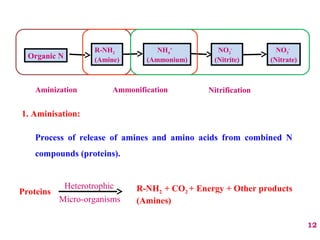
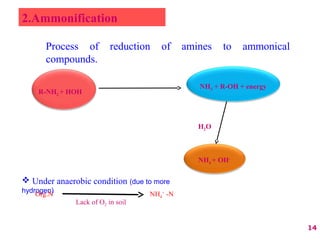
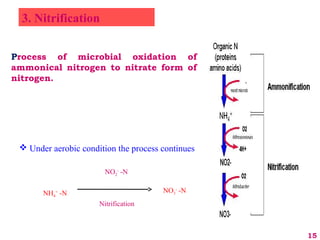
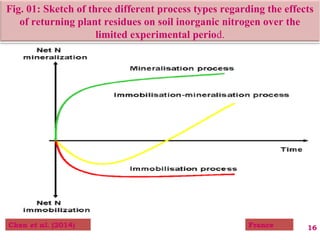
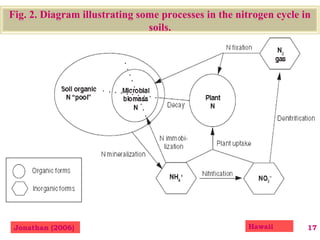
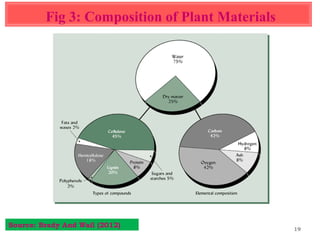
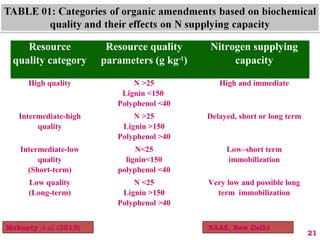
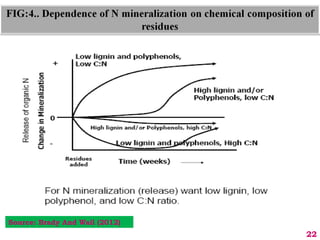
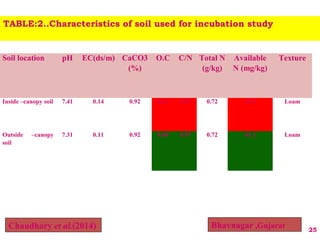
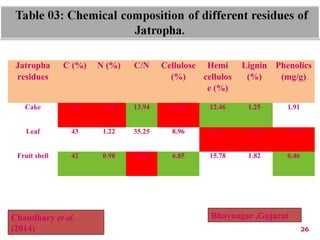
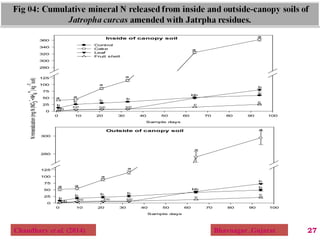
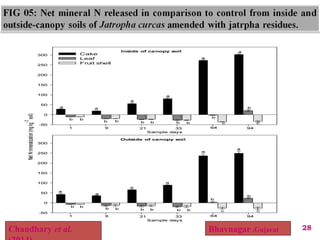
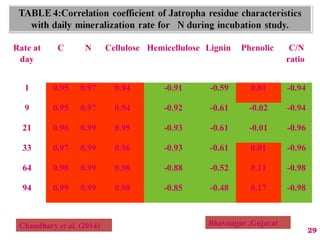
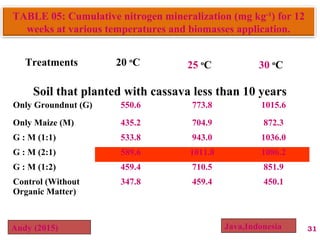
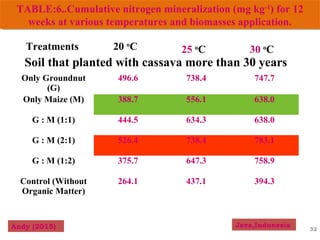
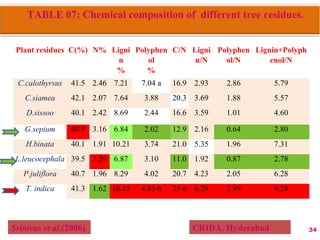
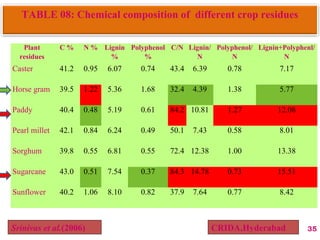
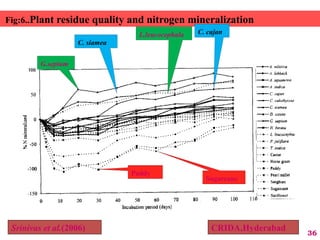
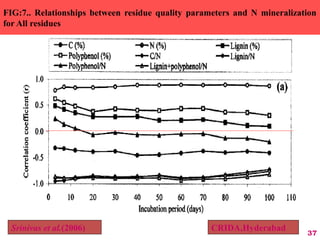
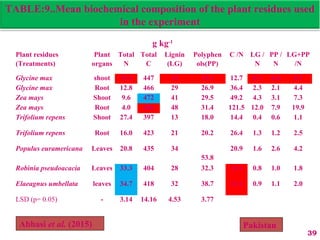
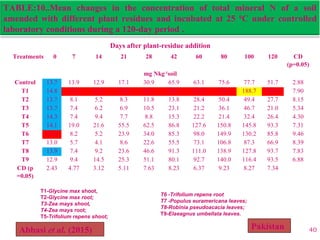
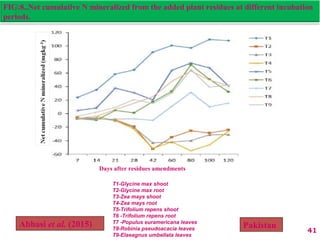
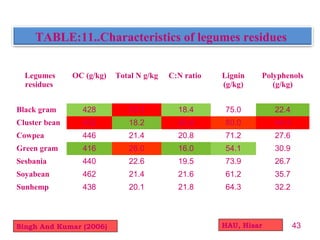
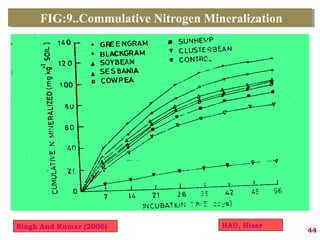
