This document provides an overview of pulmonary function tests (PFTs) including:
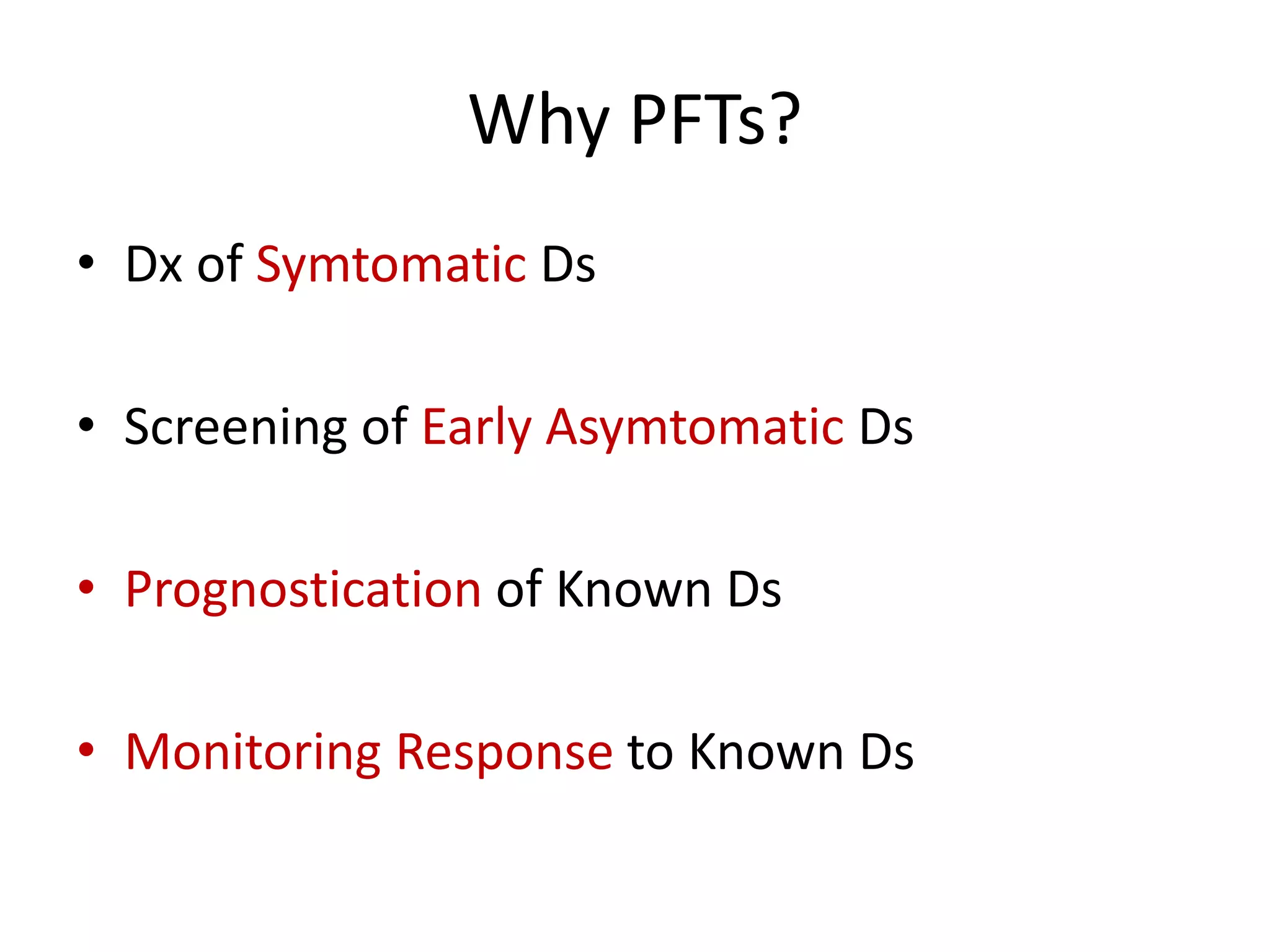
- PFTs are used to diagnose symptomatic diseases, screen for early