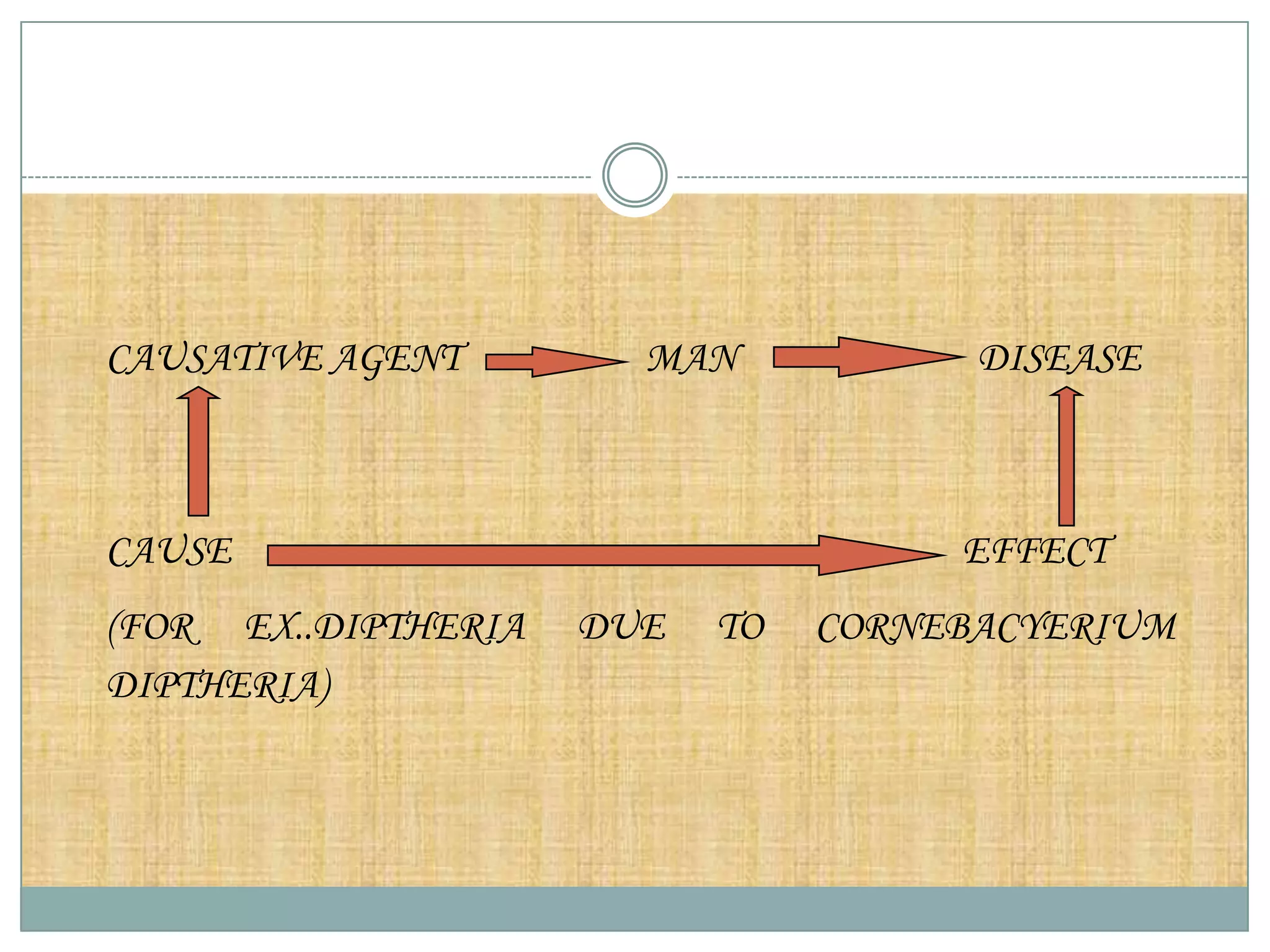
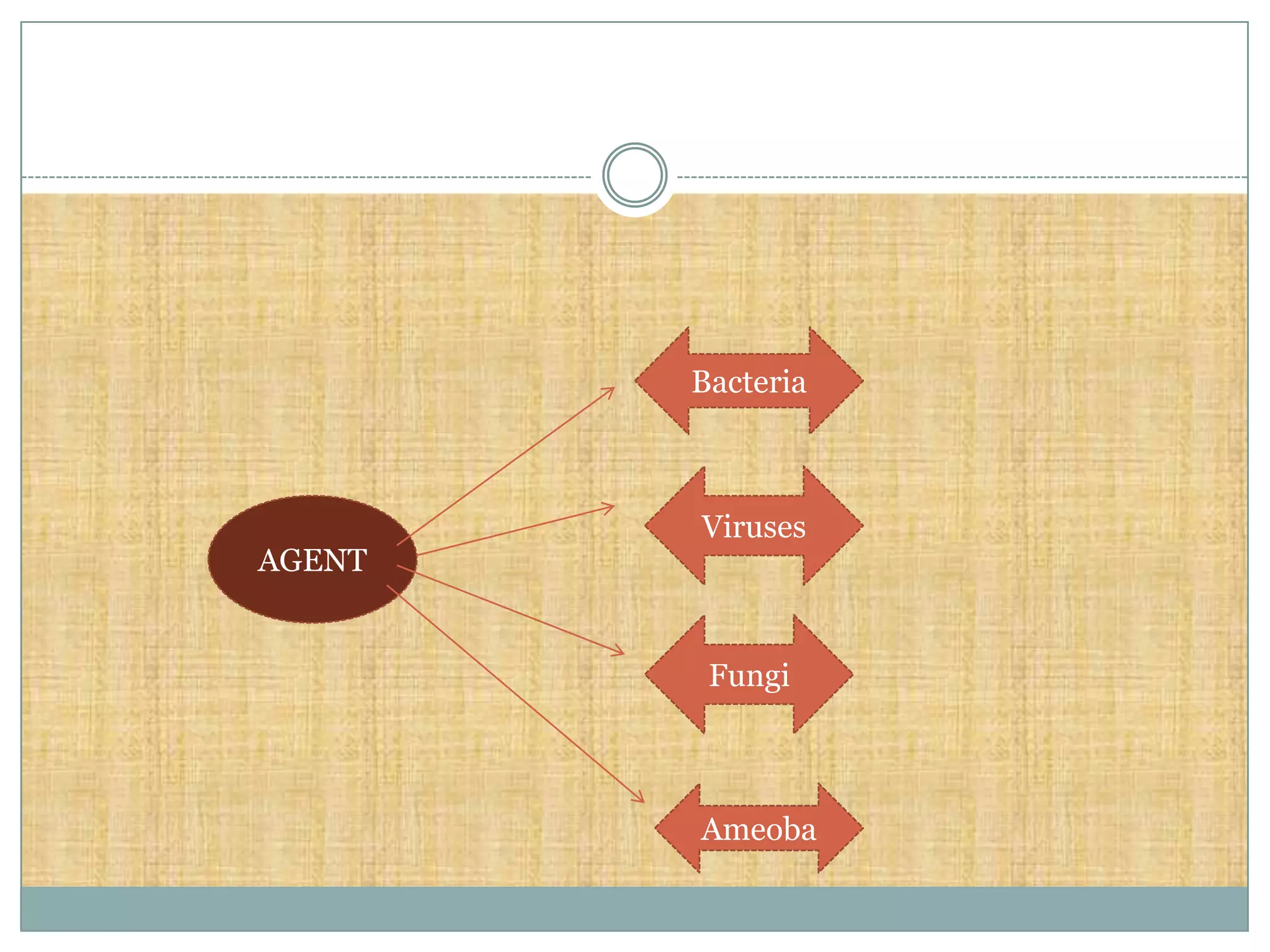
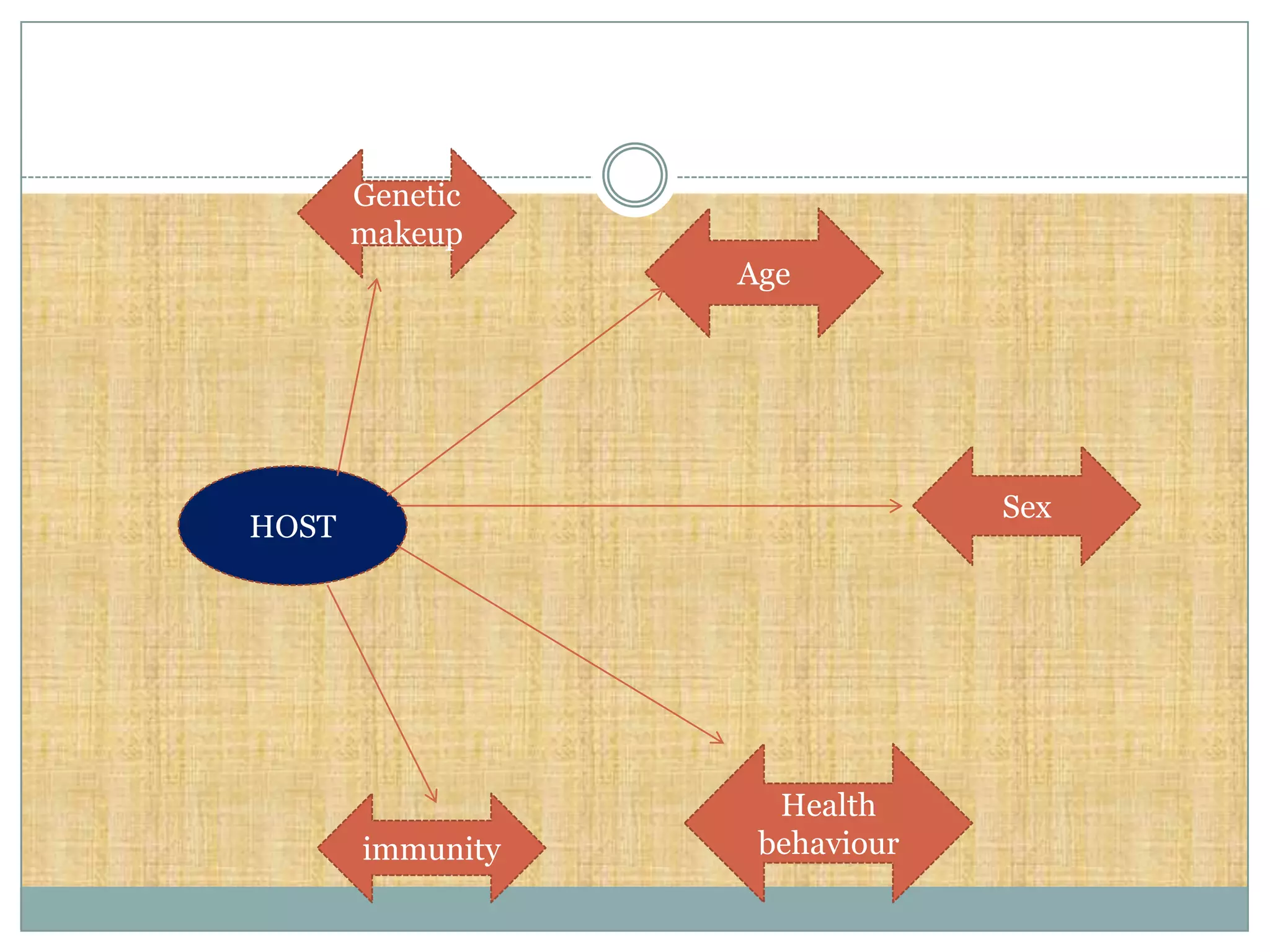
