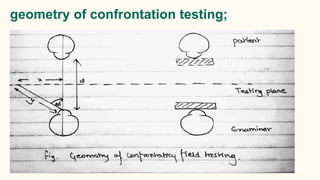
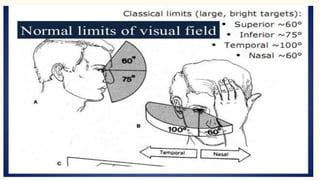
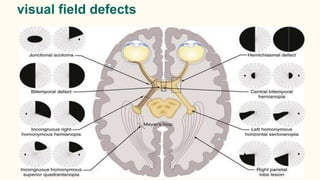
Confrontation testing is a simple preliminary test to screen for peripheral visual field defects. It does not require any equipment and can be done anywhere. The examiner positions their face about a meter in front of the patient. While the patient fixes their gaze on the examiner's eye, the examiner moves their finger in an arc from the periphery towards the center to test each half of the visual field. Any areas that the patient cannot see the finger represent potential visual field defects. While quick to perform, confrontation testing has limitations as some mild or moderate defects may be missed, and it is subjective in nature. Further visual field testing is needed to confirm any defects found.