asymptomatic diseases, prognosticate known diseases, and monitor response to treatment.
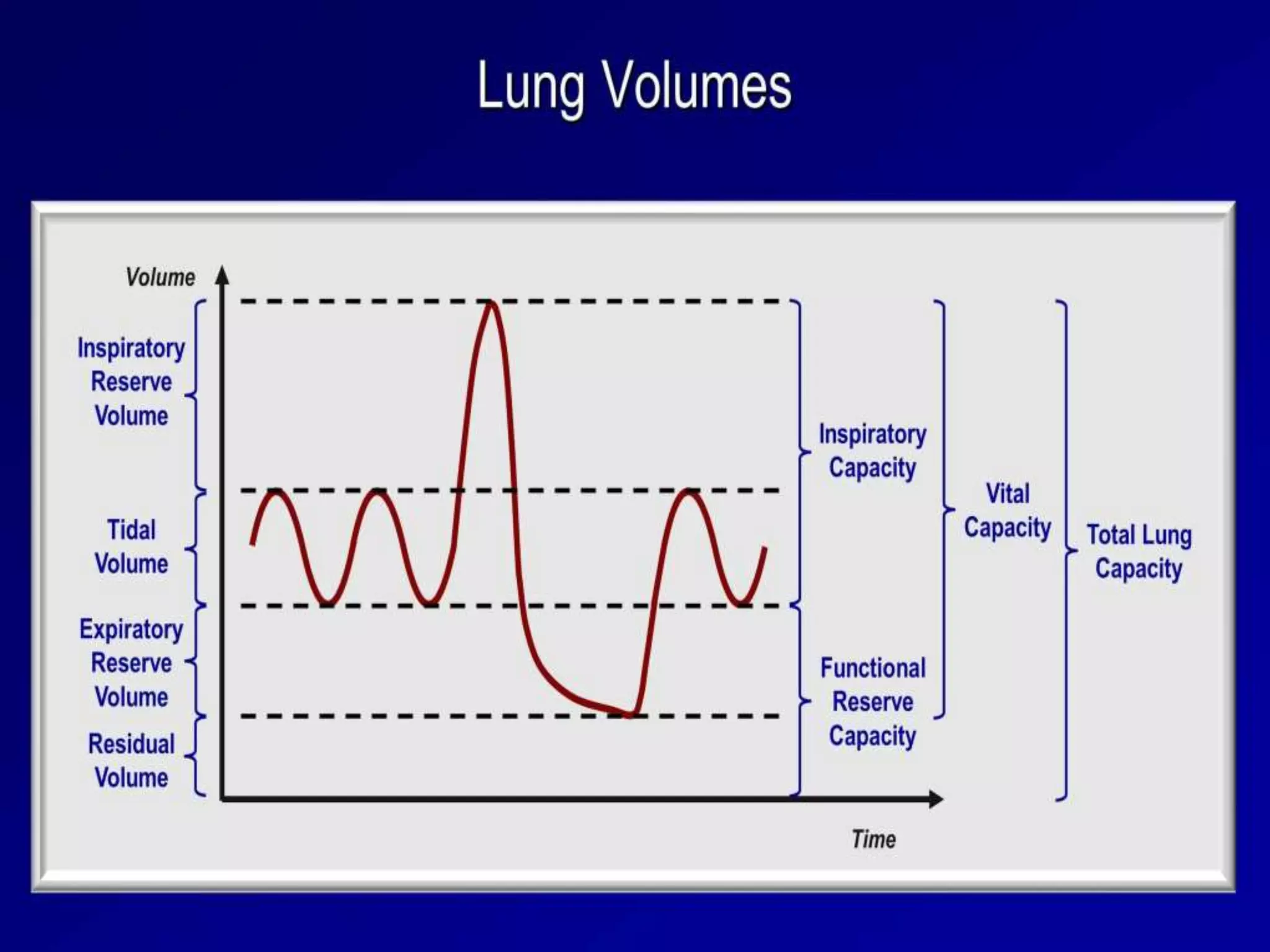
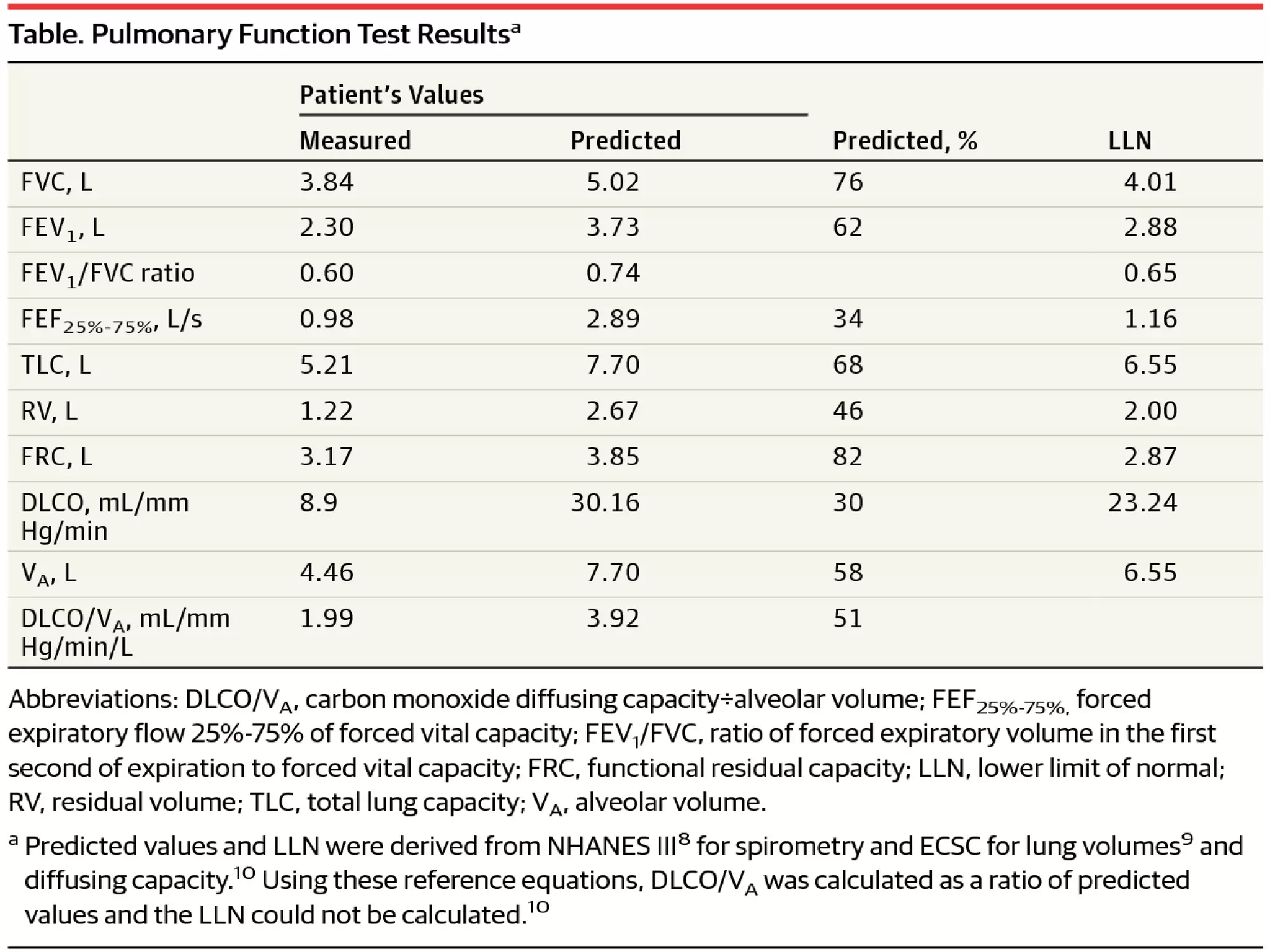
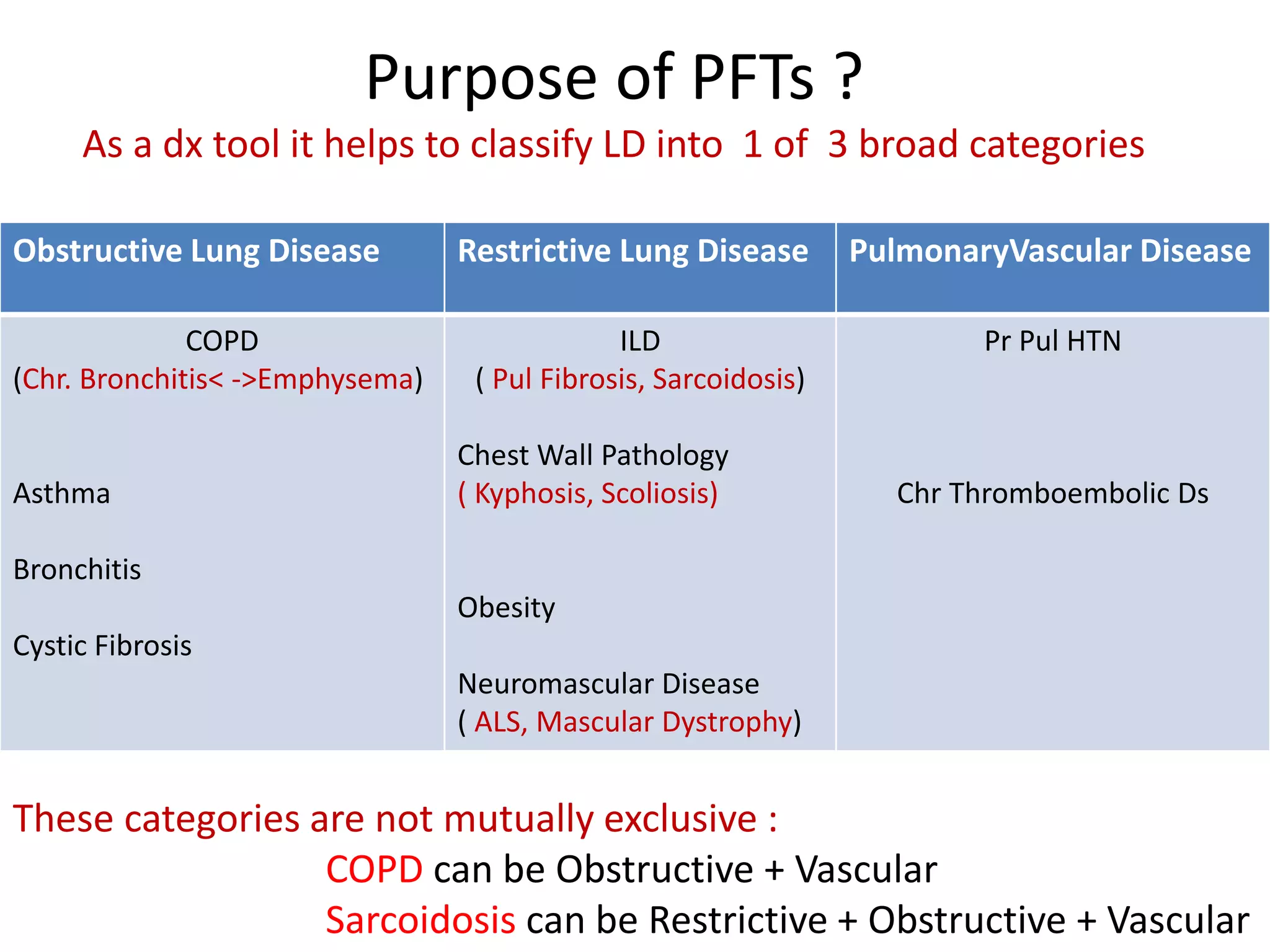
