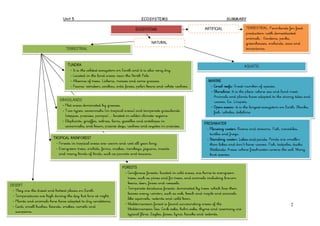
An ecosystem includes all living organisms in a particular area, as well as the physical components with which they interact. Ecosystems can be terrestrial or aquatic, and include diverse environments such as deserts, forests, grasslands, tundra, marine, and freshwater. Terrestrial ecosystems include deserts with adapted cacti and small mammals, various forest types containing different flora and fauna, grasslands that can be savannahs or prairies, and the coldest tundra near the North Pole. Aquatic ecosystems contain diverse marine life in coral reefs and the open ocean, as well as an array of freshwater organisms in rivers, lakes, and wetlands. Ecosystems can also be