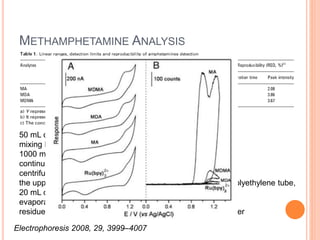
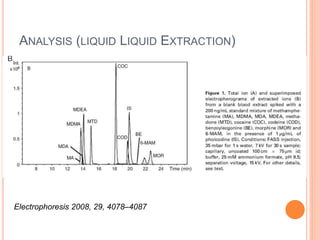
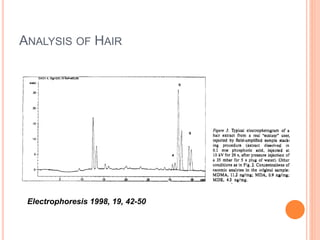
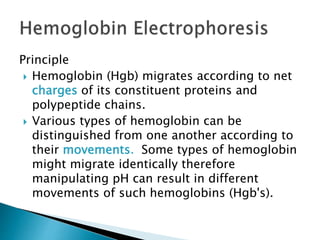
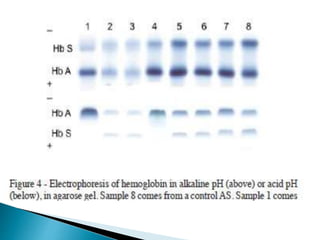
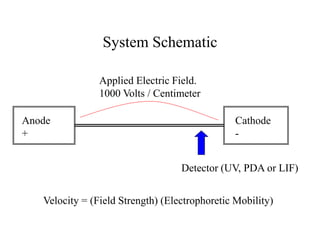
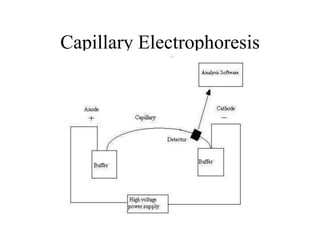
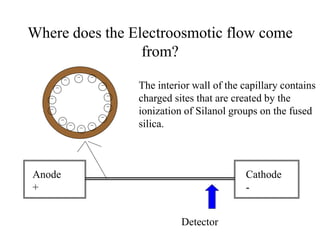
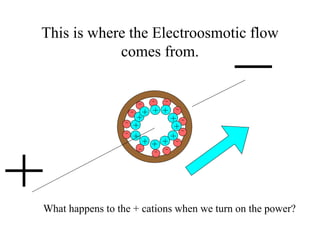
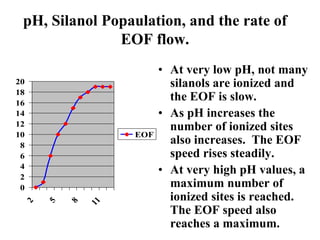
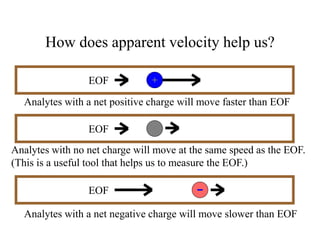
Electrophoresis is a process that separates and isolates different compounds based on their charge and size. It works by applying an electric current to a medium containing charged particles, causing the particles to migrate. The key factors affecting particle movement are net charge, size, strength of the electric field, and properties of the supporting medium. Electrophoresis can be used to identify, isolate, and determine the molecular weight of many charged biomolecules like proteins, DNA, and hemoglobin. Common applications include polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and hemoglobin electrophoresis.











![Movement of Analyte
Analyte
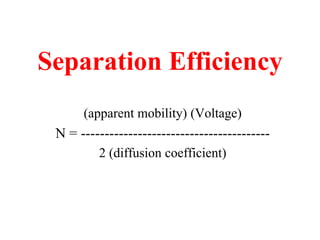
ν = µ E
ν = velocity µ = electrophoretic mobility E = Electric field
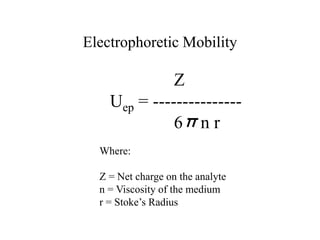
Electrophoretic mobility
µ = q/[6πηr]
q = charge η = solution viscosity r = radius
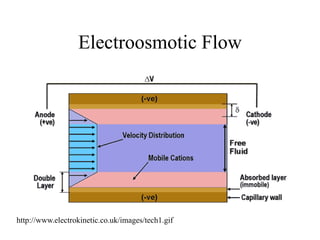
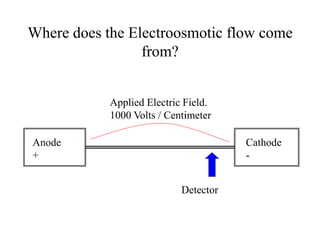
Electroosmotic flow
νEOF = [ε/4πη]ζE
ε = dielectric constant ζ = Zeta potential
Flow of migration
ν = [(μEO + μe)V]/L
V = potential L = length of capillary
Forensic Science International
77 (1996) 211 - 229](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capillaryelectrophoresis-forteaching-240123202357-1ead9ef3/85/Capillary-Electrophoresis-for-teaching-pptx-18-320.jpg)





















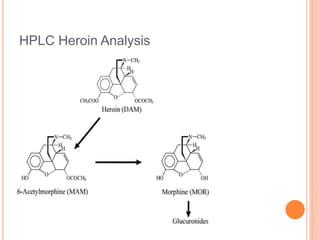
![HPLC Analysis of Heroin (SPE)
Fig. 2. (a) Representative total ion
chromatograms of all quantifiable
analytes spiked at LLQ level in
human plasma (5 ng/mL). The
intensity of the deuterated analytes
was above 2500 [cps]. (b)
Representative total ion
chromatograms of random chosen
patient’ plasma sample. (c) Total ion
chromatogram of a plasma sample
of a non-drug using volunteer. (A)
M3G and M3G-d3; (B) morphine
and morphine-d3; (C) M6G; (D) 6-
MAM; (E) heroin and heroin-d6;
(F) = methadone and methadone-
d9; (G) EMDP; (H) cocaine; (I)
benzoylecgonine.
DIODE ARRAY AND TRIPLE MS
5 ng/ml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capillaryelectrophoresis-forteaching-240123202357-1ead9ef3/85/Capillary-Electrophoresis-for-teaching-pptx-66-320.jpg)