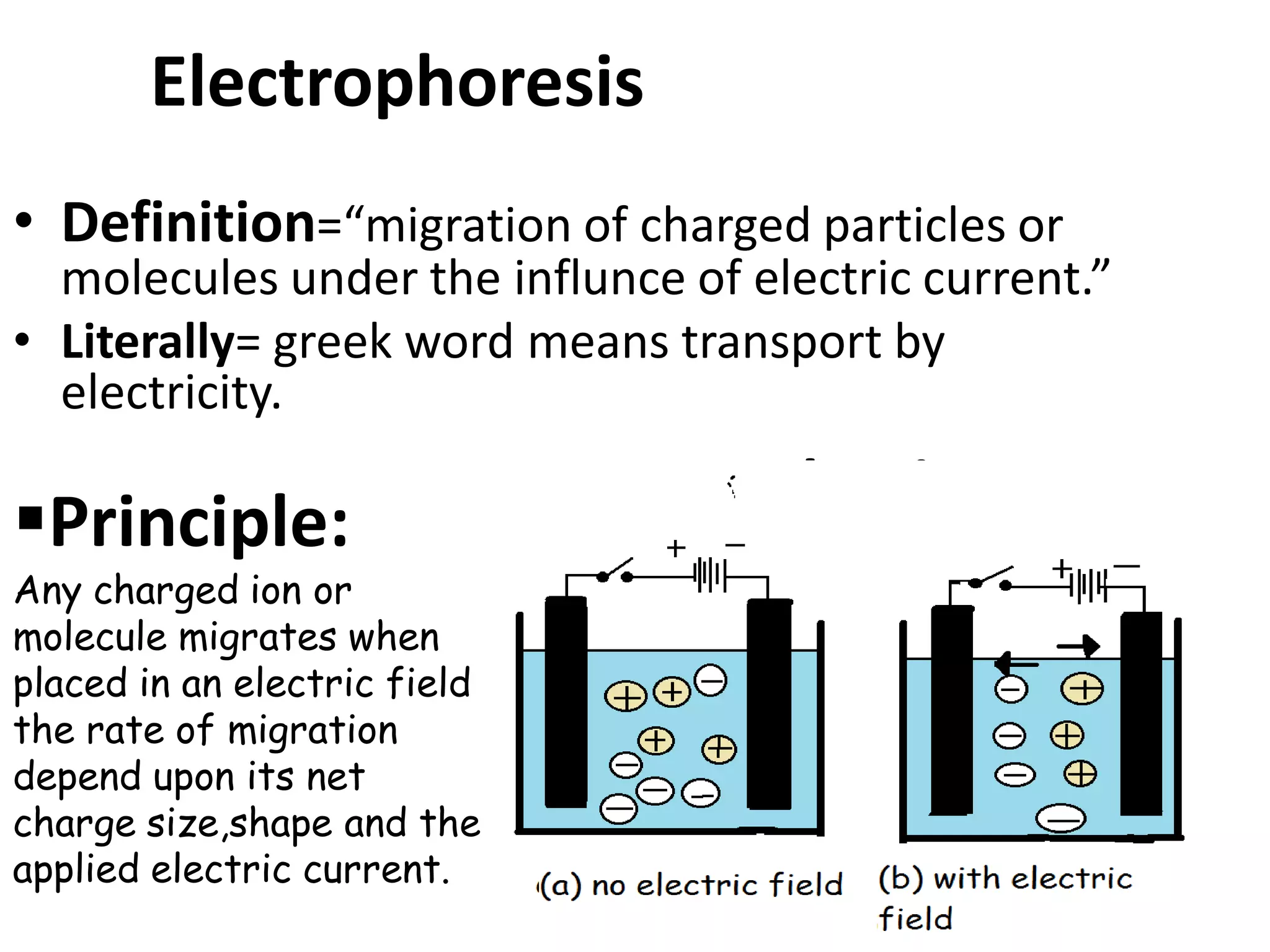
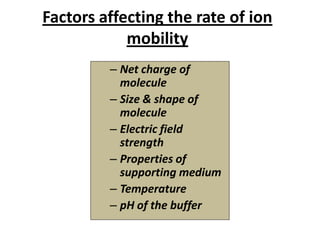
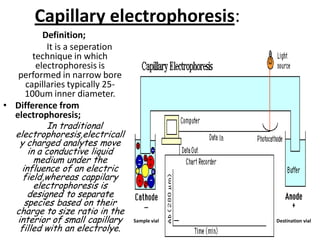
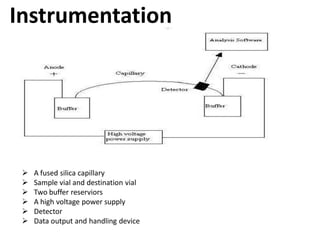
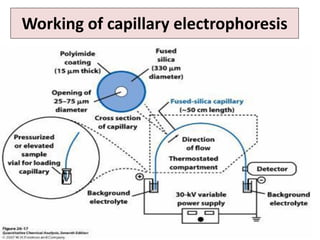
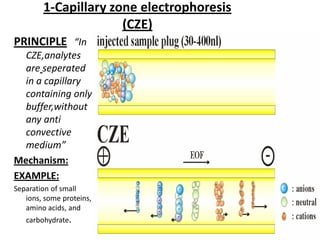
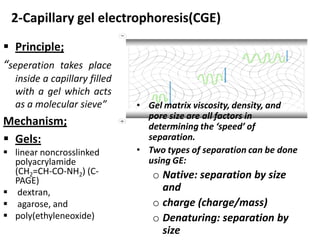
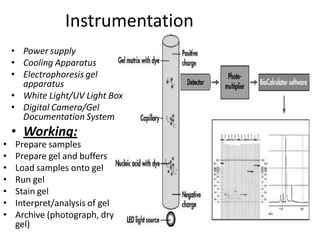
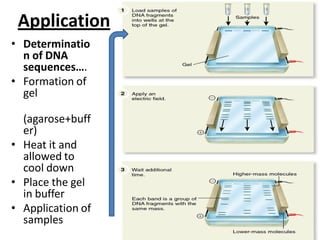
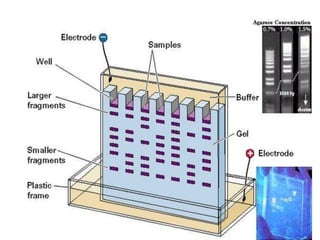
Capillary electrophoresis is a separation technique where electrophoresis is performed inside narrow capillaries. Charged molecules or ions migrate through the capillary under the influence of an electric field. The rate of migration depends on factors like the molecule's net charge, size, shape, and the electric field strength. There are two main types - capillary zone electrophoresis, which separates analytes in buffer alone, and capillary gel electrophoresis, which uses a gel matrix to separate based on size. Capillary electrophoresis has applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, forensics, foods, and biosciences for analyzing substances like DNA, proteins, metals, and organic compounds.