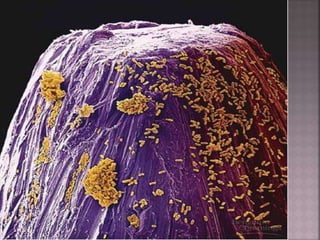
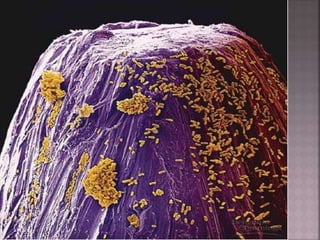
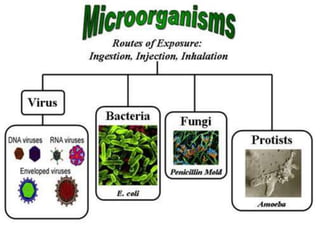
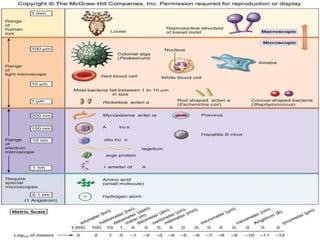
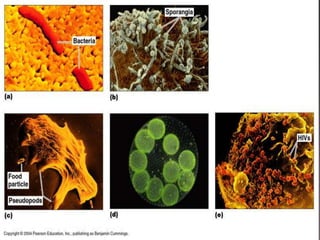
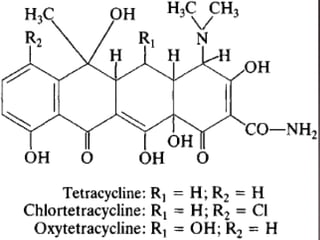
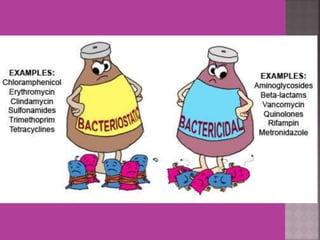
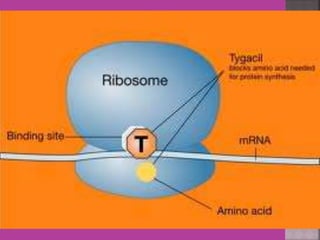
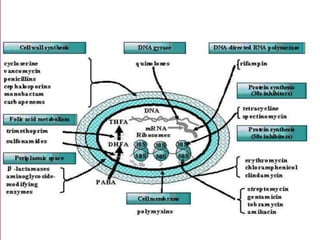
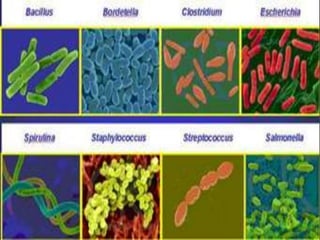
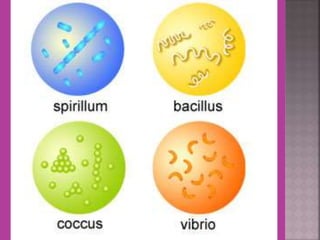
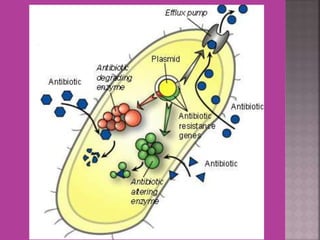
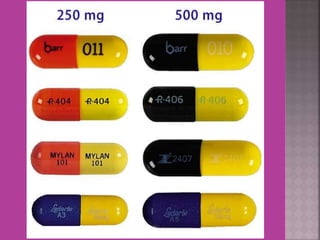
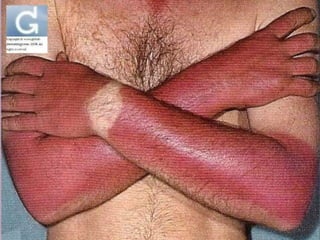
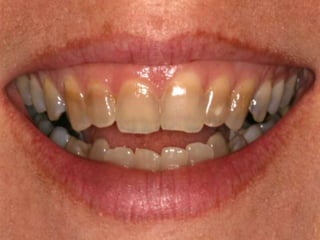
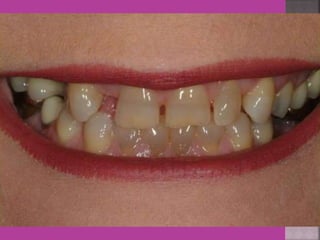
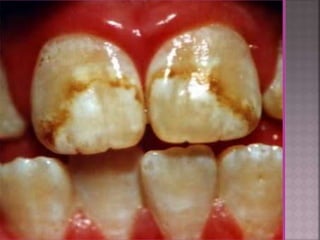
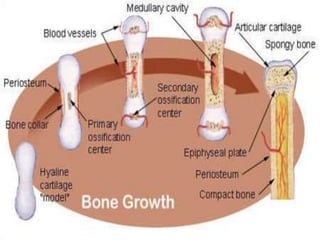
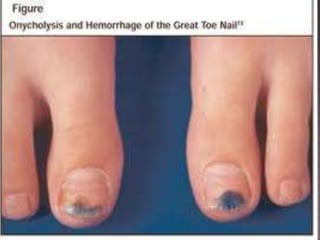
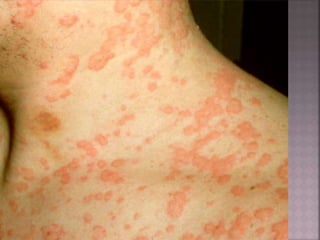
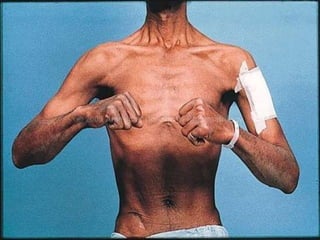
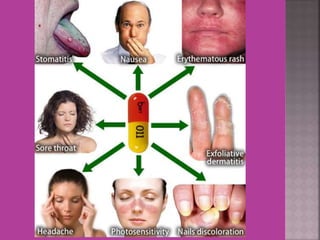
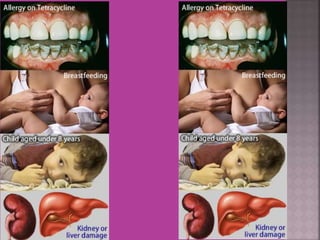
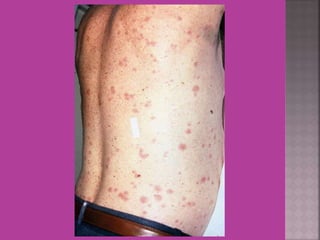
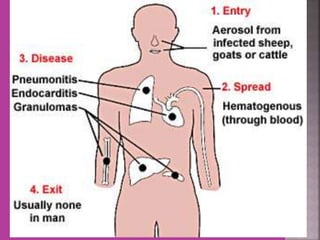