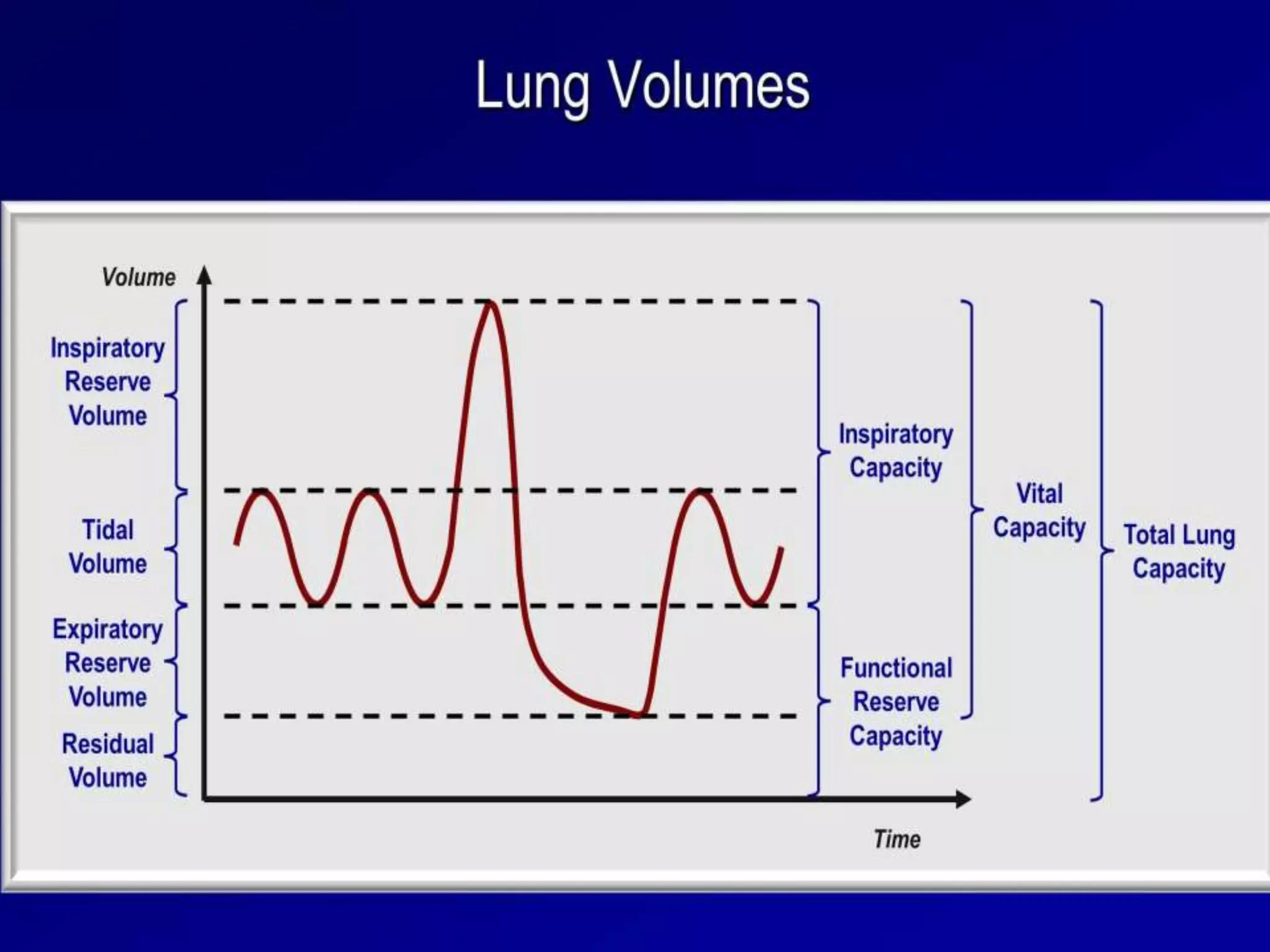
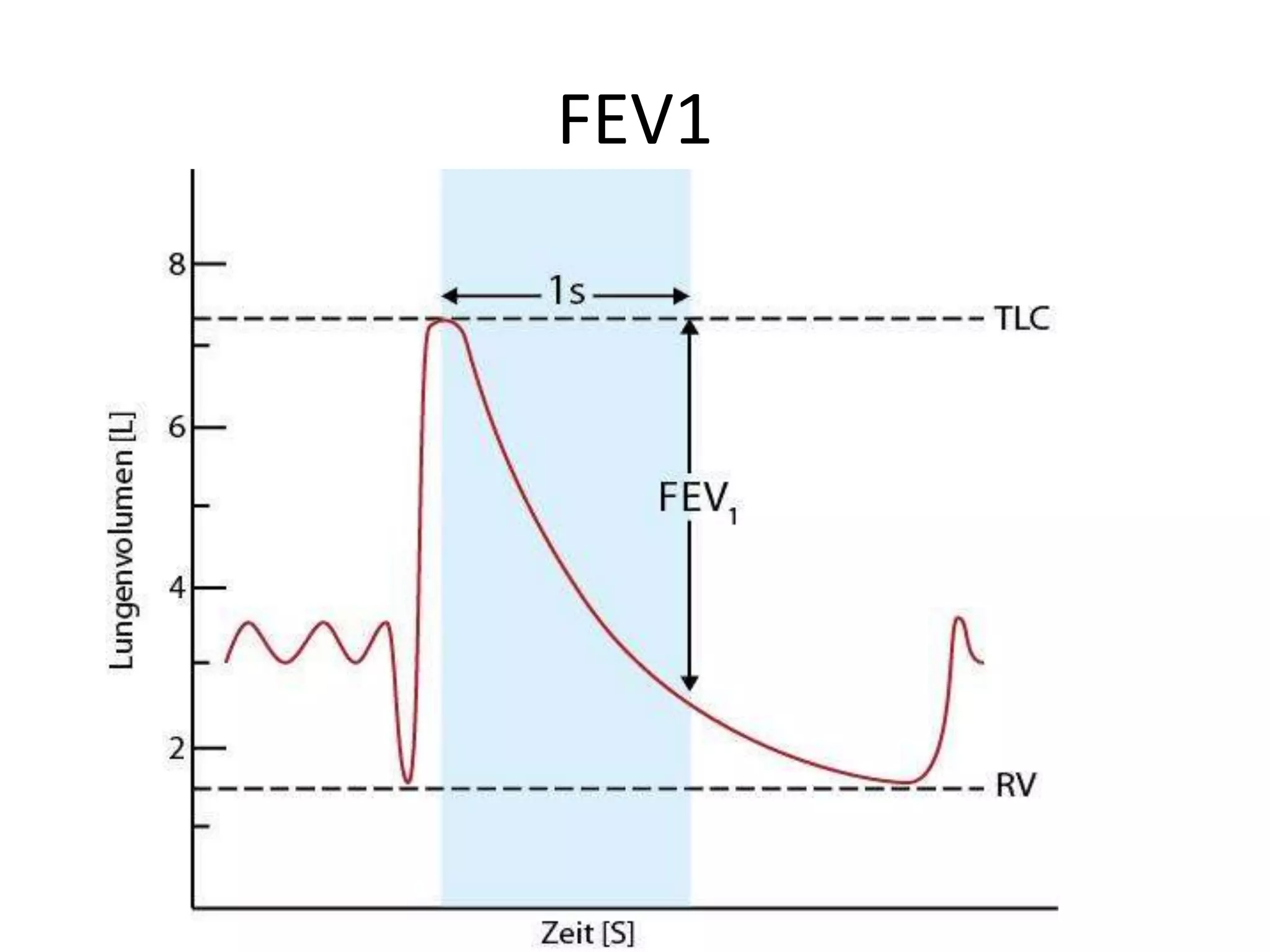
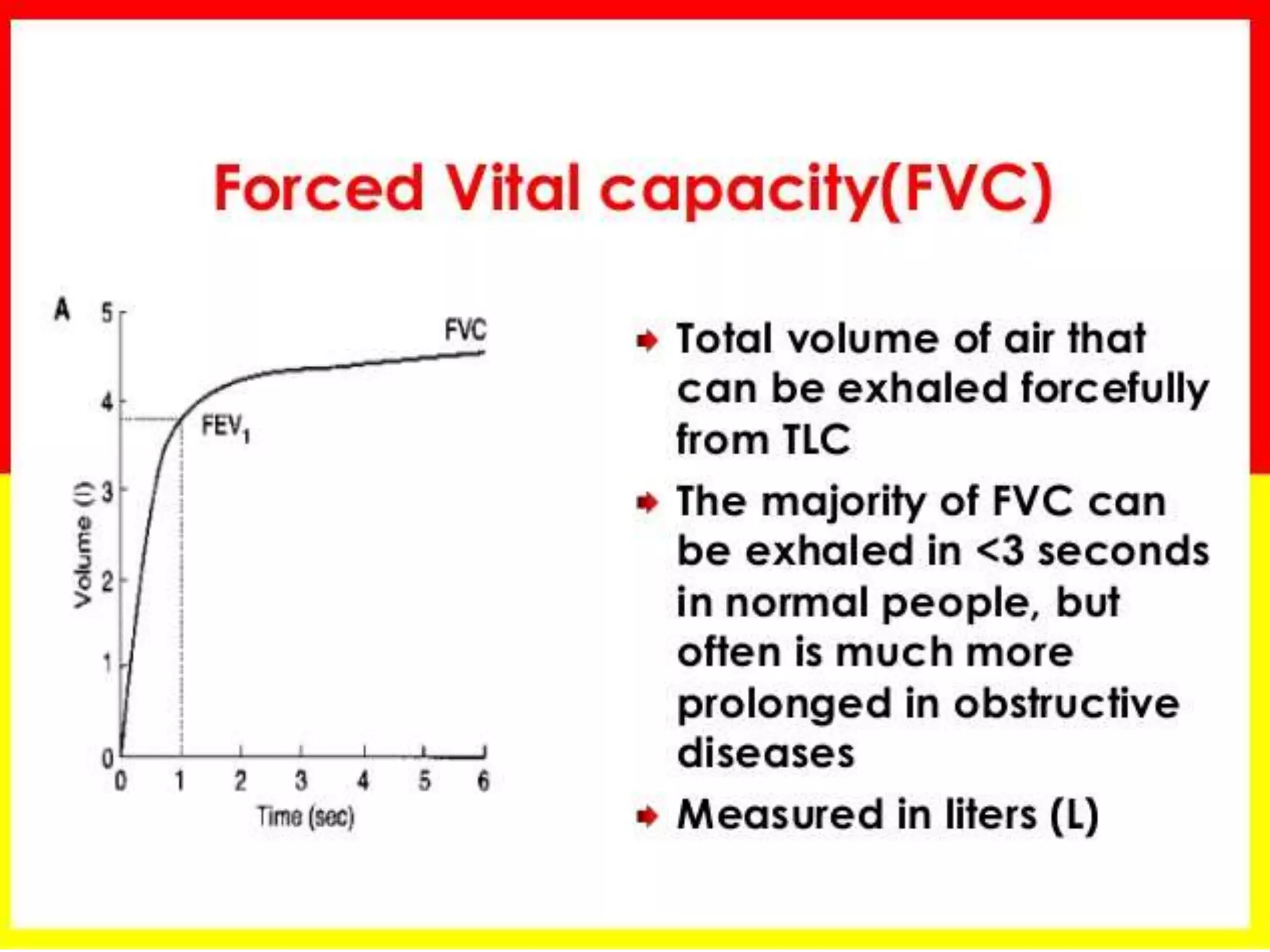
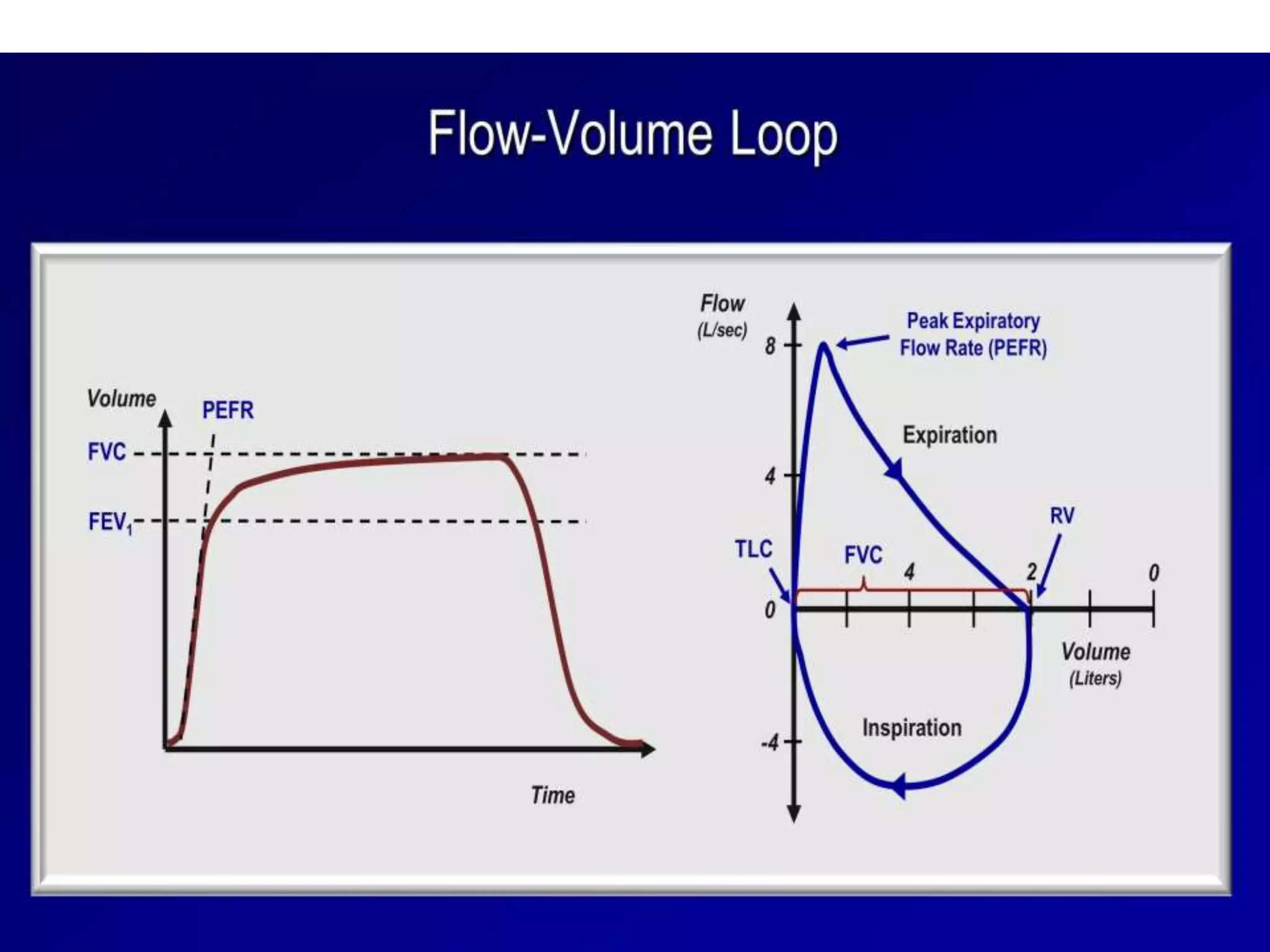
