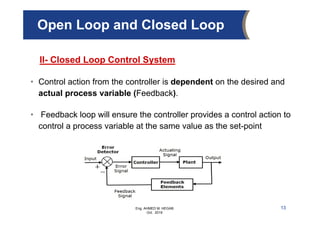
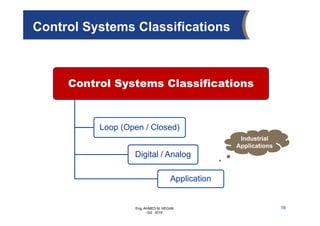
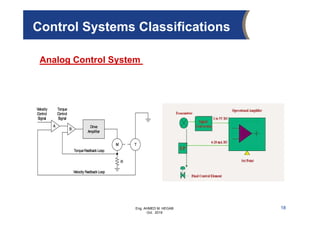
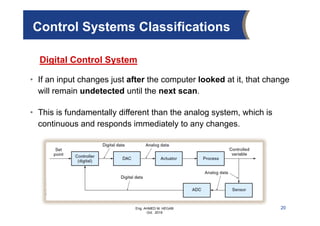
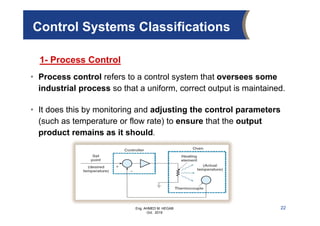
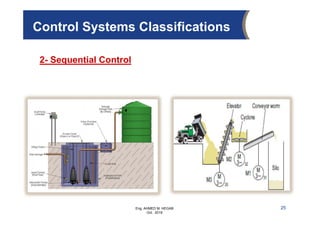
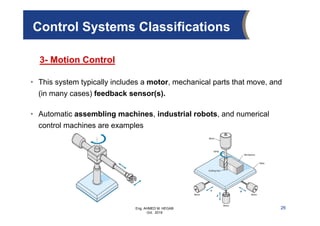
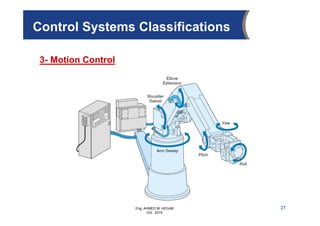
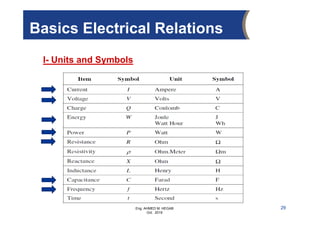
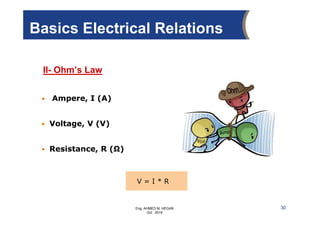
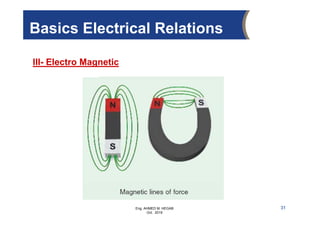
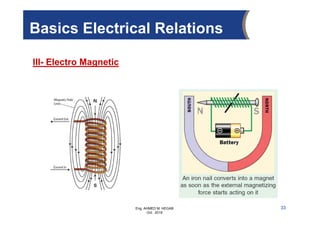
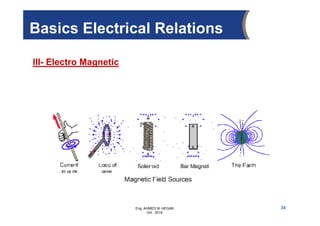
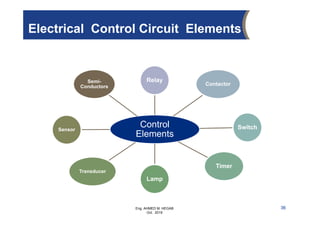
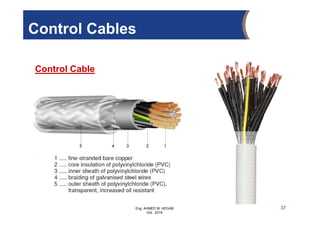
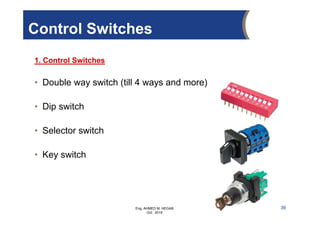
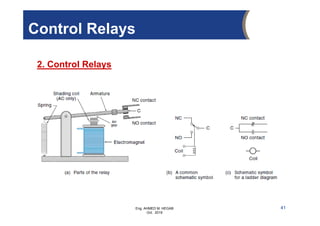
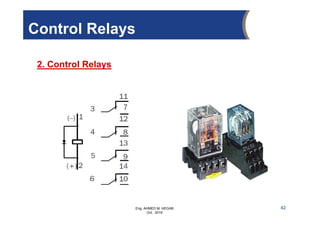
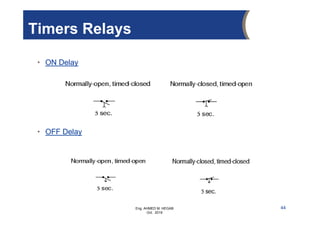
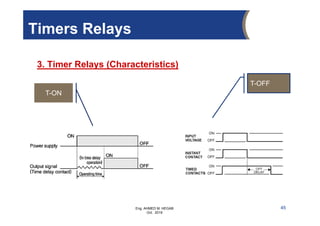
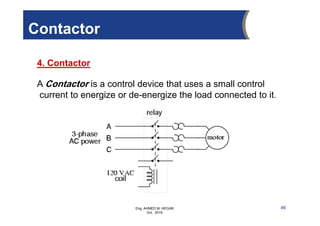
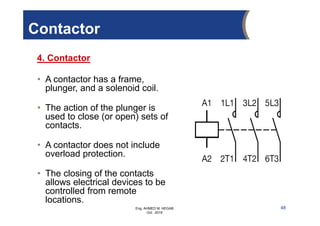
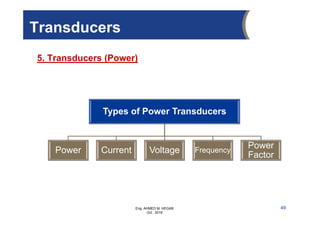
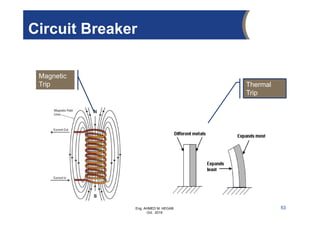