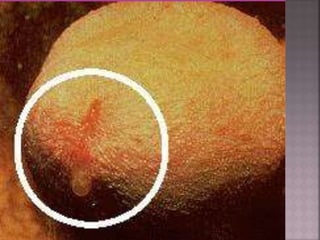
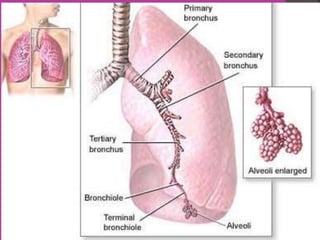
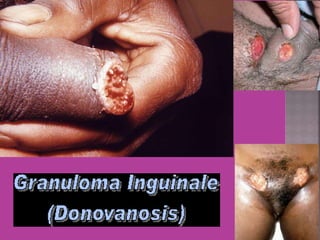
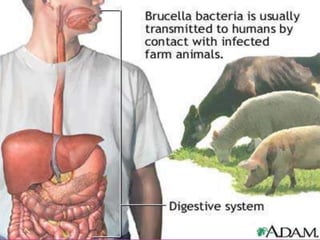
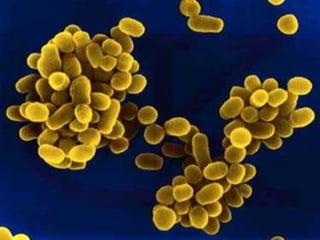
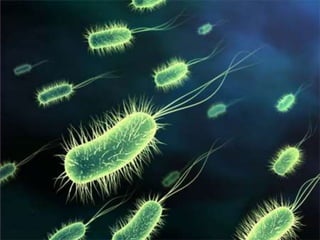
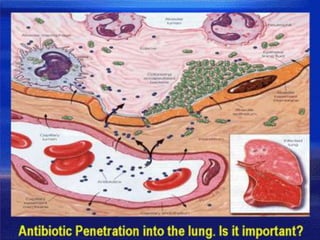
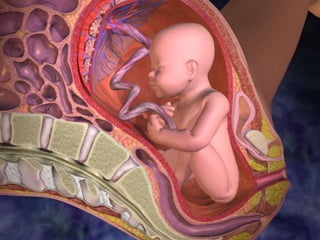
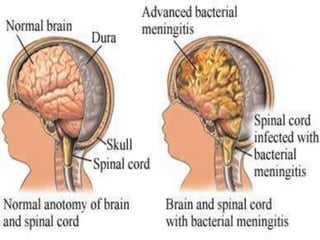
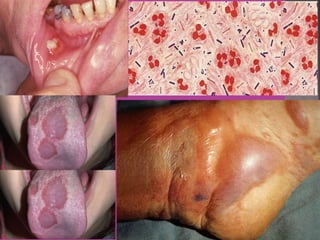
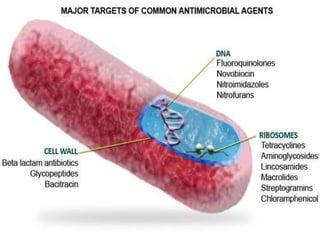
This document discusses tetracycline antibiotics. It notes that tetracyclines suppress a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as other microorganisms. They work by inhibiting protein synthesis by binding to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. Common side effects include gastrointestinal irritation. Tetracyclines are generally not recommended as first-line treatment but may be used for selected infections like rickettsial diseases. Newer tetracycline derivatives like doxycycline and minocycline have improved properties like better absorption and tissue penetration.