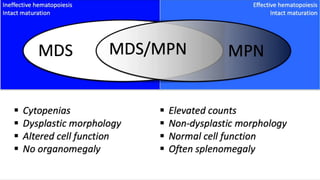
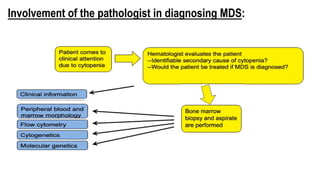
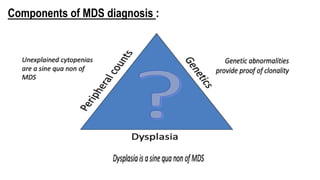
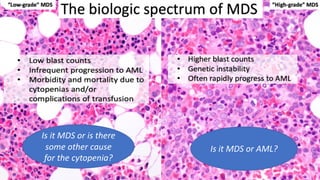
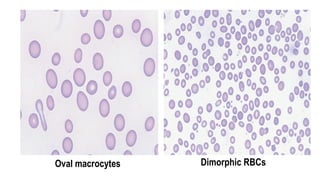
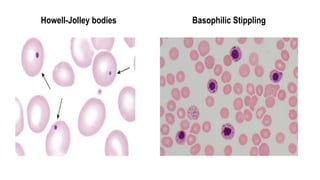
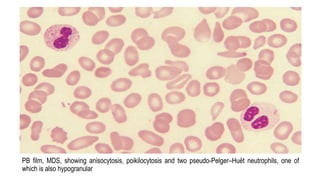
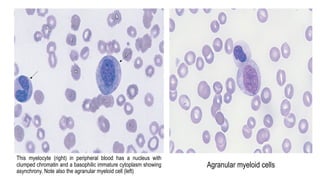
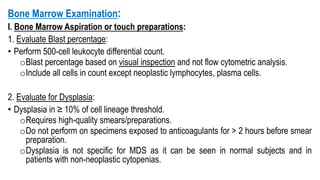
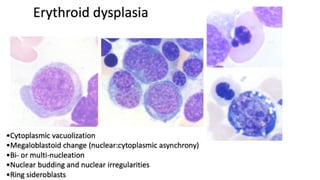
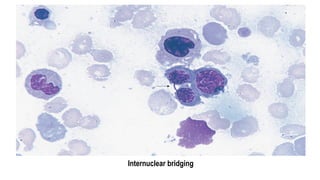
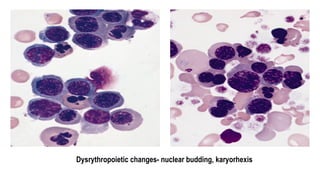
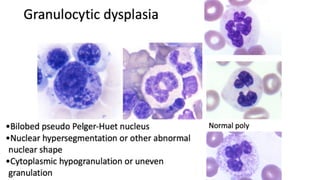
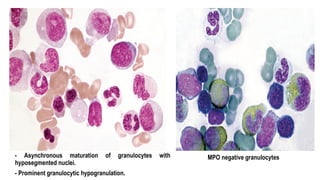
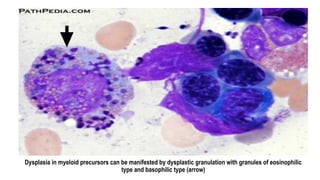
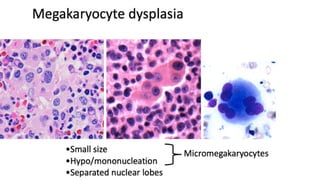
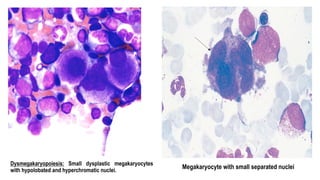
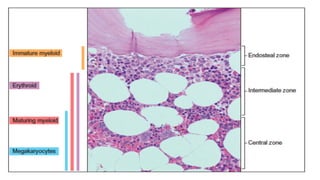
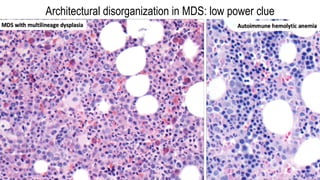
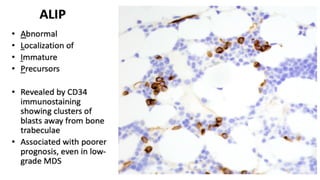
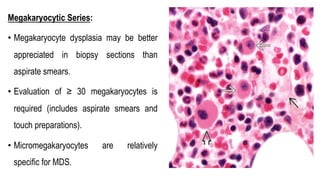
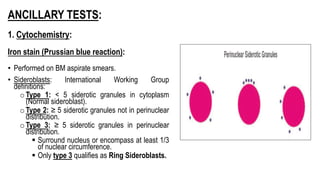
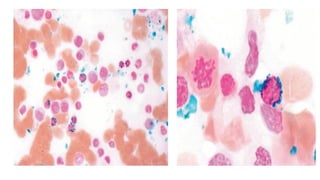
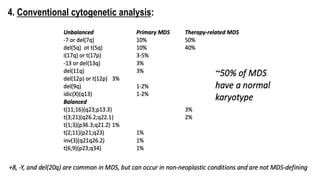
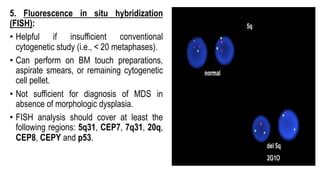
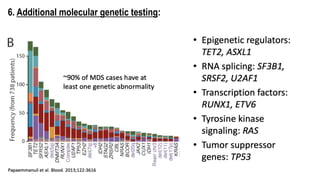
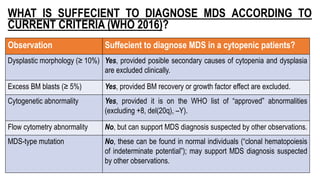