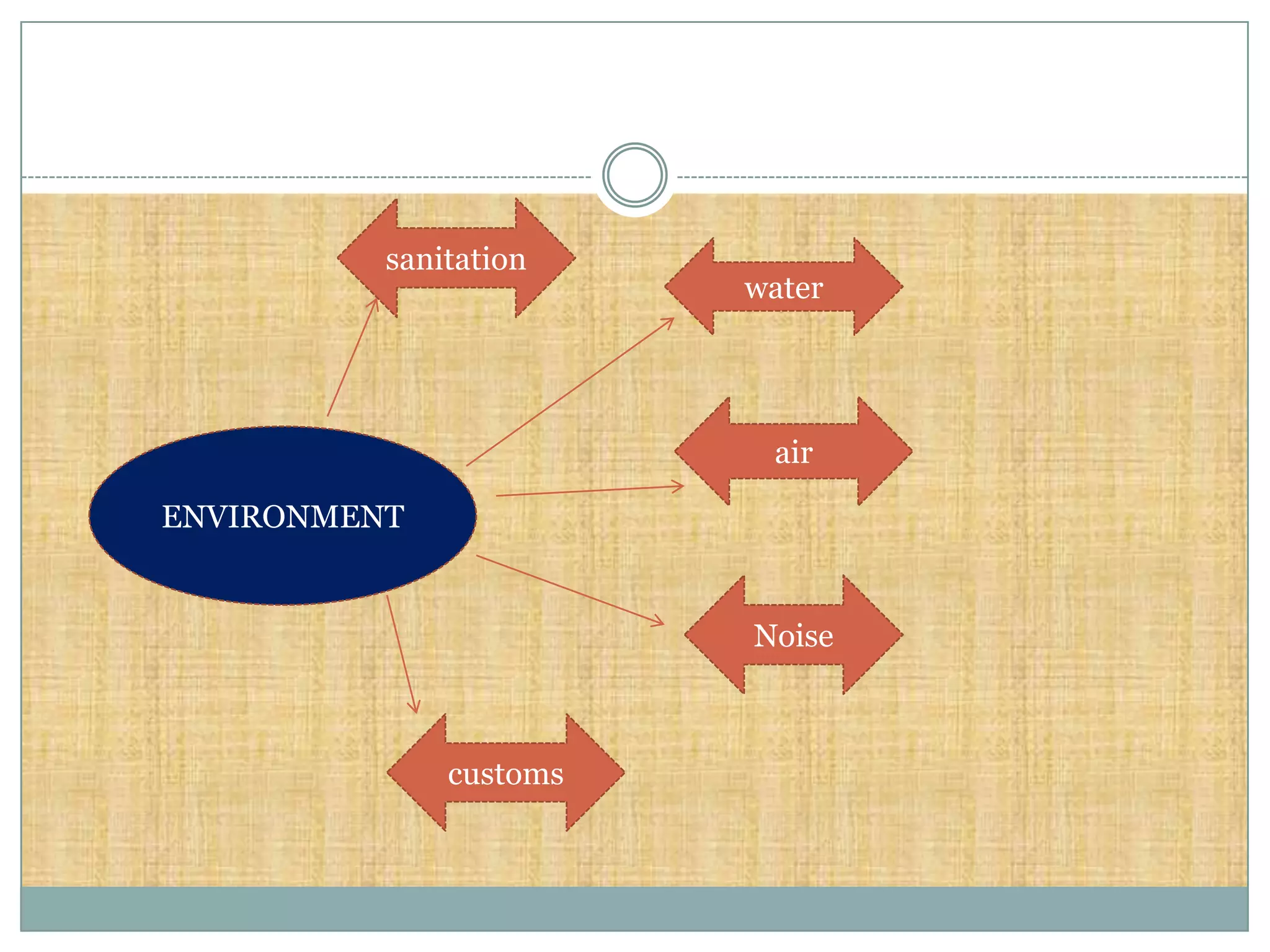
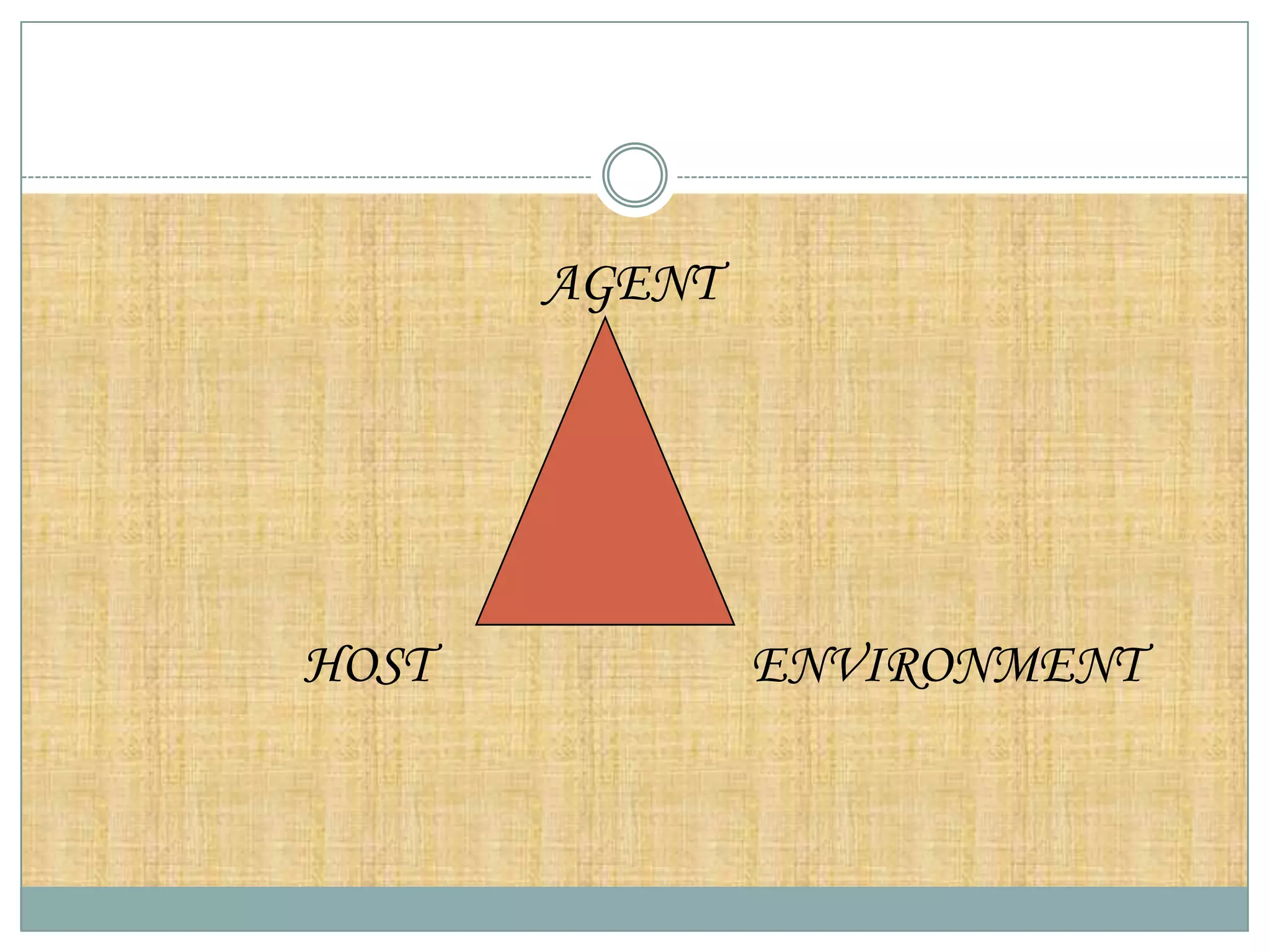