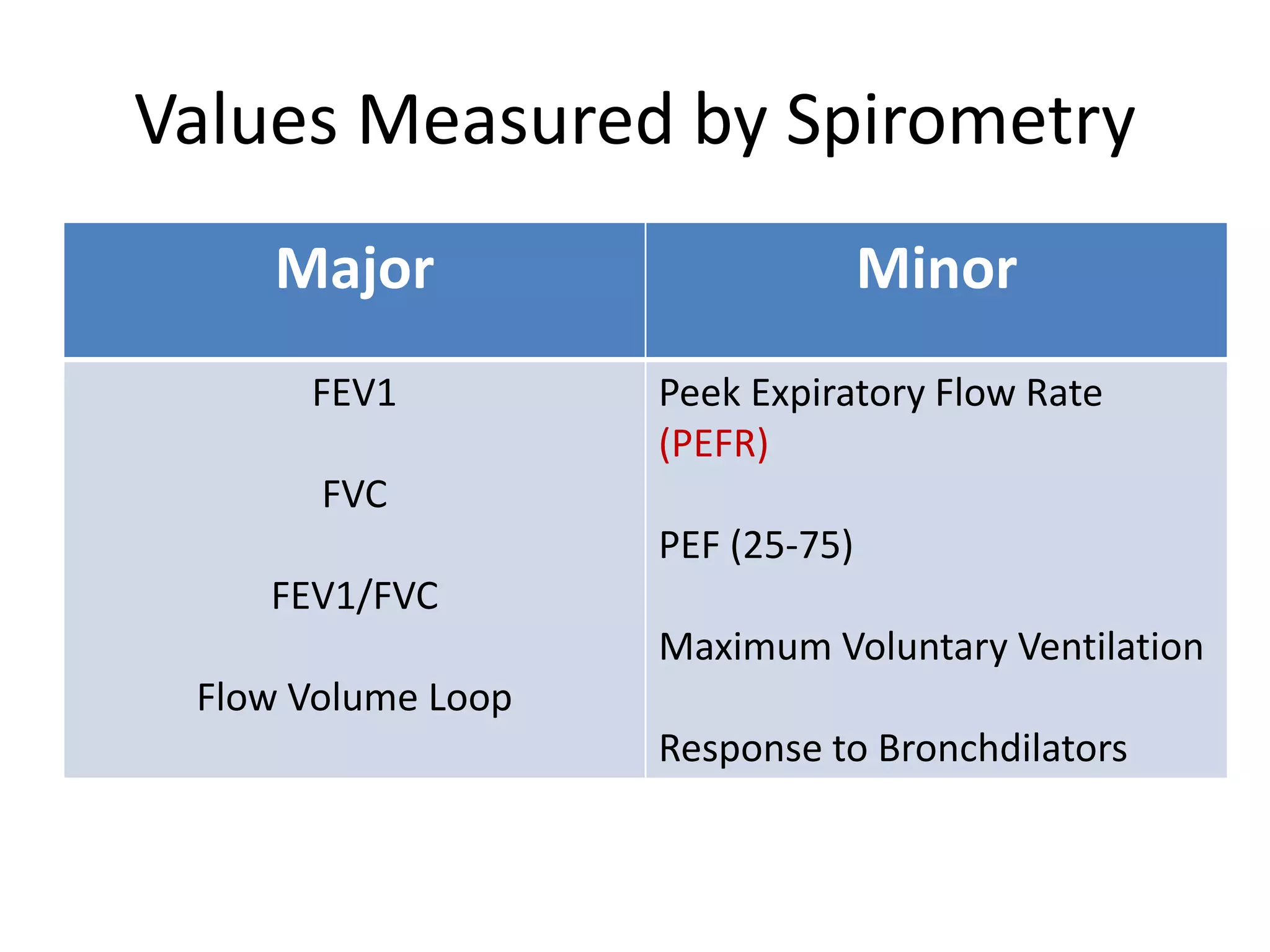
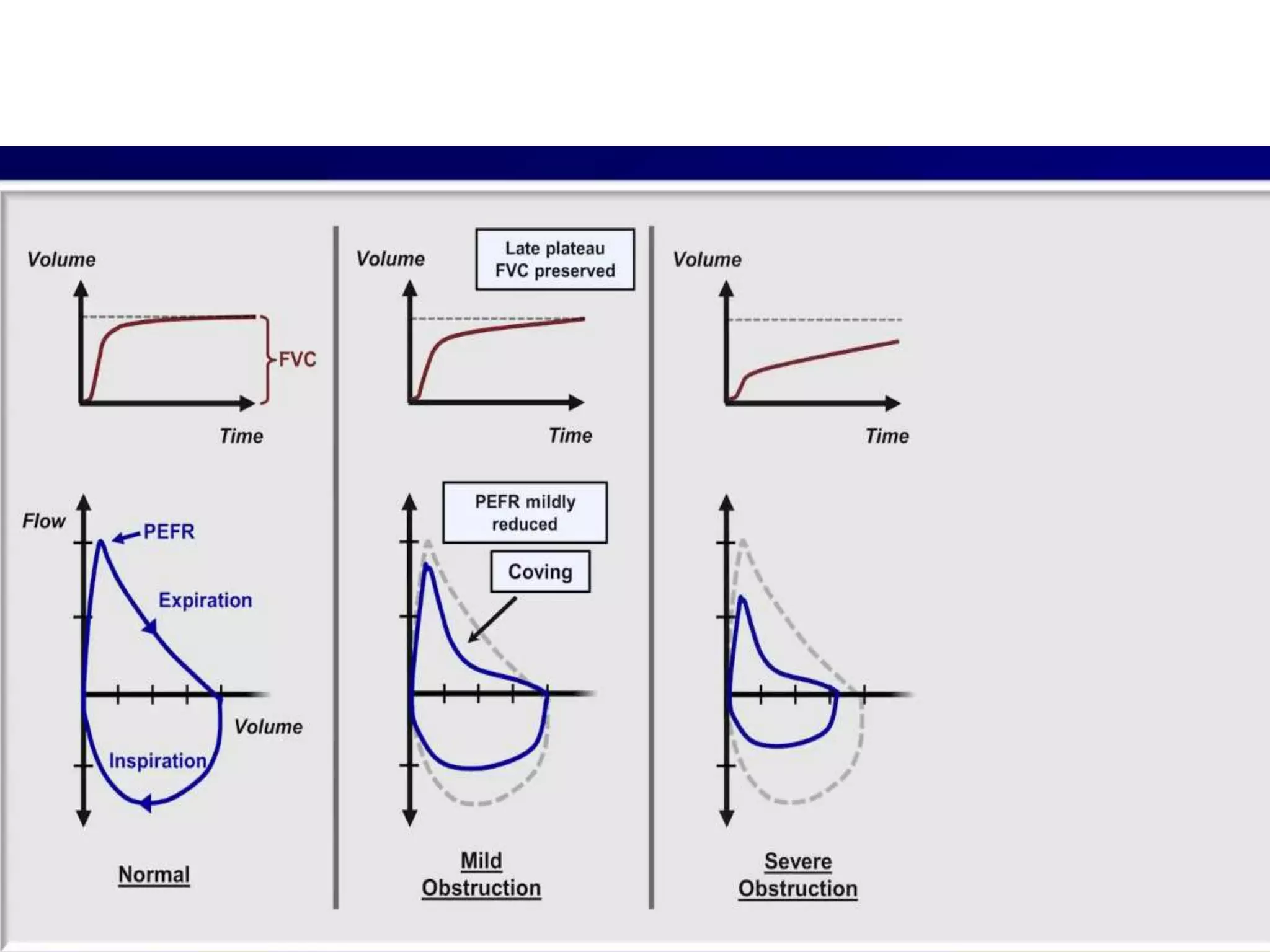
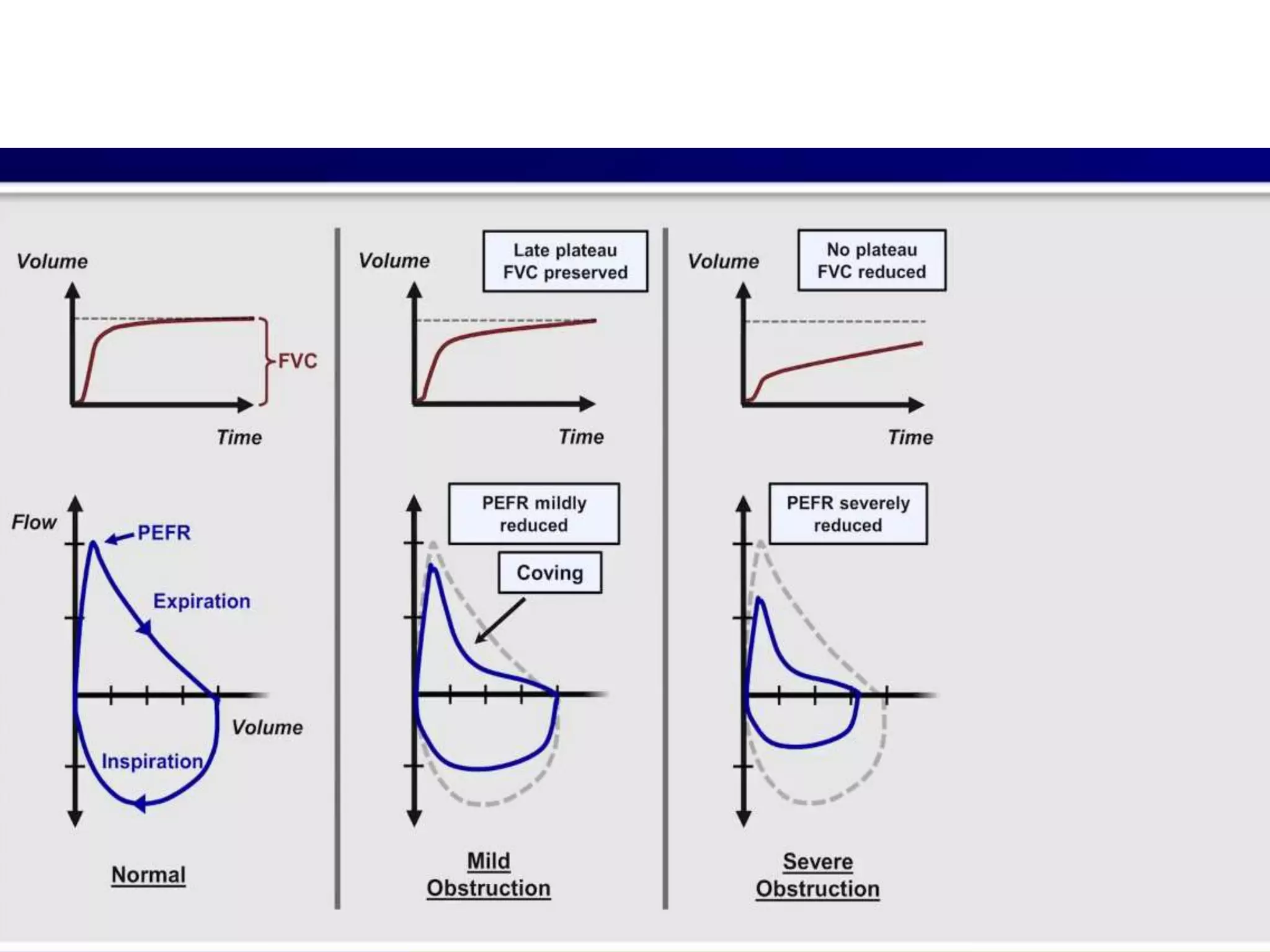
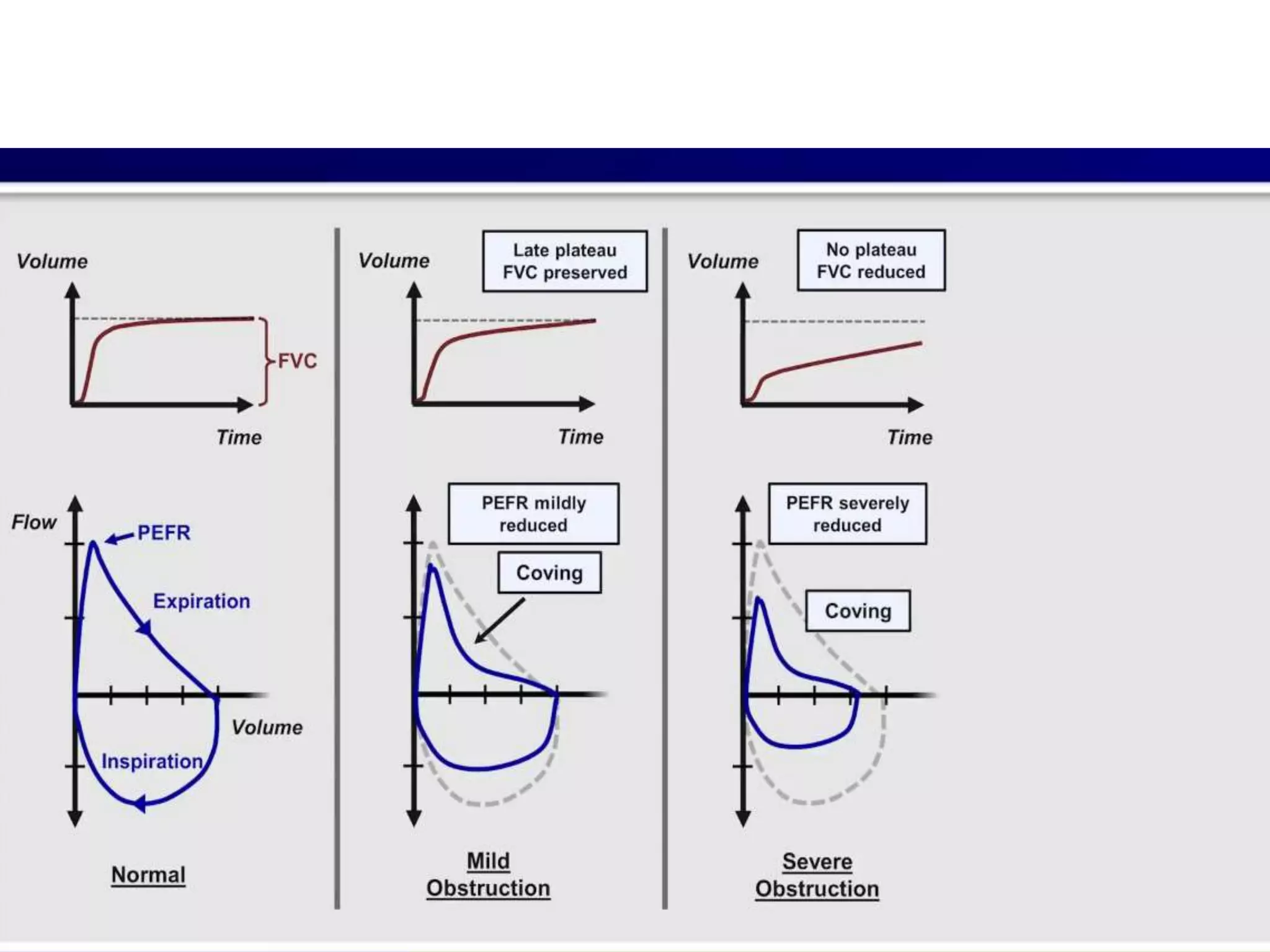
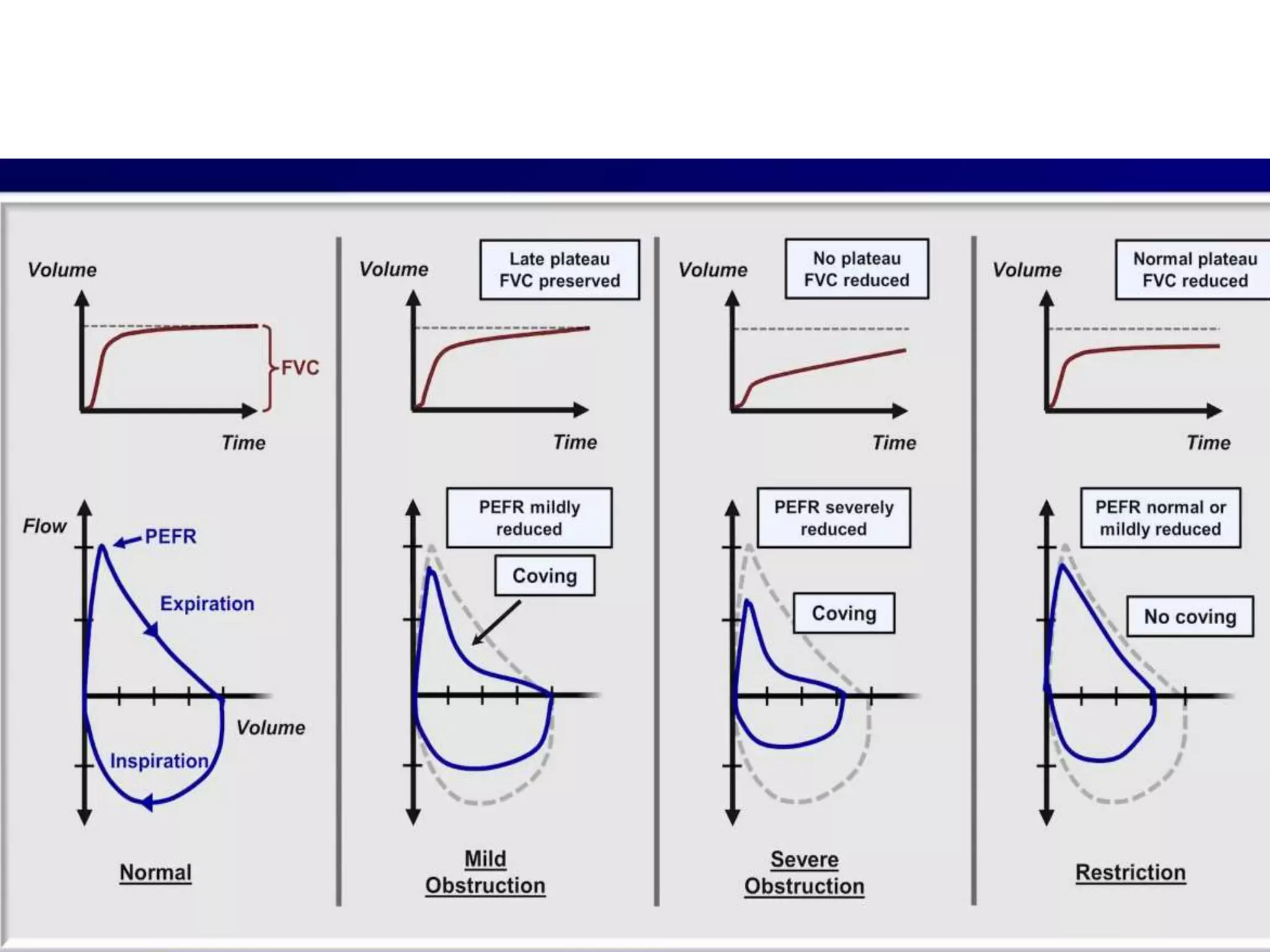
