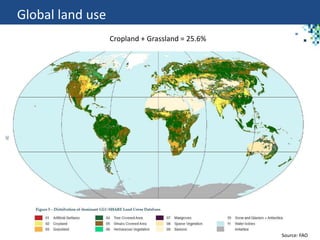
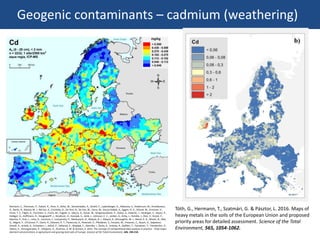
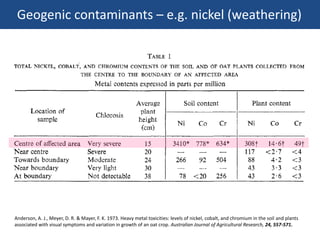
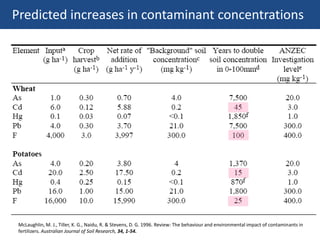
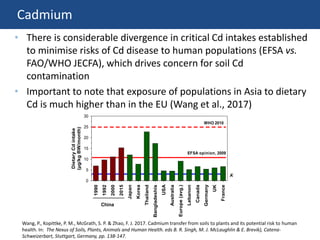
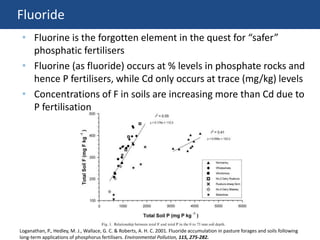
The document discusses the drivers of soil pollution in agricultural fields, focusing on both geogenic and anthropogenic sources of contaminants, particularly from fertilizers. Key contaminants such as cadmium and fluorine are highlighted, with emphasis on their impact on soil quality, crop uptake, and potential human health risks. The document underscores the importance of managing inputs and agronomic practices to mitigate these risks, especially in regions with high natural contaminant levels.