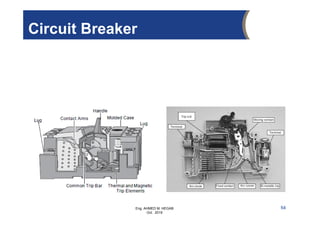
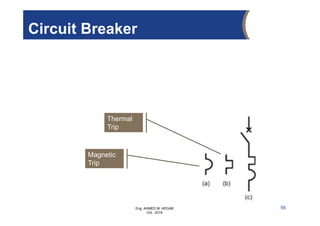
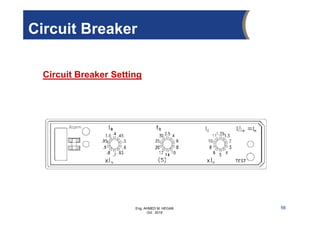
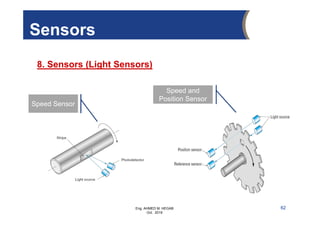
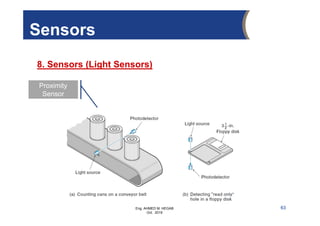
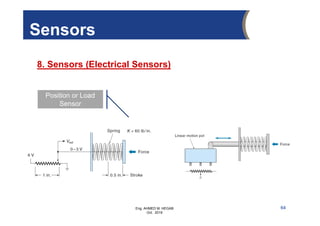
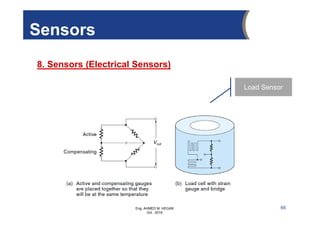
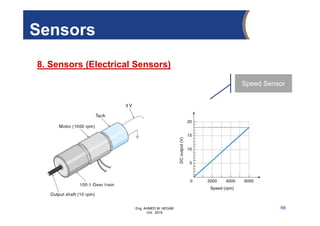
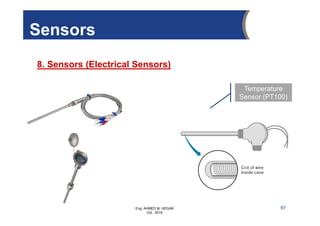
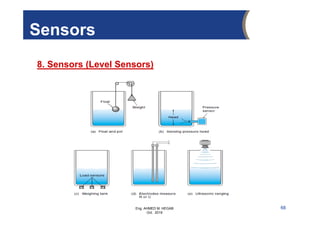
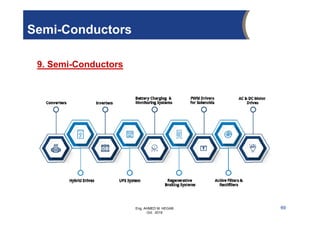
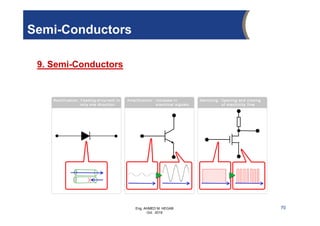
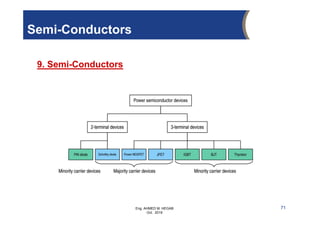
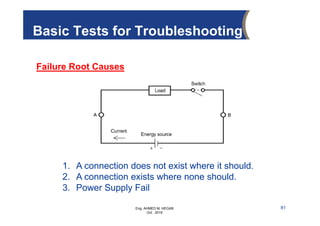
The document provides an overview of electrical control systems, detailing their structure, classifications, and applications. It explains the differences between open-loop and closed-loop control systems, along with relevant components like relays, sensors, and circuit breakers. Troubleshooting techniques for control circuits and electrical testing devices are also discussed, emphasizing systematic approaches to identifying and correcting faults.