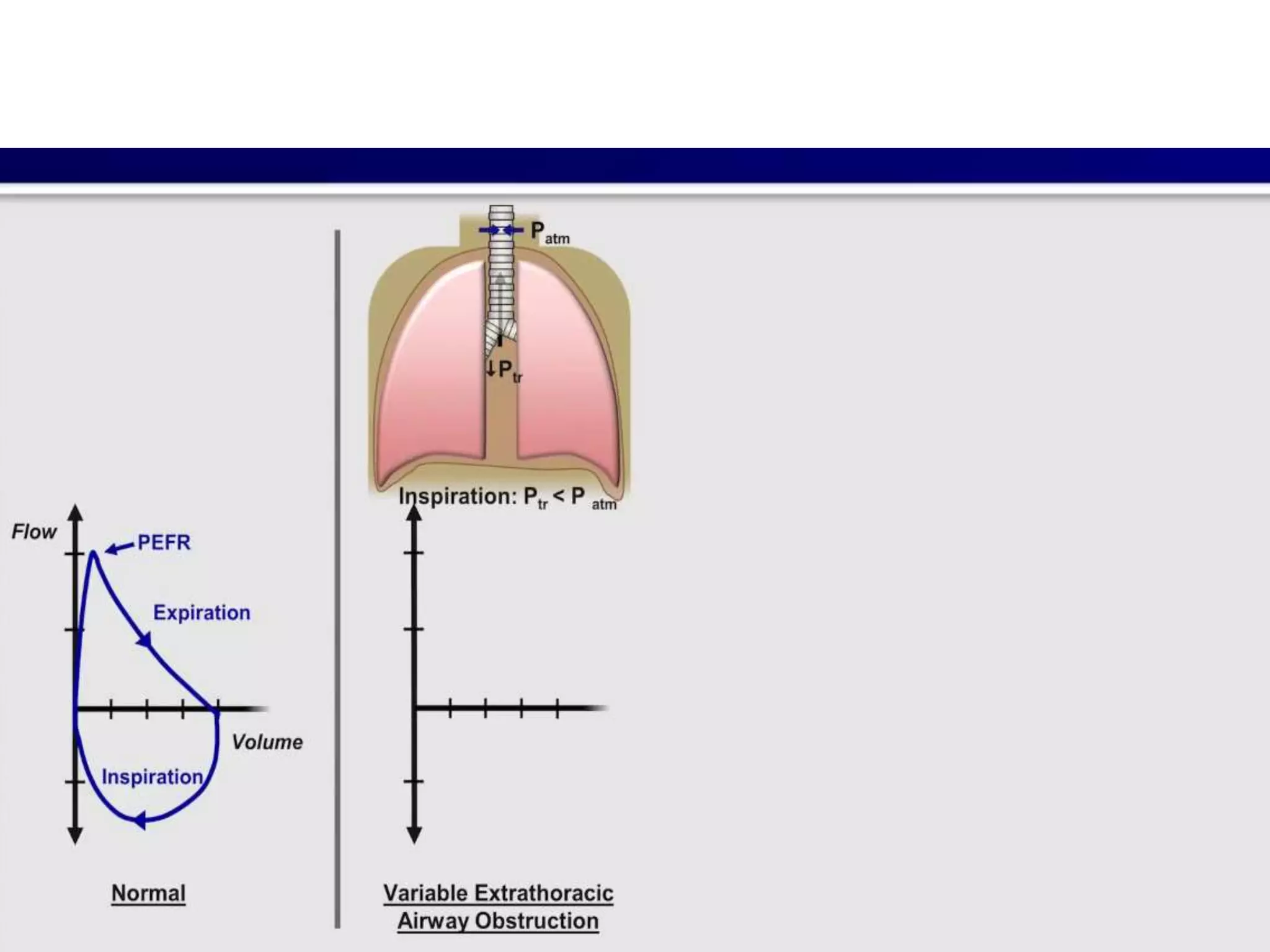
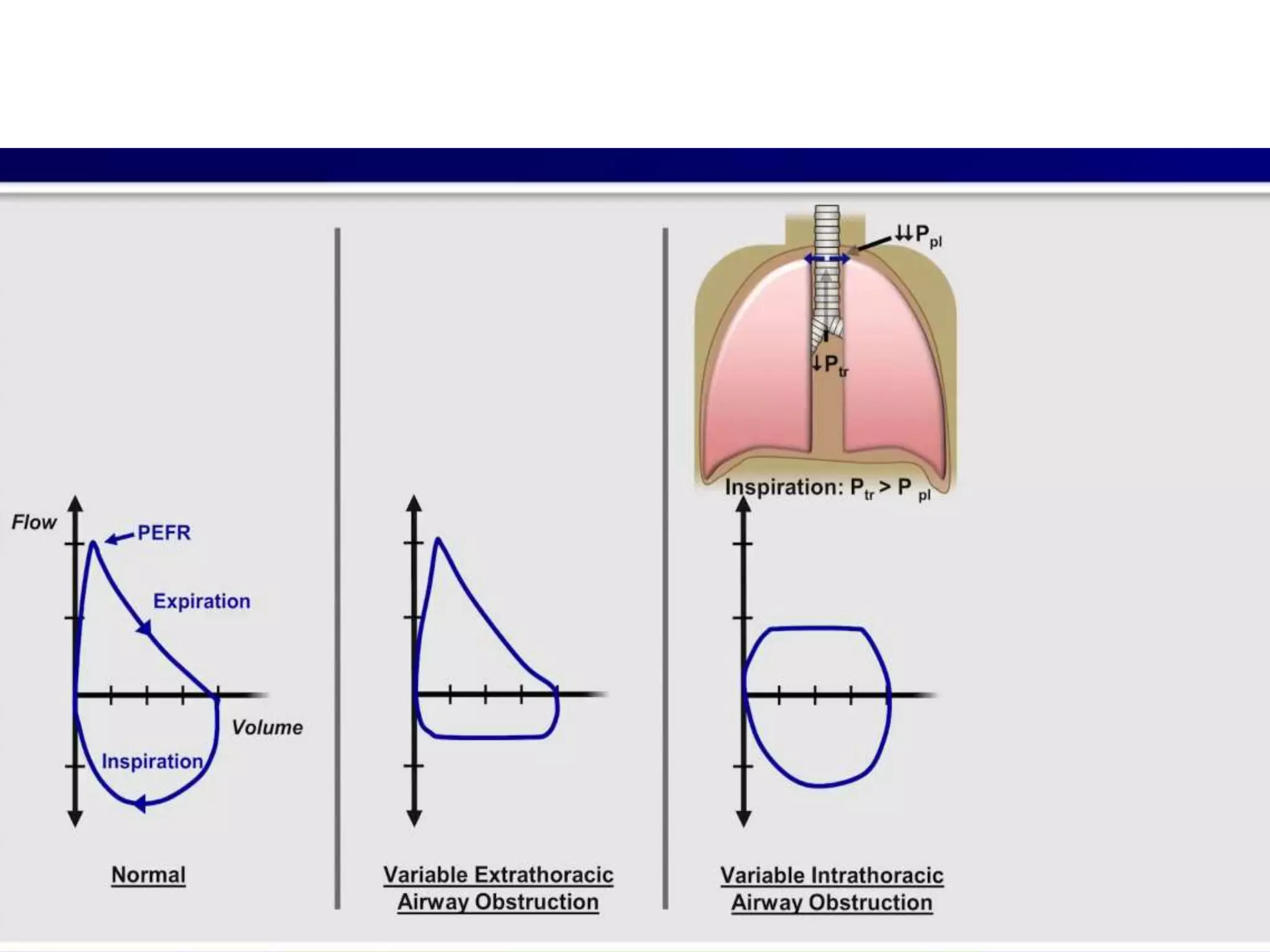
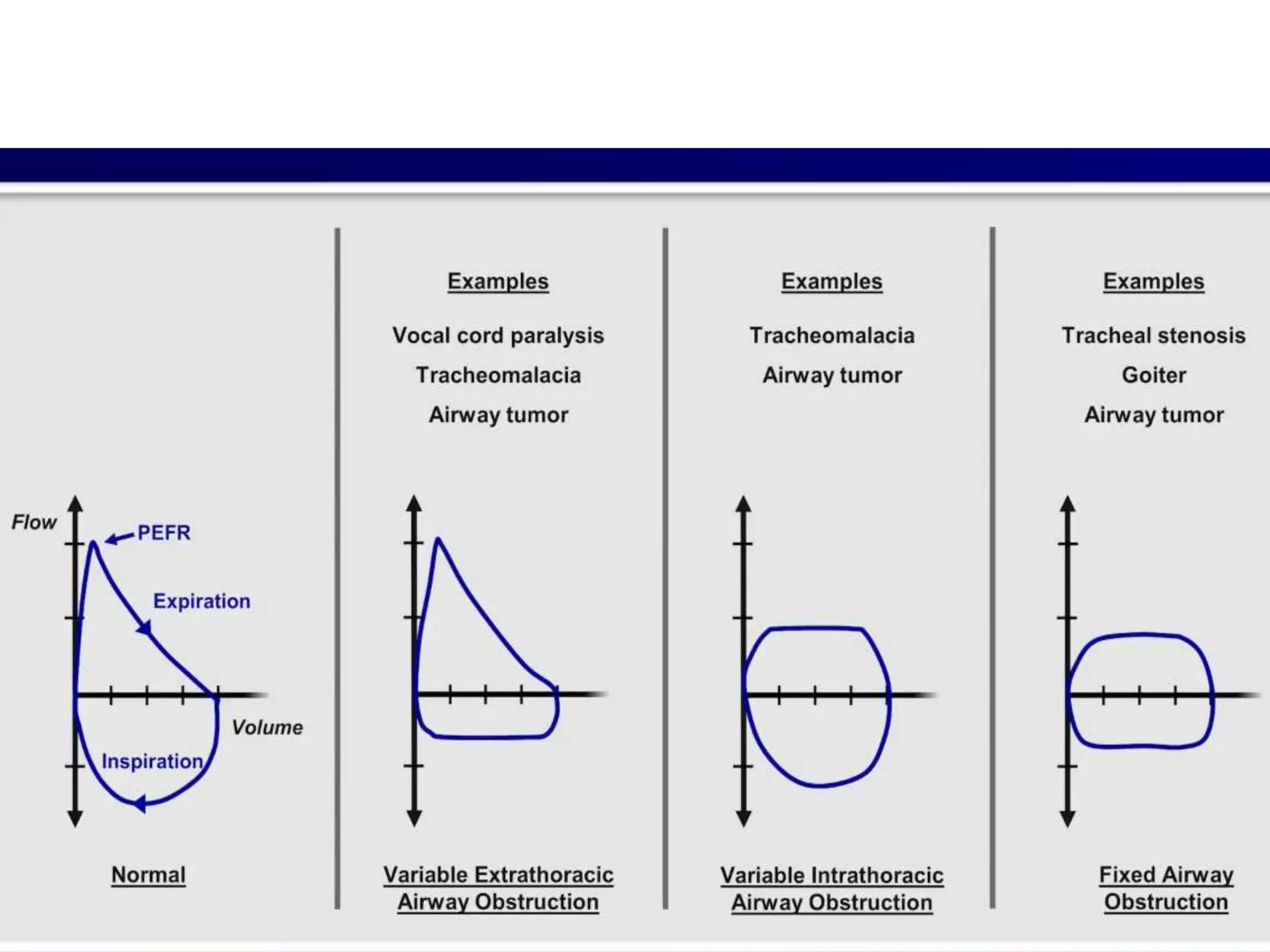
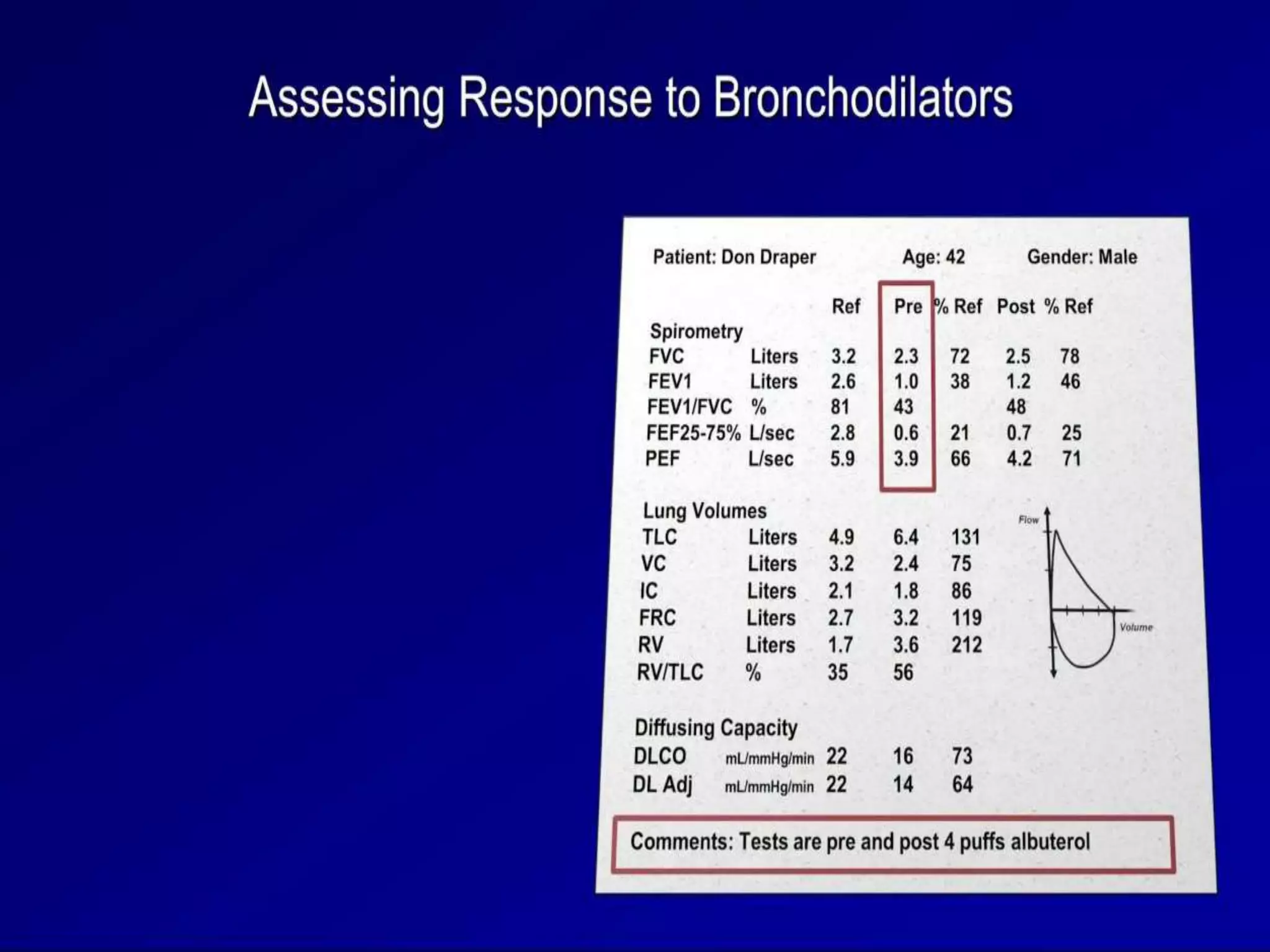
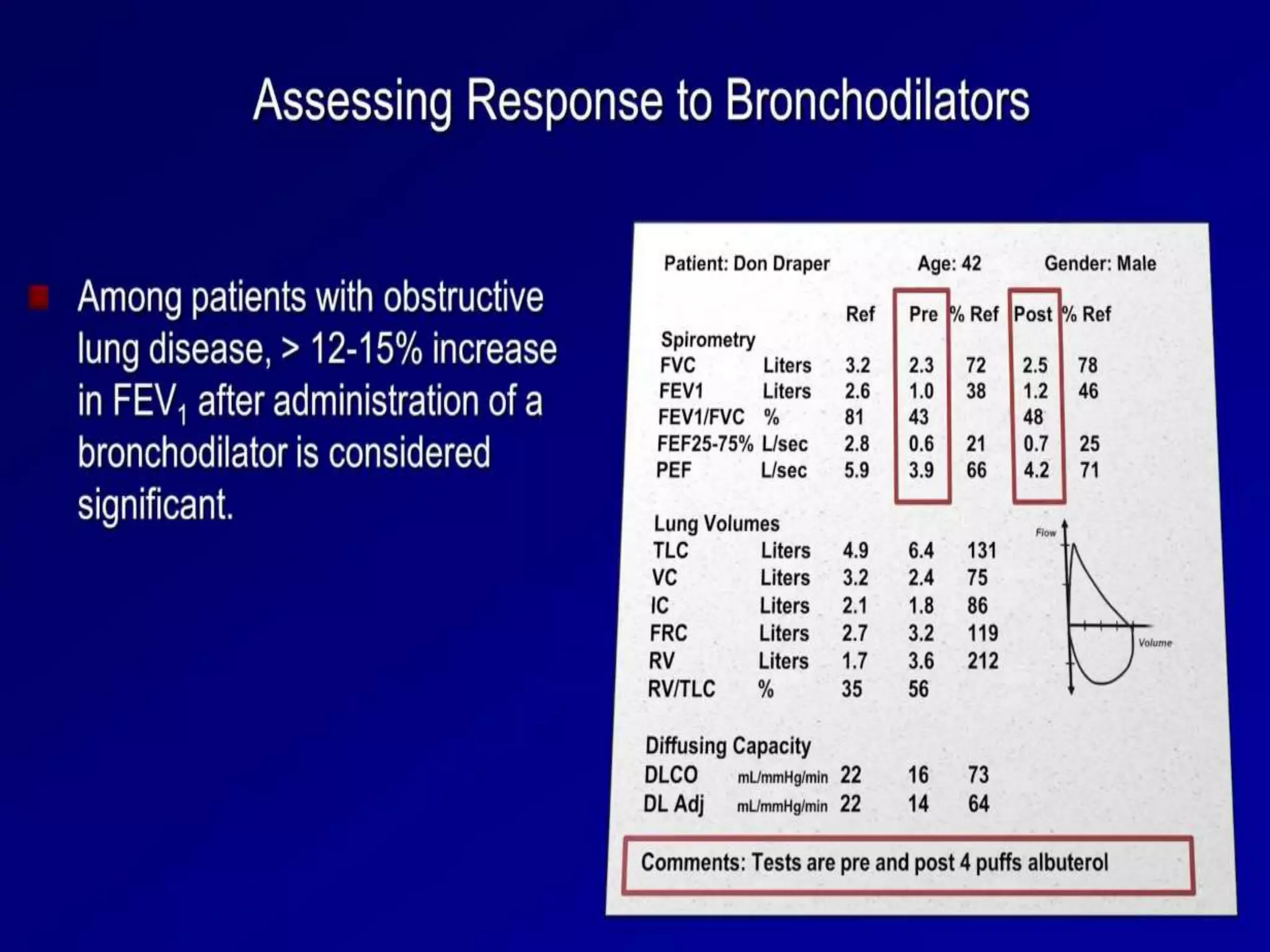
