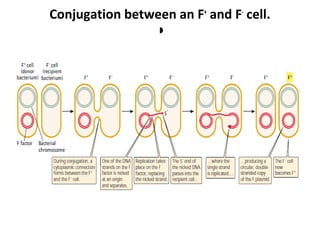
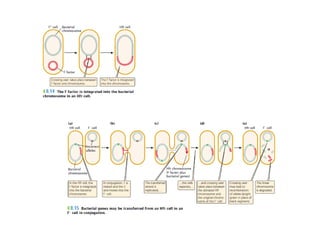
E. Coli is a common bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other warm-blooded organisms. It can exist harmlessly or cause food poisoning. E. Coli reproduces through cell division and genetic transfer between F+ and F- cells. The life cycle involves conjugation where the F plasmid transfers DNA between cells. E. Coli is widely studied due to its rapid reproduction, hardiness, and ability to accept foreign DNA, making it useful for biotechnology and protein production.