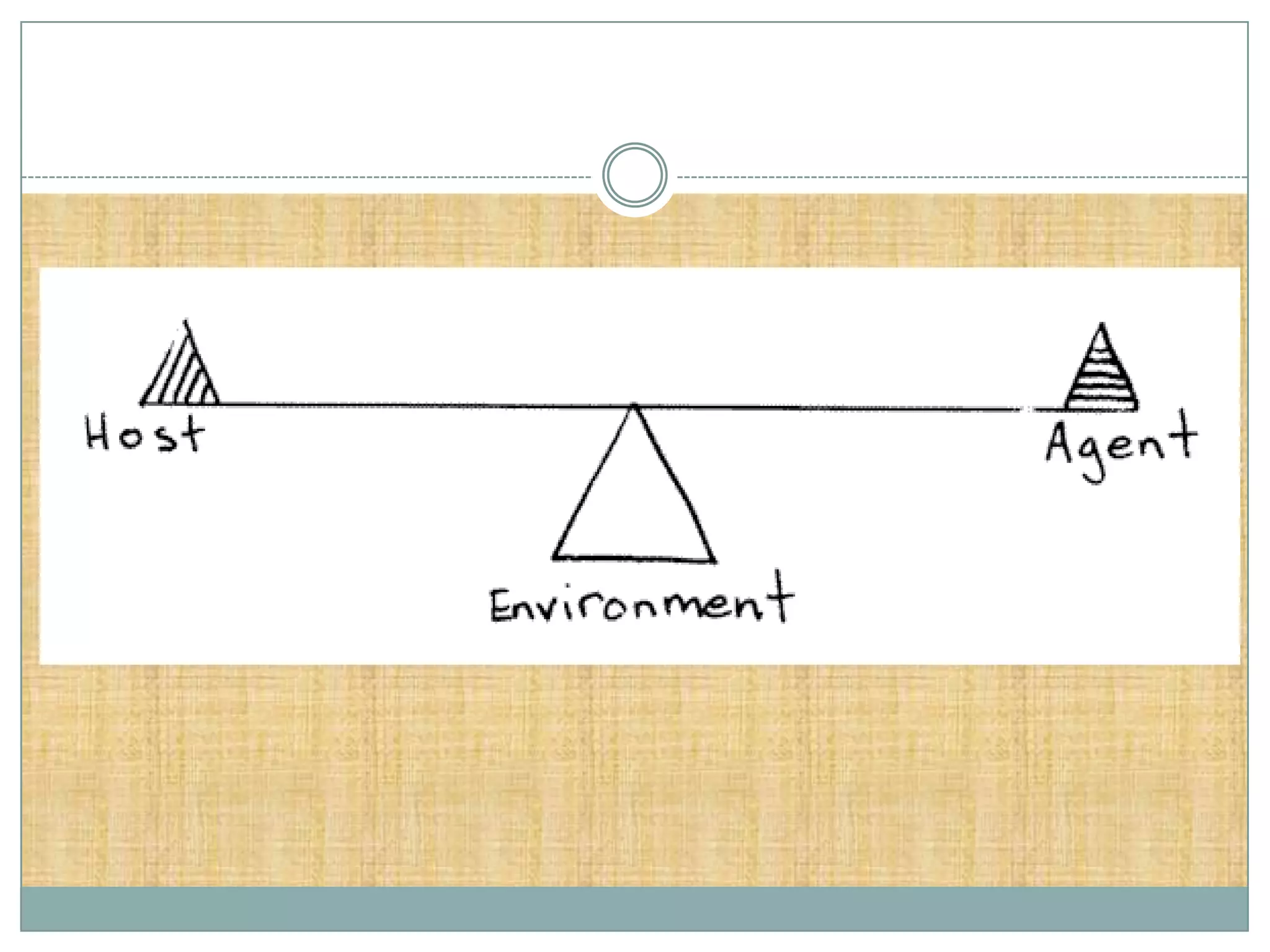
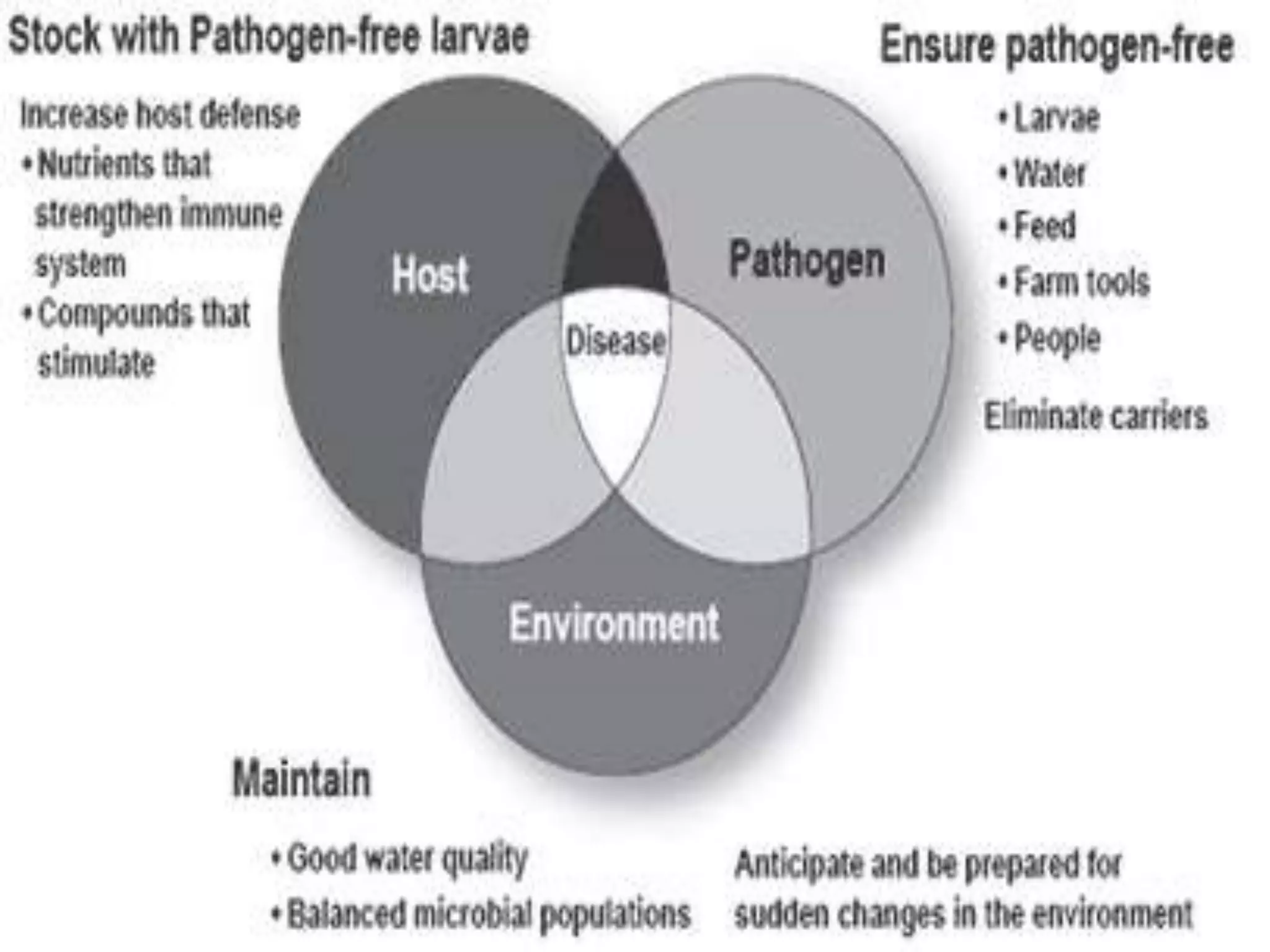
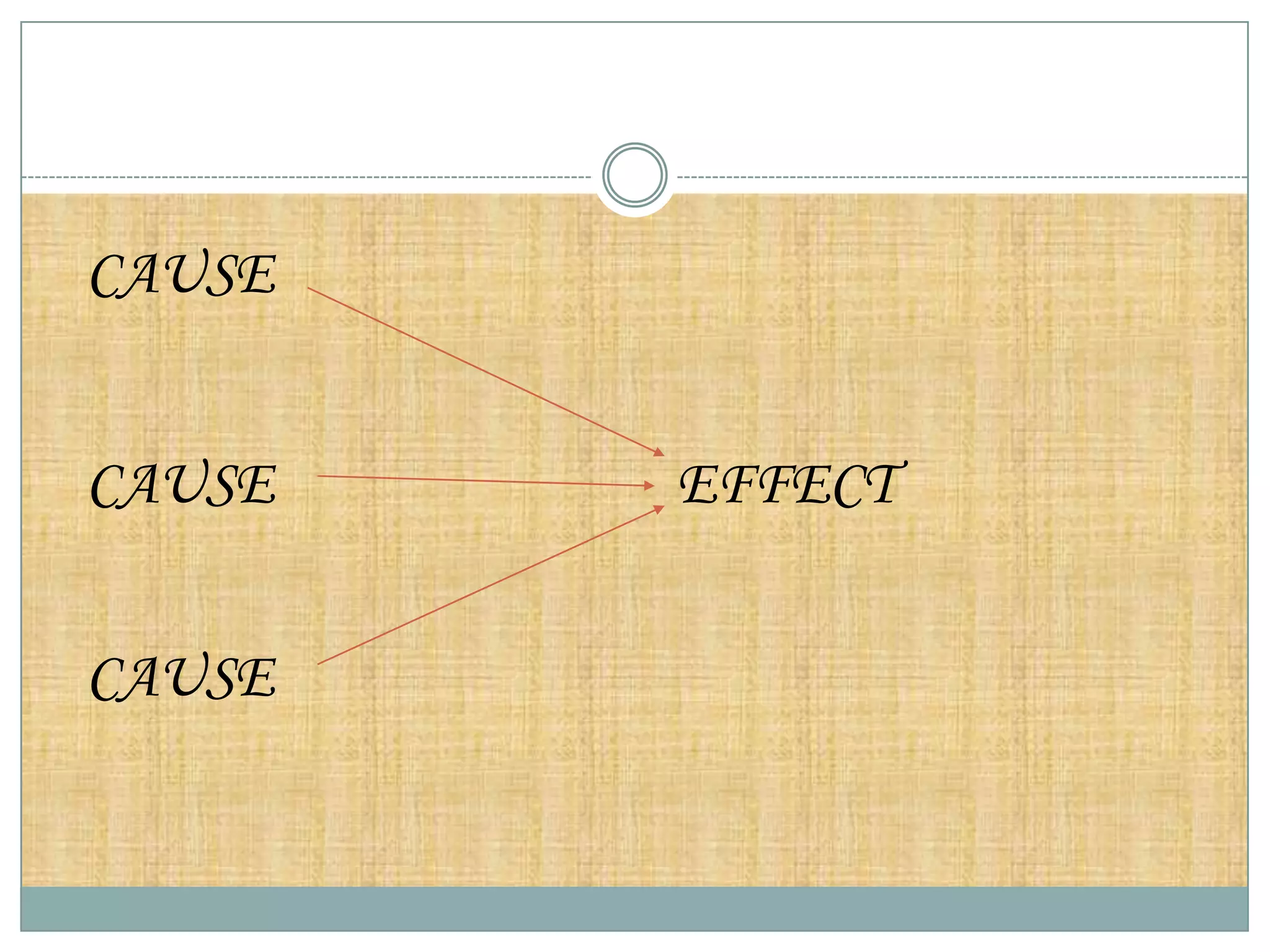