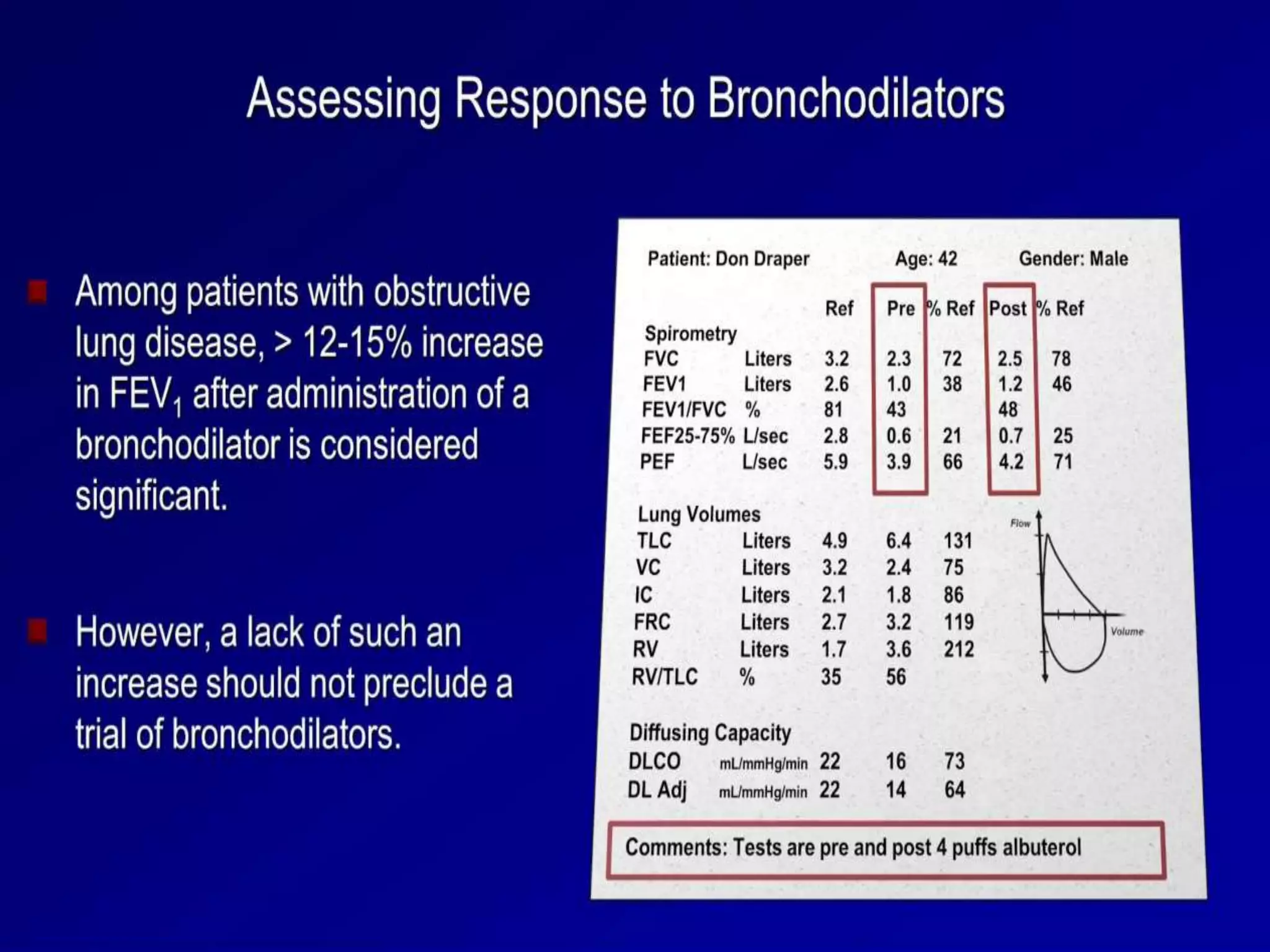
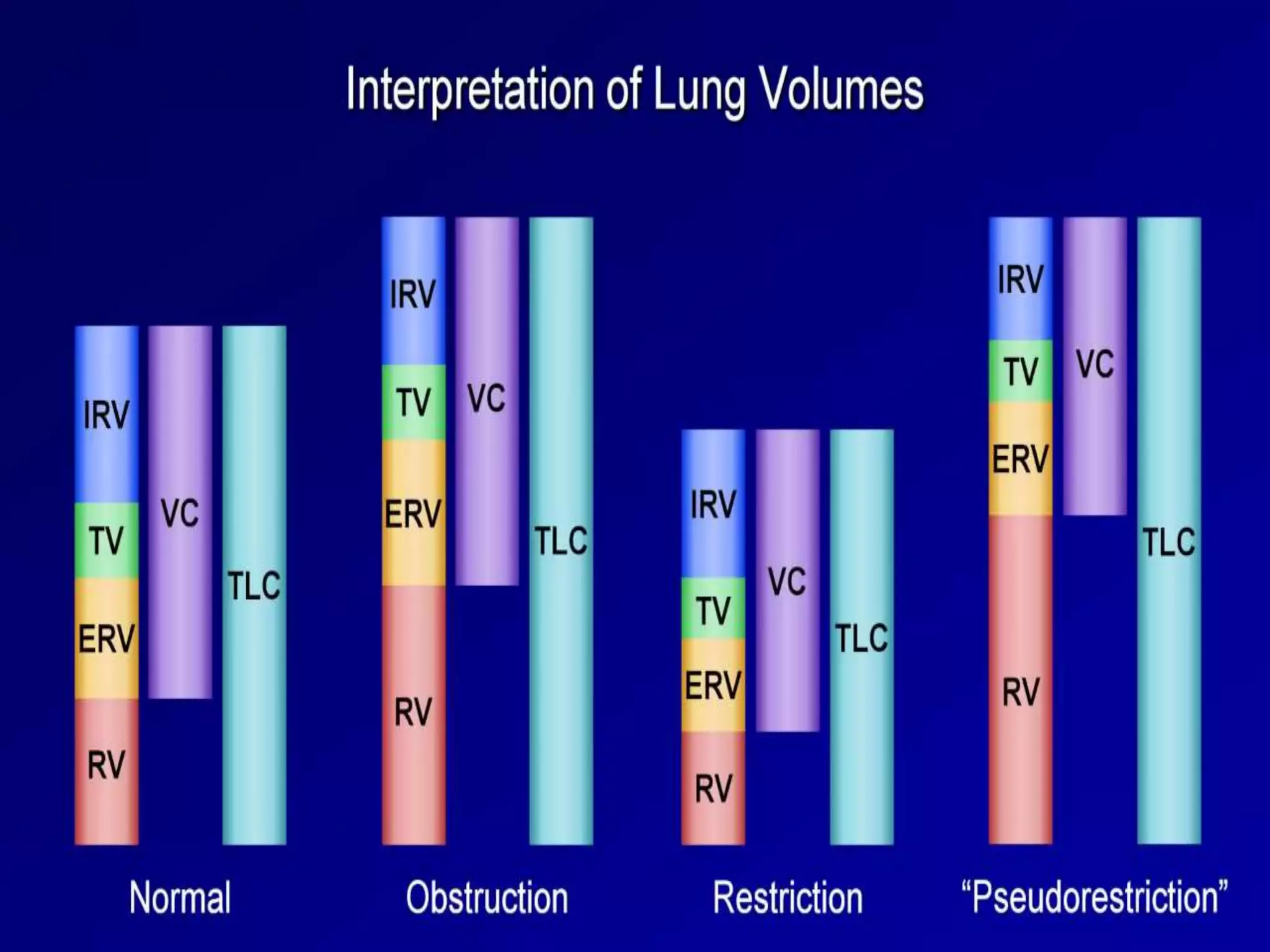
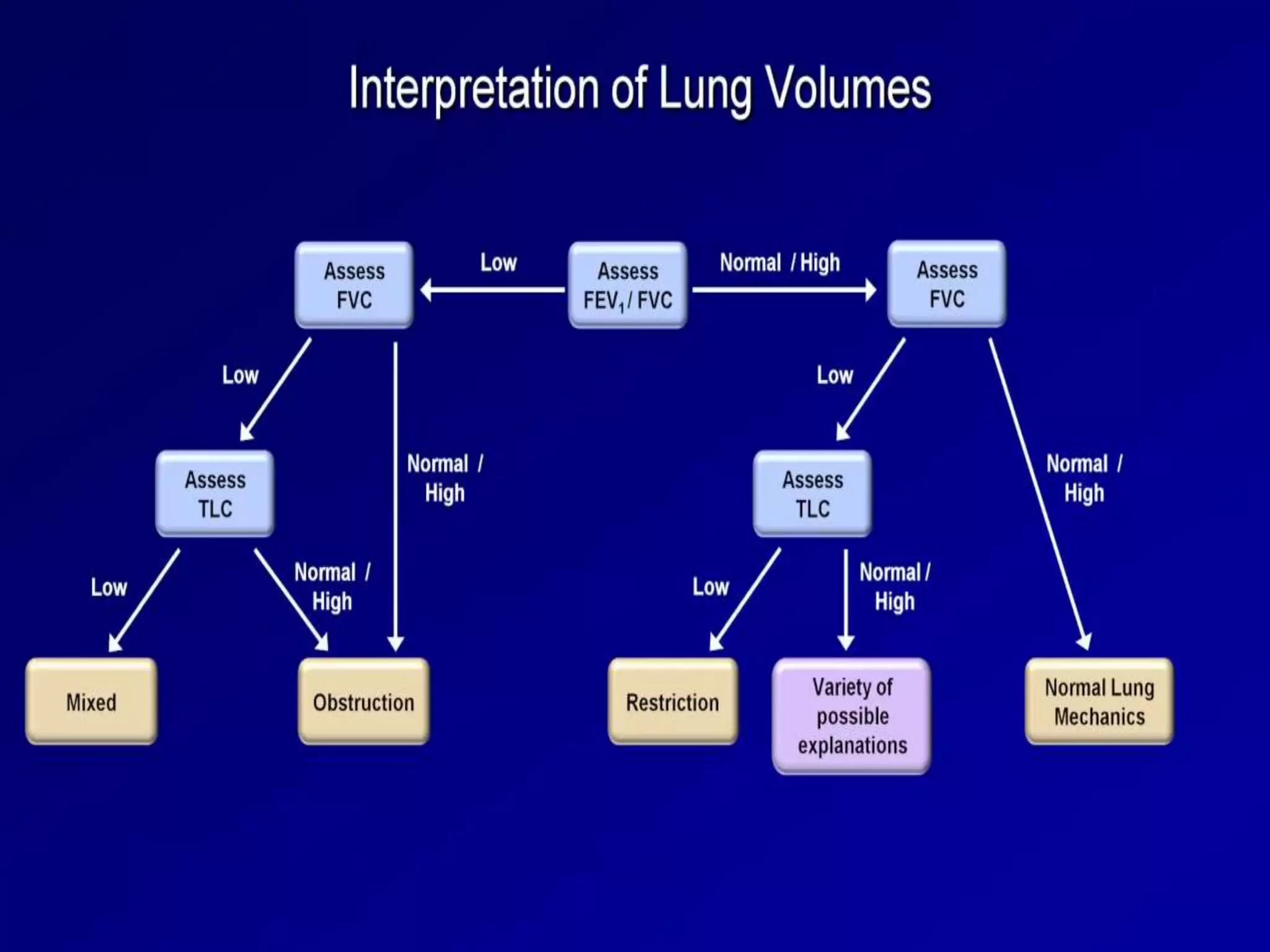
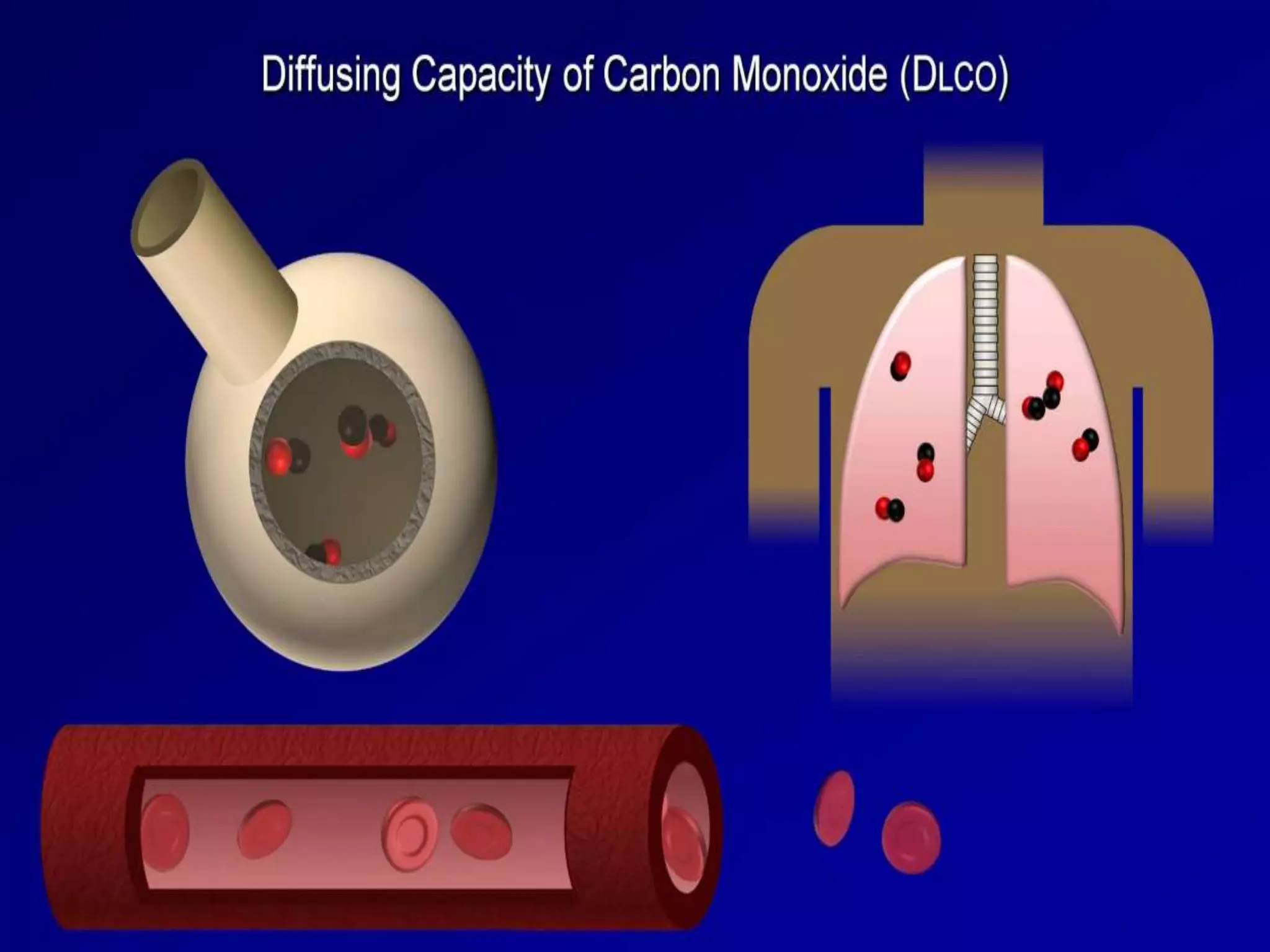