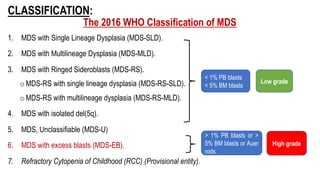
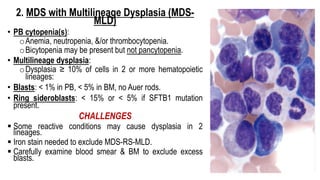
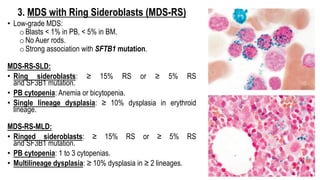
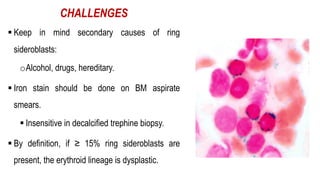
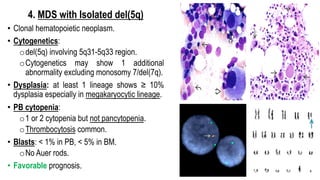
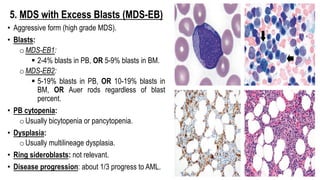
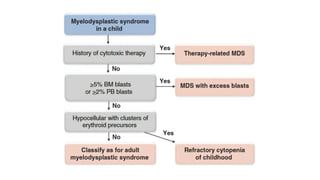
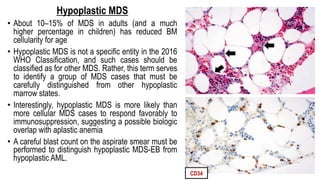
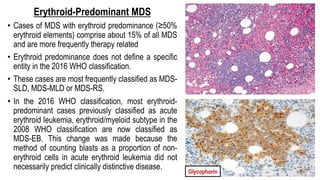
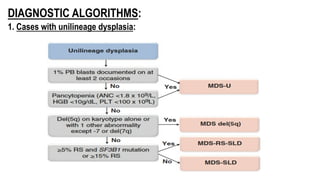
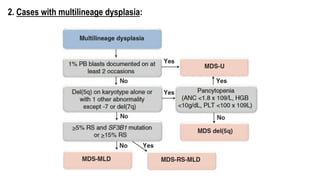
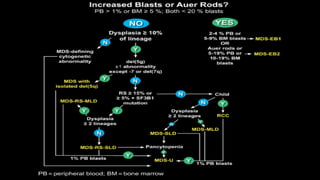
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and peripheral blood cytopenias. The key criteria for diagnosing MDS include persistent cytopenia in one or more cell lines, dysplastic features in 10% or more of cells in one or more myeloid lineages, and less than 20% blasts in the bone marrow. The pathologist plays an important role in establishing the diagnosis by evaluating peripheral blood smears and bone marrow aspirates and biopsies for evidence of cytopenia, dysplasia, blast percentage, and other findings. Accurate classification and diagnosis of MDS requires integration of morphological, cytogenetic, molecular