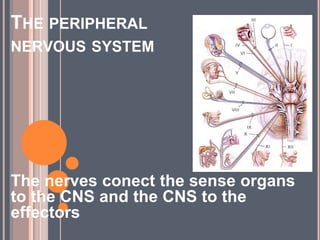
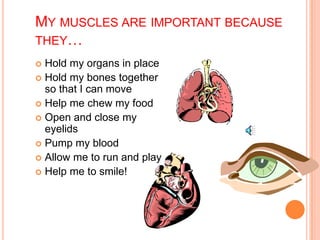
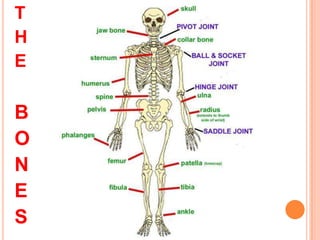
The document provides information about the human nervous system and its interaction with the senses. It discusses:
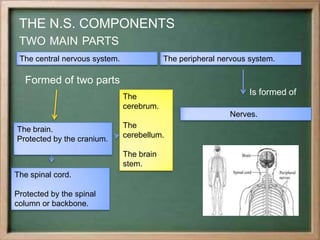
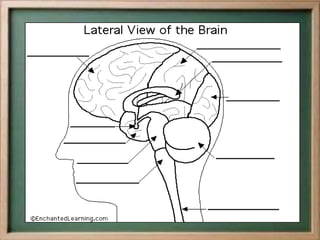
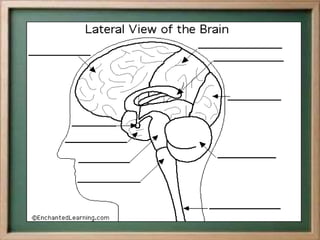
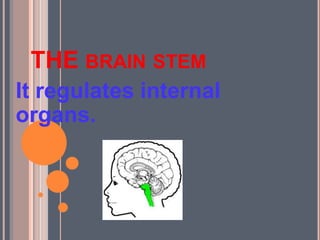
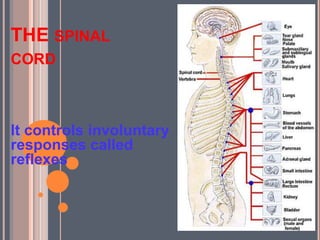
- The central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which includes nerves.
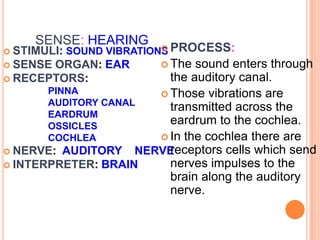
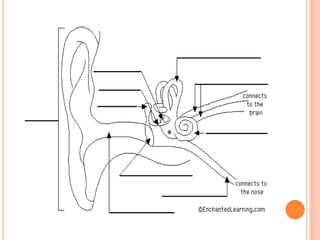
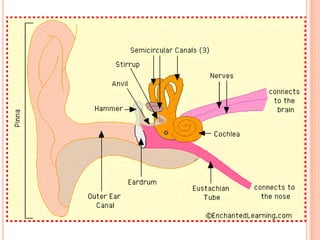
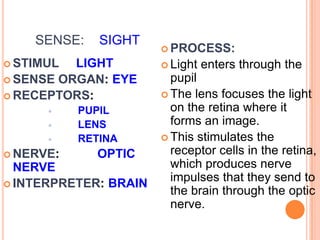
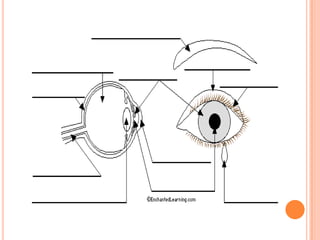
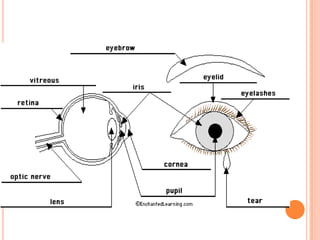
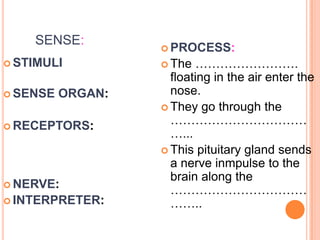
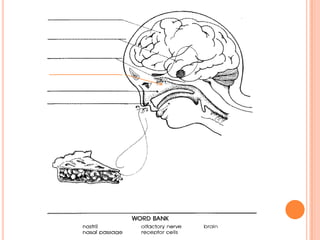
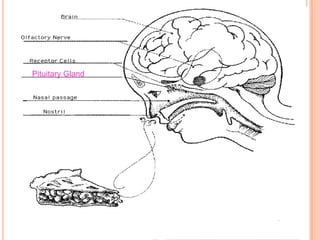
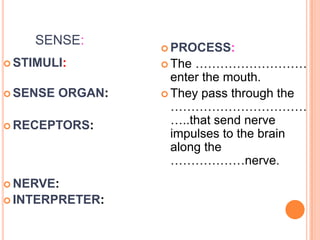
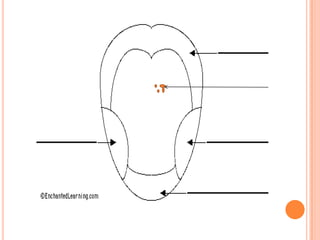
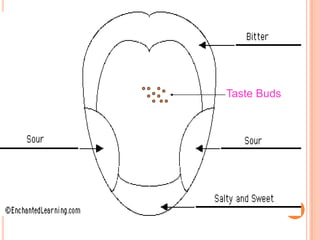
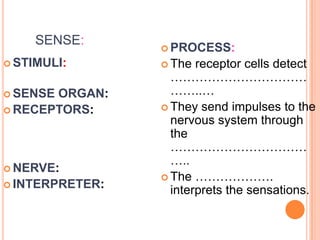
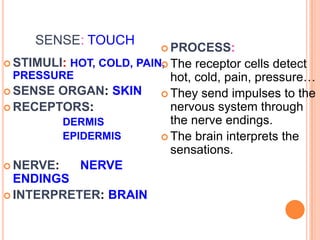
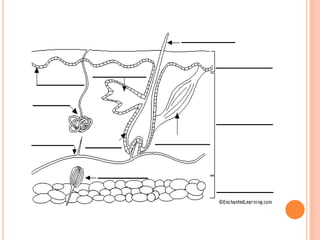
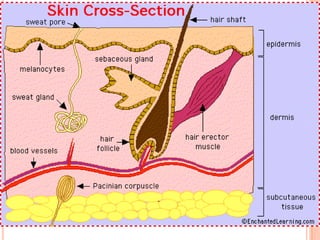
- The five senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste, touch) and the organs, receptors, nerves, and processes involved with each sense.
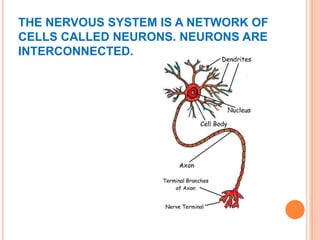
- Components of the nervous system like neurons, receptors, effectors and their functions in receiving stimuli, interpreting responses, and executing responses.
- The locomotor system, including the muscular and skeletal systems, bones, joints, muscles and tendons and their roles in movement and protection.