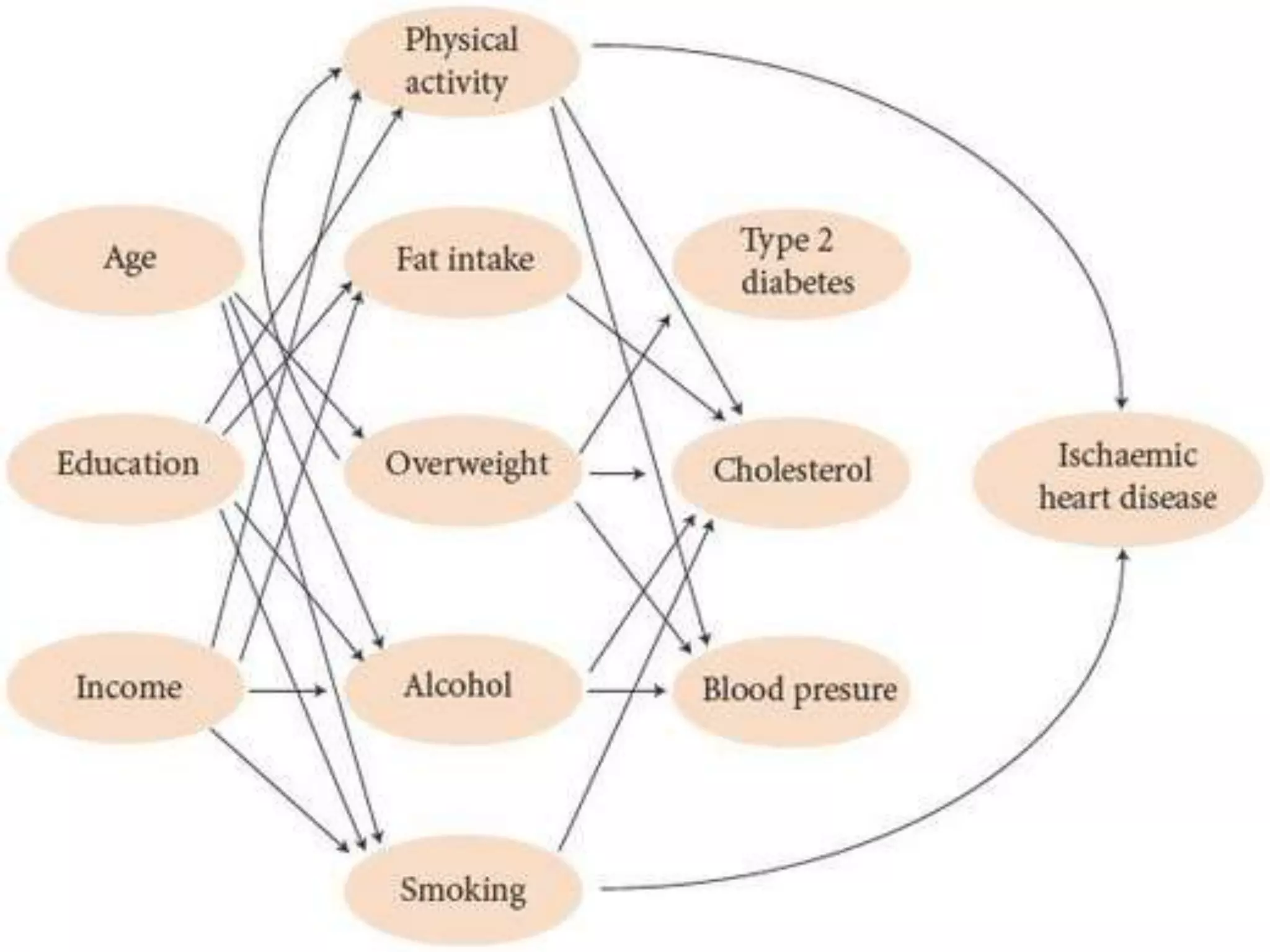
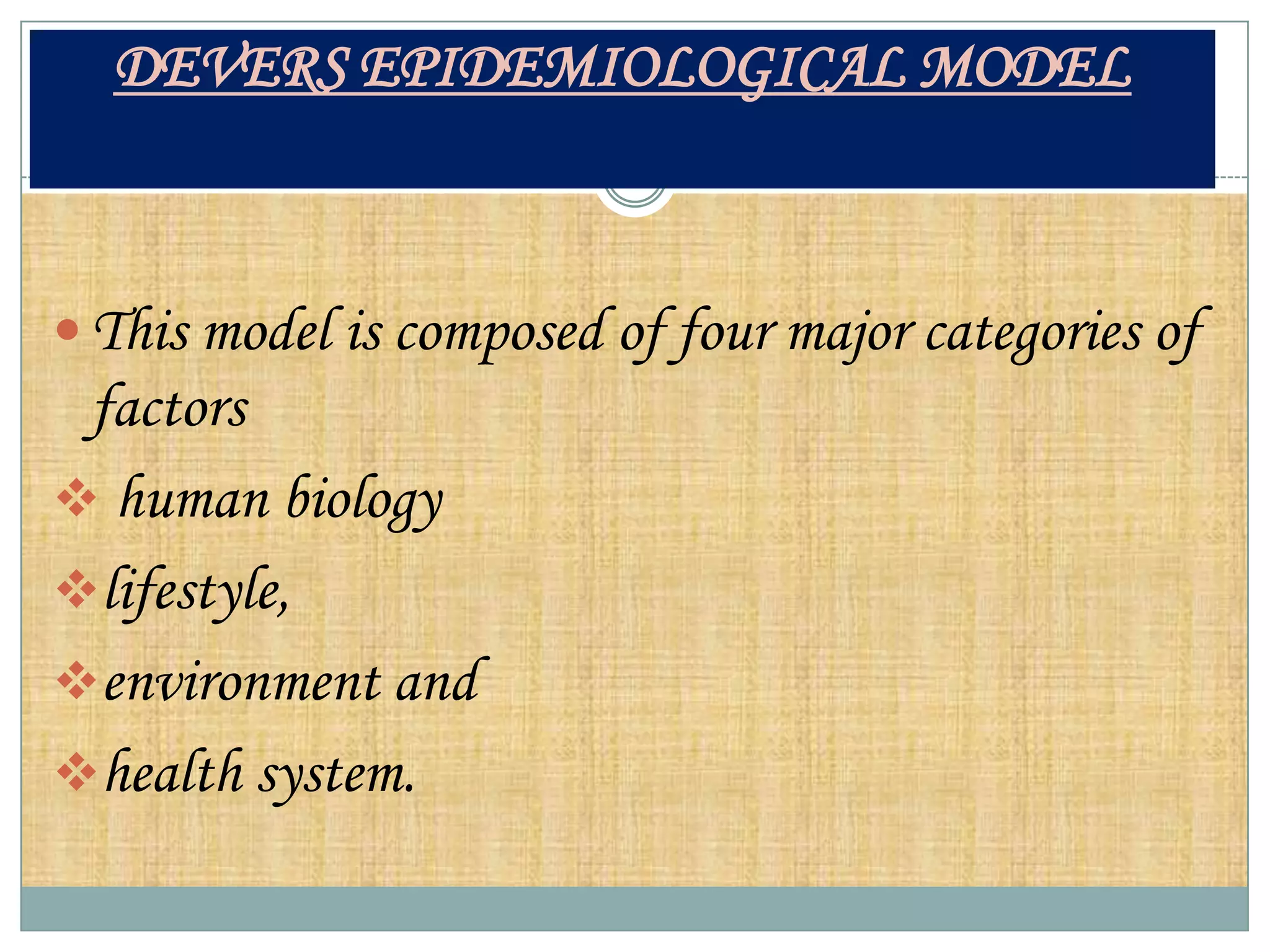
The document discusses various theories of disease causation including the germ theory, epidemiological triad, multifactorial causation theory, and web of causation. It also covers the Devers epidemiological model and describes the spectrum and iceberg models of disease. Nurses can play an important role in disease prevention through activities like early diagnosis, treatment, notification of diseases, identifying infection sources, and providing health education.