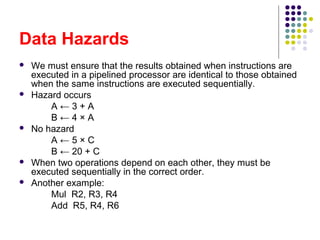
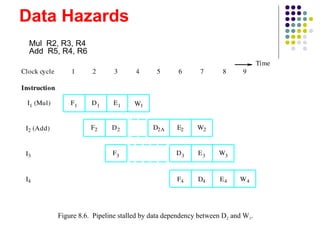
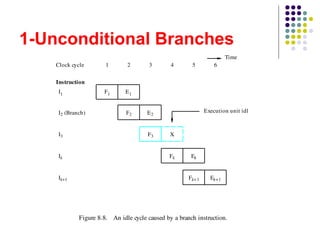
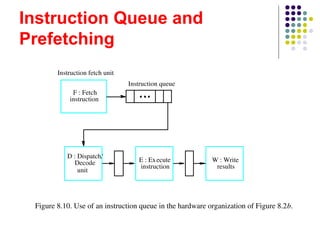
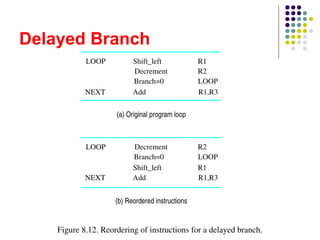
The document discusses pipelining in computer architecture, defining it as a technique for decomposing sequential processes into concurrent suboperations, akin to an assembly line. It elaborates on the advantages and disadvantages of pipelining, the types of pipelines (hardware and software), performance impacts due to hazards, and addressing modes, with a specific focus on RISC architecture. Additionally, it highlights the role of cache memory in enhancing pipelined execution efficiency and details issues like data and instruction hazards that can disrupt pipeline performance.










![Role of Cache Memory
Each pipeline stage is expected to complete in one
clock cycle.
The clock period should be long enough to let the
slowest pipeline stage to complete.
Faster stages can only wait for the slowest one to
complete.
Since main memory is very slow compared to the
execution, if each instruction needs to be fetched
from main memory, pipeline is almost useless.[ten
times greater than the time needed to perform
pipeline stage]
Fortunately, we have cache.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerarchitecturepipelining-170927140404/85/Computer-architecture-pipelining-15-320.jpg)

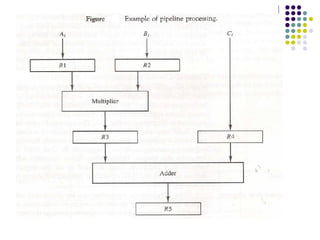
![Arithmetic Pipeline
Floating-point adder/subtracter
[1] Compare the exponents
[2] Align the mantissa
[3] Add/sub the mantissa
[4] Normalize the result
X = A x 10a
= 0.9504 x 103
Y = B x 10b
= 0.8200 x 102
1) Compare exponents :
3 - 2 = 1
2) Align mantissas
X = 0.9504 x 103
Y = 0.08200 x 103
3) Add mantissas
Z = 1.0324 x 103
4) Normalize result
Z = 0.10324 x 104
R
Compare
exponents
by subtraction
a b
R
Choose exponent
Exponents
R
A B
Align mantissa
Mantissas
Difference
R
Add or subtract
mantissas
R
Normalize
result
R
R
Adjust
exponent
R
Segment 1:
Segment 2:
Segment 3:
Segment 4:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerarchitecturepipelining-170927140404/85/Computer-architecture-pipelining-18-320.jpg)
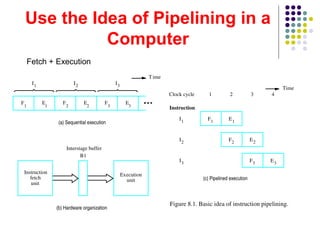
![INSTRUCTION CYCLE
Six Phases* in an Instruction Cycle
[1] Fetch an instruction from memory
[2] Decode the instruction
[3] Calculate the effective address of the operand
[4] Fetch the operands from memory
[5] Execute the operation
[6] Store the result in the proper place
* Some instructions skip some phases
* Effective address calculation can be done in the part of the decoding phase
* Storage of the operation result into a register is done automatically in the execution
phase
==> 4-Stage Pipeline
[1] FI: Fetch an instruction from memory
[2] DA: Decode the instruction and calculate the effective address of the operand
[3] FO: Fetch the operand
[4] EX: Execute the operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerarchitecturepipelining-170927140404/85/Computer-architecture-pipelining-19-320.jpg)