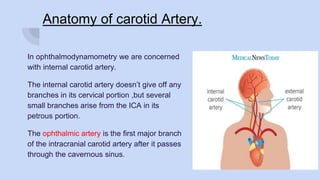
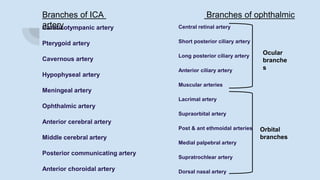
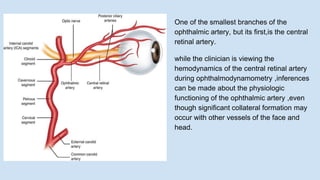
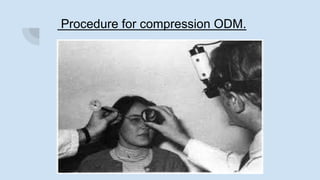
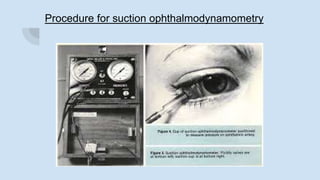
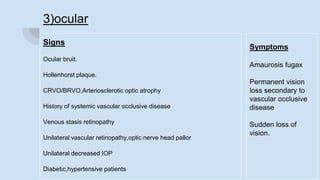
Ophthalmodynamometry is a clinical procedure that measures the pressure in the ophthalmic artery to assess patency of the internal carotid artery. It involves applying pressure to the eye until the central retinal artery collapses, noting the diastolic and systolic pressures. This provides information about blood flow through the ophthalmic artery and can detect carotid artery occlusive diseases, helping prevent strokes. The procedure has been used since the early 1900s and modern methods include compression or suction ophthalmodynamometry. Precautions must be taken and it can detect conditions affecting the carotid or cerebral vasculature.