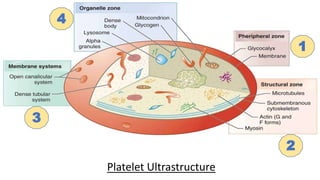
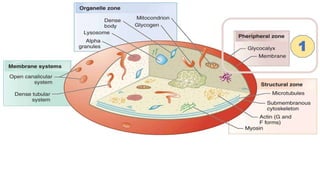
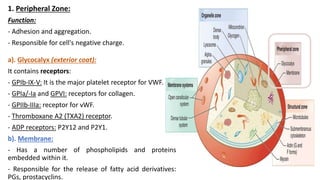
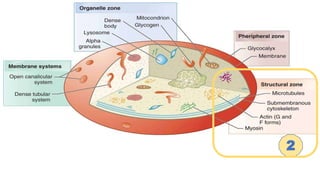
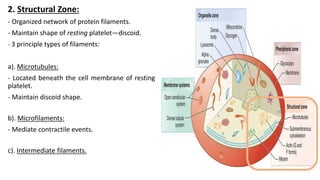
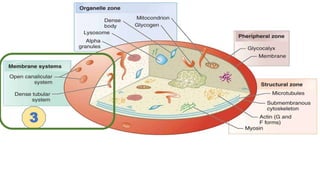
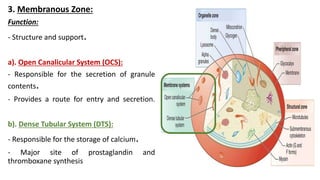
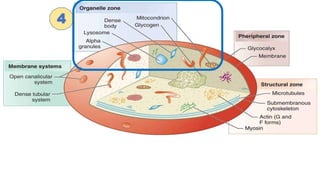
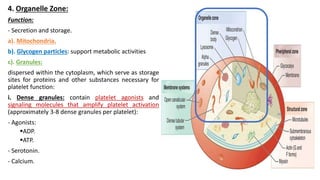
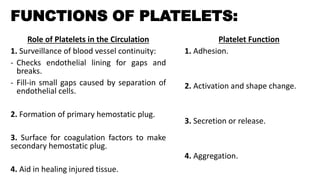
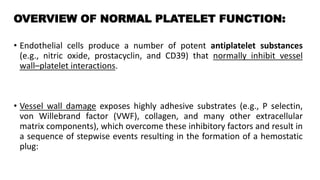
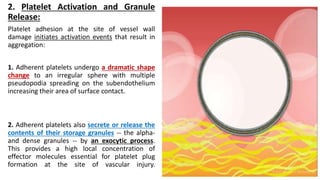
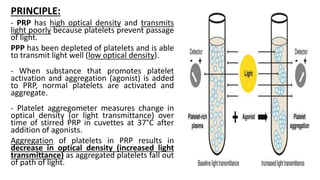
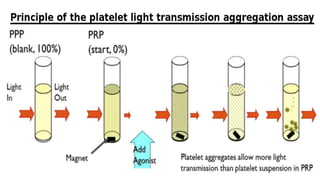
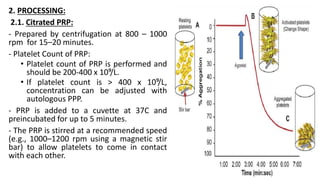
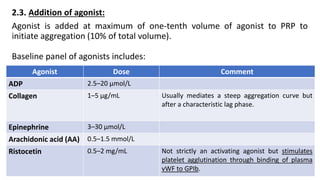
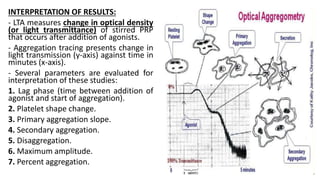
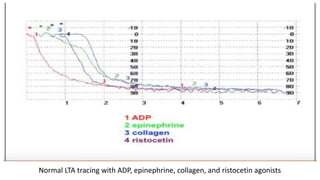
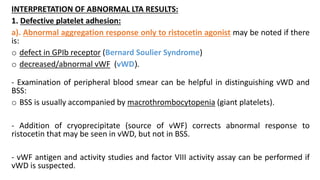
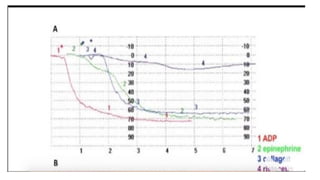
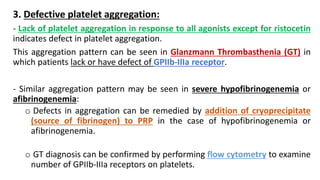
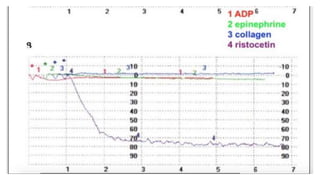
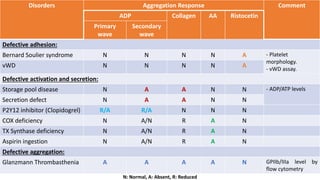
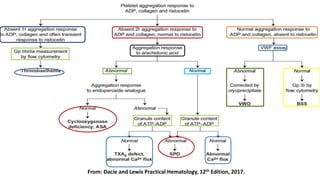
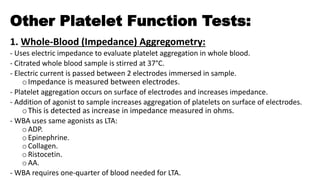
Platelet function testing assesses platelet adhesion, activation, granule release and aggregation in response to agonists using light transmission platelet aggregometry (LTA) as the gold standard test. Abnormal LTA results can indicate defects in platelet adhesion receptors, activation and secretion, aggregation receptors, or the thromboxane pathway. The pattern of abnormal aggregation in response to different agonists helps localize the platelet function defect.