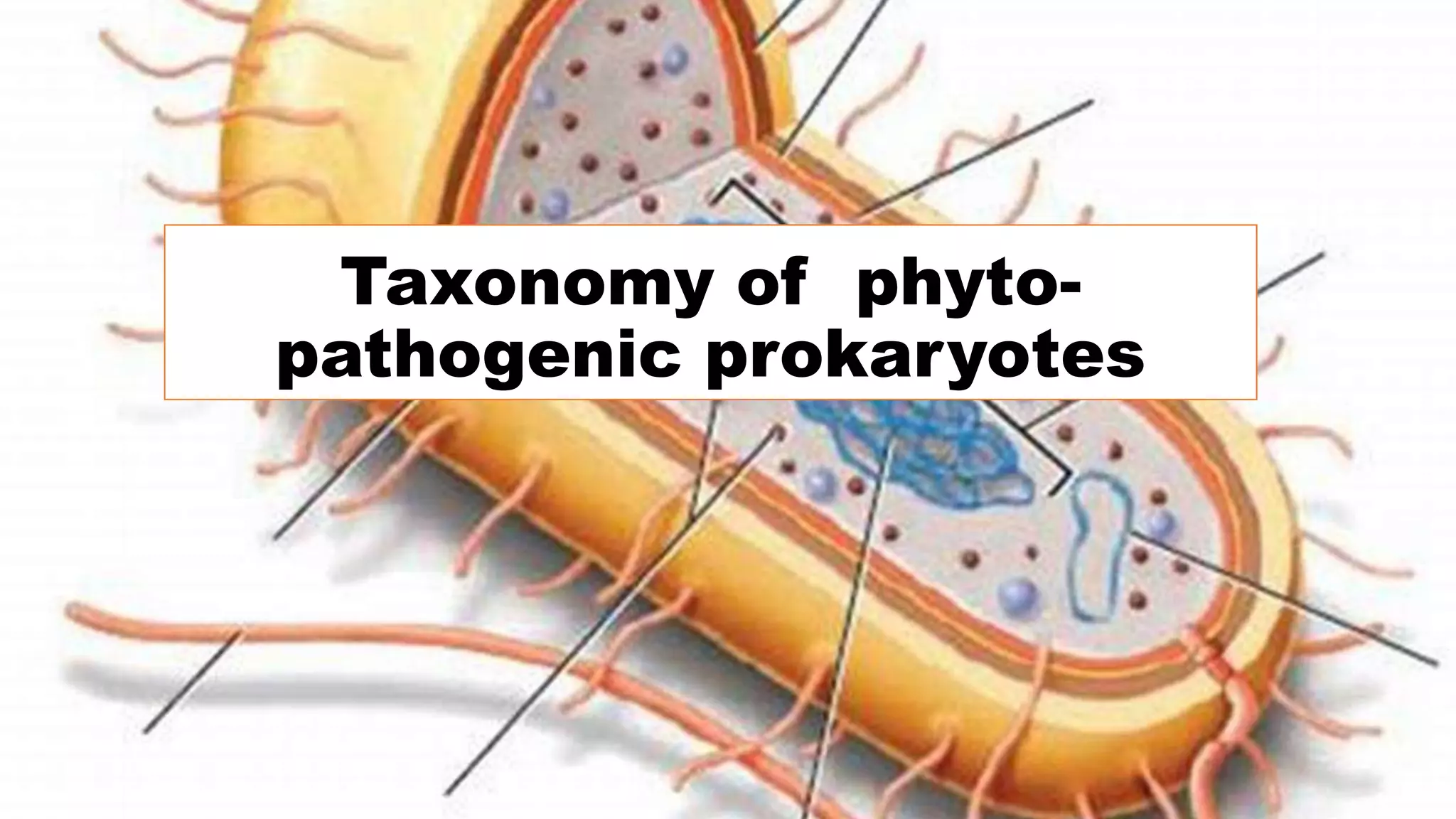
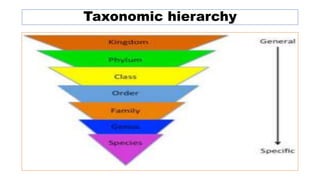
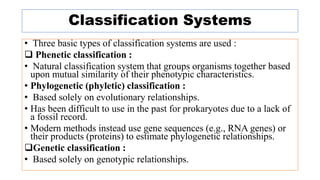
The document provides an overview of the taxonomy of phytopathogenic prokaryotes, detailing the hierarchical classification of organisms, including definitions and significant classification systems. It discusses the importance of taxonomy in organizing microbial information and identifying organisms, and outlines the contributions of notable figures in the field, including the development of nomenclature codes. Furthermore, it highlights the classification of phytopathogenic bacteria and the pathovar concept for distinguishing strains based on pathogenicity to different plant hosts.