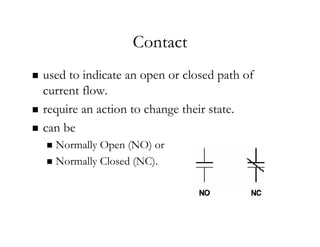
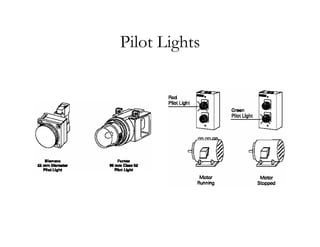
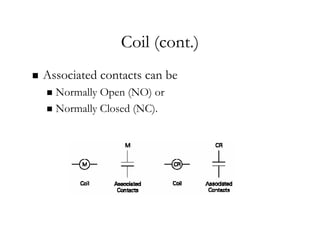
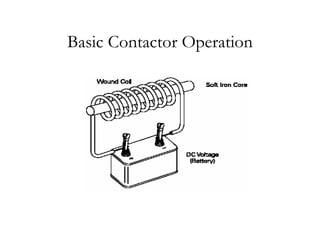
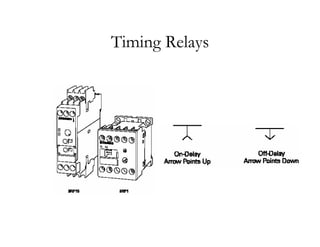
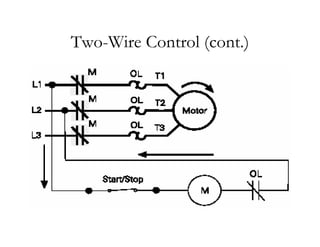
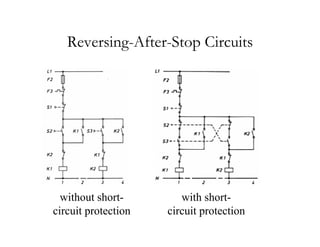
The document provides an overview of control components and circuits in electrotechnology, detailing the purpose and operation of electrical devices like magnetic contactors and relays. It covers various symbols used in line diagrams and explains the differences between control and power circuits, including the function of control devices like pushbuttons and switches. Additionally, it discusses two-wire and three-wire control circuits, emphasizing low-voltage protection and operational safety in motor control applications.