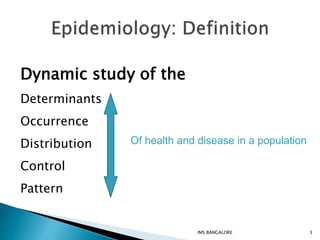
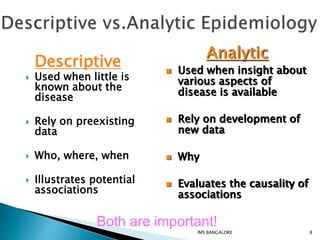
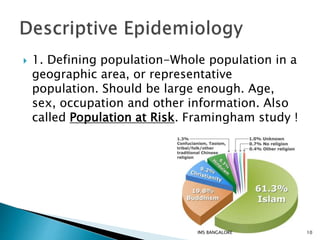
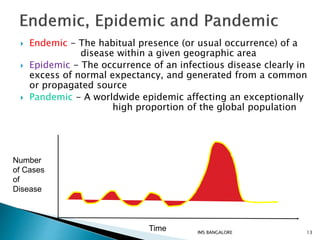
This document discusses epidemiological methods for studying the distribution and determinants of health events and applying that knowledge to disease control. It defines descriptive epidemiology as the study of disease occurrence, distribution, and patterns in populations. Descriptive methods are observational and can be cross-sectional or longitudinal. Descriptive epidemiology provides insights into disease frequency, trends, and risk factors to inform public health planning and resource allocation.