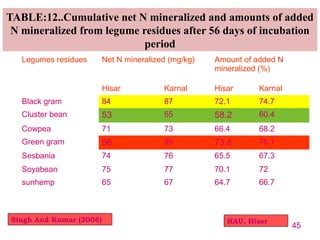
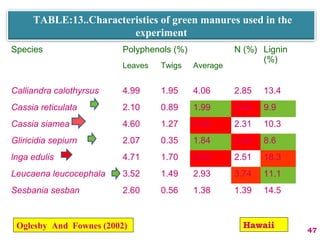
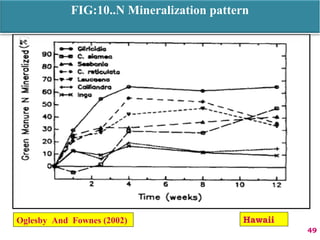
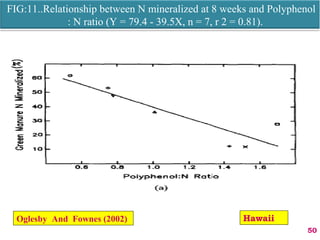
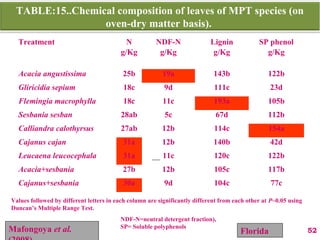
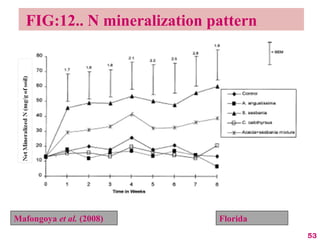
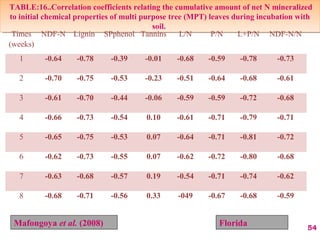
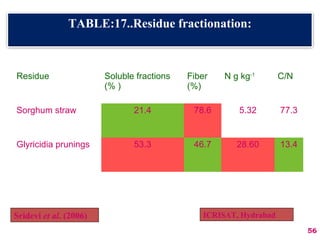
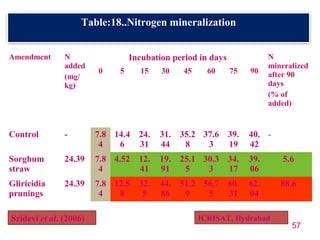
The document discusses the effect of chemical composition of plant residues on nitrogen mineralization in soil. It presents findings from several case studies and research papers. The chemical composition of different plant residues like lignin, polyphenols and C:N ratio affects their decomposition rate and impacts nitrogen mineralization. Plant residues high in nitrogen and low in lignin and polyphenols decompose faster, releasing nitrogen for plant uptake. The studies show crop residues and tree leaves with higher lignin and polyphenol content immobilize soil nitrogen during decomposition.