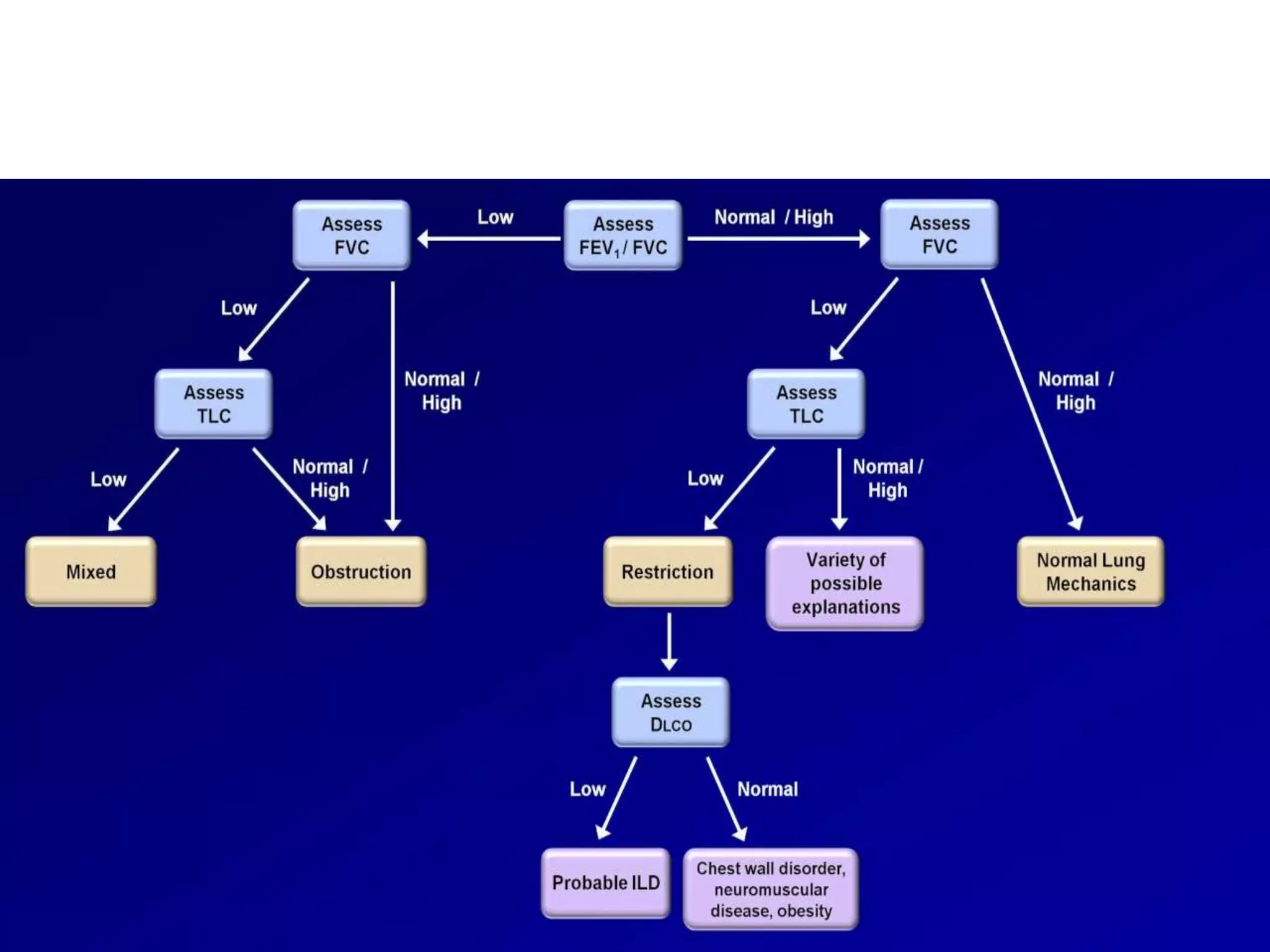
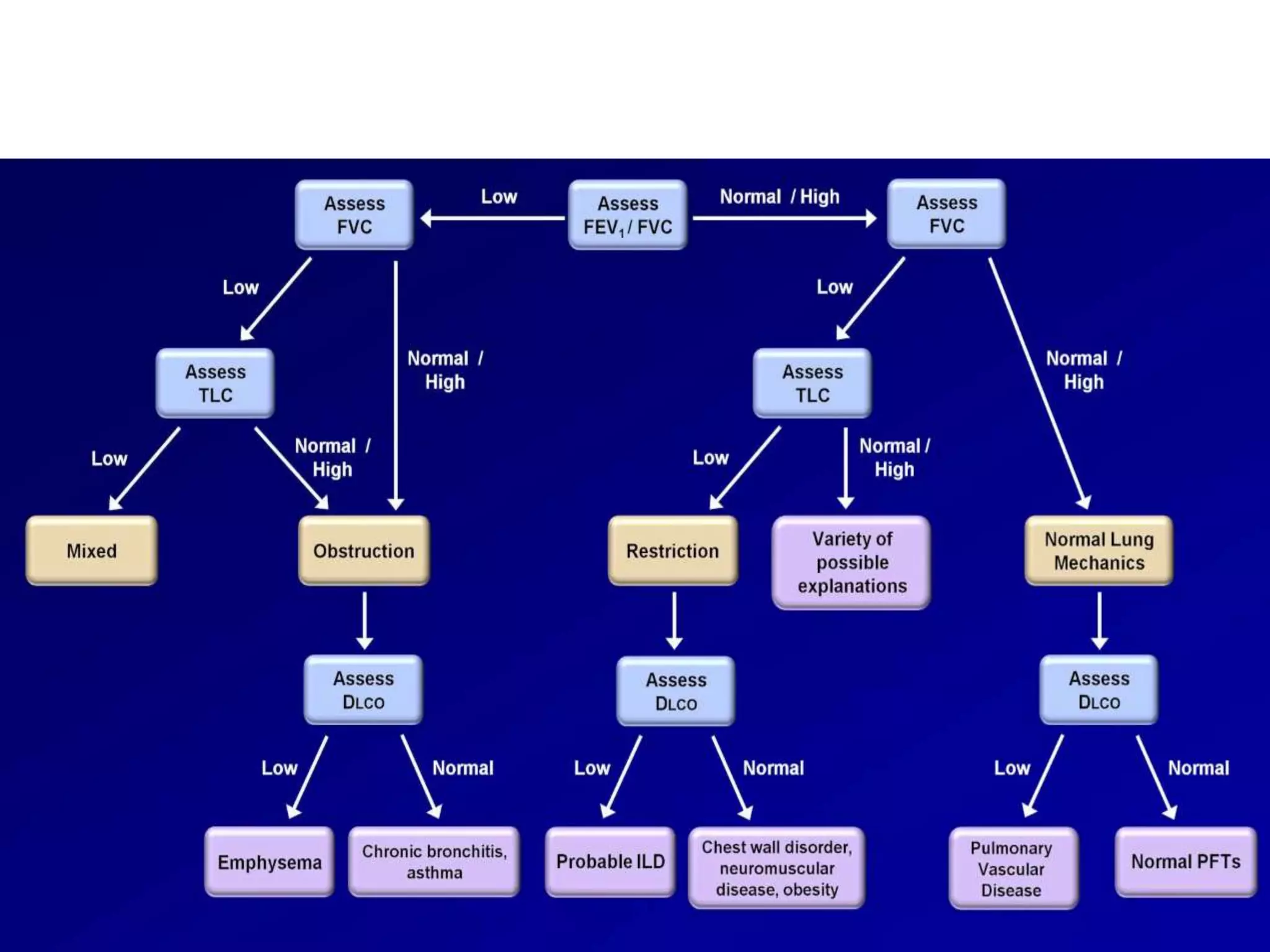
- Spirometry specifically measures airflow and lung volumes through tests like FEV1 and FVC to classify obstructive, restrictive, or pulmonary vascular lung diseases.
- COPD severity is staged based on post-bronchodilator FEV1 levels according to GOLD criteria, with lower FEV1 indicating more severe COPD.