Bacteria &; prokaryotes
•Download as PPT, PDF•
1 like•308 views
Bacterial and prokaryotes
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Nomenclature, classification and identification of bacteria by Anil Shrestha

Nomenclature, classification and identification of bacteria by Anil Shrestha
Classification of Bacteria- Alka Kumari, Assistant Professor

Classification of Bacteria- Alka Kumari, Assistant Professor
Basis of bacterial classification by Anil Shrestha

Basis of bacterial classification by Anil Shrestha
Similar to Bacteria &; prokaryotes
Similar to Bacteria &; prokaryotes (7)
Were identifying an unknown bacteria in lab. What I want to know i.pdf

Were identifying an unknown bacteria in lab. What I want to know i.pdf
More from Bahauddin Zakariya University lahore
More from Bahauddin Zakariya University lahore (20)
Electrophoresis and electrodialysis_yansee_maria_jiaxuan

Electrophoresis and electrodialysis_yansee_maria_jiaxuan
Recently uploaded
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases. It is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with HIV, most commonly during unprotected sex (sex without a condom or HIV medicine to prevent or treat HIV), or through sharing injection drug equipment.
Seasonal influenza (the flu) is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses. It is common in all parts of the world. Most people recover without treatment.
Influenza spreads easily between people when they cough or sneeze. Vaccination is the best way to prevent the disease.
Symptoms of influenza include acute onset of fever, cough, sore throat, body aches and fatigue.
Treatment should aim to relieve symptoms. People with the flu should rest and drink plenty of liquids. Most people will recover on their own within a week. Medical care may be needed in severe cases and for people with risk factors.
There are 4 types of influenza viruses, types A, B, C and D. Influenza A and B viruses circulate and cause seasonal epidemics of disease.
Influenza A viruses are further classified into subtypes according to the combinations of the proteins on the surface of the virus. Currently circulating in humans are subtype A(H1N1) and A(H3N2) influenza viruses. The A(H1N1) is also written as A(H1N1)pdm09 as it caused the pandemic in 2009 and replaced the previous A(H1N1) virus which had circulated prior to 2009. Only influenza type A viruses are known to have caused pandemics.
Influenza B viruses are not classified into subtypes but can be broken down into lineages. Influenza type B viruses belong to either B/Yamagata or B/Victoria lineage.
Influenza C virus is detected less frequently and usually causes mild infections, thus does not present public health importance.
Influenza D viruses primarily affect cattle and are not known to infect or cause illness in people.HIV AND INFULENZA VIRUS PPT HIV PPT INFULENZA VIRUS PPT

HIV AND INFULENZA VIRUS PPT HIV PPT INFULENZA VIRUS PPTABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
Recently uploaded (20)
MSC IV_Forensic medicine - Mechanical injuries.pdf

MSC IV_Forensic medicine - Mechanical injuries.pdf
Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx

Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx
Heat Units in plant physiology and the importance of Growing Degree days

Heat Units in plant physiology and the importance of Growing Degree days
Film Coated Tablet and Film Coating raw materials.pdf

Film Coated Tablet and Film Coating raw materials.pdf
Harry Coumnas Thinks That Human Teleportation is Possible in Quantum Mechanic...

Harry Coumnas Thinks That Human Teleportation is Possible in Quantum Mechanic...
POST TRANSCRIPTIONAL GENE SILENCING-AN INTRODUCTION.pptx

POST TRANSCRIPTIONAL GENE SILENCING-AN INTRODUCTION.pptx
ANITINUTRITION FACTOR GYLCOSIDES SAPONINS CYANODENS

ANITINUTRITION FACTOR GYLCOSIDES SAPONINS CYANODENS
HIV AND INFULENZA VIRUS PPT HIV PPT INFULENZA VIRUS PPT

HIV AND INFULENZA VIRUS PPT HIV PPT INFULENZA VIRUS PPT
Bacteria &; prokaryotes
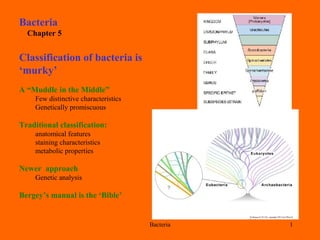
- 1. Bacteria 1 Bacteria Chapter 5 Classification of bacteria is ‘murky’ A “Muddle in the Middle” Few distinctive characteristics Genetically promiscuous Traditional classification: anatomical features staining characteristics metabolic properties Newer approach Genetic analysis Bergey’s manual is the ‘Bible’
- 2. Bacteria 2 Classification based upon anatomical features 3 common shapes Some unusual shapes also:
- 3. Bacteria 3 Classification based upon anatomical features Other unusual bacteria Spirochetes Cell wall-less Stalked Filamentous Myxobacteria fruiting bodiesStreptomyces
- 4. Bacteria 4 Classification based upon staining Gram Positive vs Gram Negative Hans Christian Gram -- 1884 -- Crystal violet Gram positive structure -- thick layer of peptidoglycan Gram negative structure -- inner vs outer membranes -- lipopolysaccharides and endotoxins Acid fast staining -- Mycobacterium Penicillin action Effect of penicillin
- 5. Bacteria 5 Classification based upon metabolism -- will explore further later Heterotrophic Autotrophic Photosynthetic bacteria -- cyanobacteria -- purple sulfur bacteria Chemoautotrophic ‘Metabolically defective’ Rickettsia Chlamydia Rocky Mountain Rocky Mountain Spotted fever wood tick R. rickettsii Image from (and good source for more about Chlamydia) http://www.chlamydiae.com/docs/biology/biol_devcycle.asp
- 6. Bacteria 6 Why are bacteria so small? Size affects ‘surface to volume’ ratio Advantages of large S/V: diffusion rates metabolic rates reproductive rates Limits to size reduction? ‘defective’ bacteria Really big bacteria? -- Epulopiscium fishelsoni Epulopiscium web site http://www.micro.cornell.edu/cals/micro/research/labs/ angert-lab/epulopiscium.cfm
- 7. Bacteria 7 Why study Bacterial Cell Structure? Mechanisms of virulence Drug development Identification Some cell exterior structures cell membrane (lipid bilayer) cell wall (Gram-pos vs Gram-neg) glycocalyx (capsule vs slime layer) flagellum (prokaryotic vs eukaryotic) pilus (adhesion vs sex)
- 8. Bacteria 8 Cell Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayers Membrane proteins Membrane fluidity Membranes of thermophilic archaebacteria
- 9. Bacteria 9 Bacterial Flagella Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic Arrangements monotrichous lopho- amphi- peri- How do we know movement is rotational? Bacterial Flagella
- 10. Bacteria 10 How do flagellated bacteria move? ‘Run and Tumble’ patternChromatium motility
- 11. Bacteria 11 Spirochetes -- very strange structure -- e.g., Borrelia, Treponema Axial filaments Outer sheath Motility Borrelia Movement
- 12. Bacteria 12 Fimbriae and Pili Fimbriae adhesion to surfaces Pili (pilus) genetic recombination other functions?
- 13. Bacteria 13 The glycocalyx Functions adherence virulence prevent desiccation Composition Capsule layers vs Slime layers “xantham gum”(Xanthomonas) Strep Pneumo
- 14. Bacteria 14 Endospores Formation and regrowth Special properties? -- desiccated -- DNA binding proteins -- Ca-dipicolinic acid Magnetotactic bacteria -- possess magnetosomes Endospore formation Magnetotactic Bacteria
