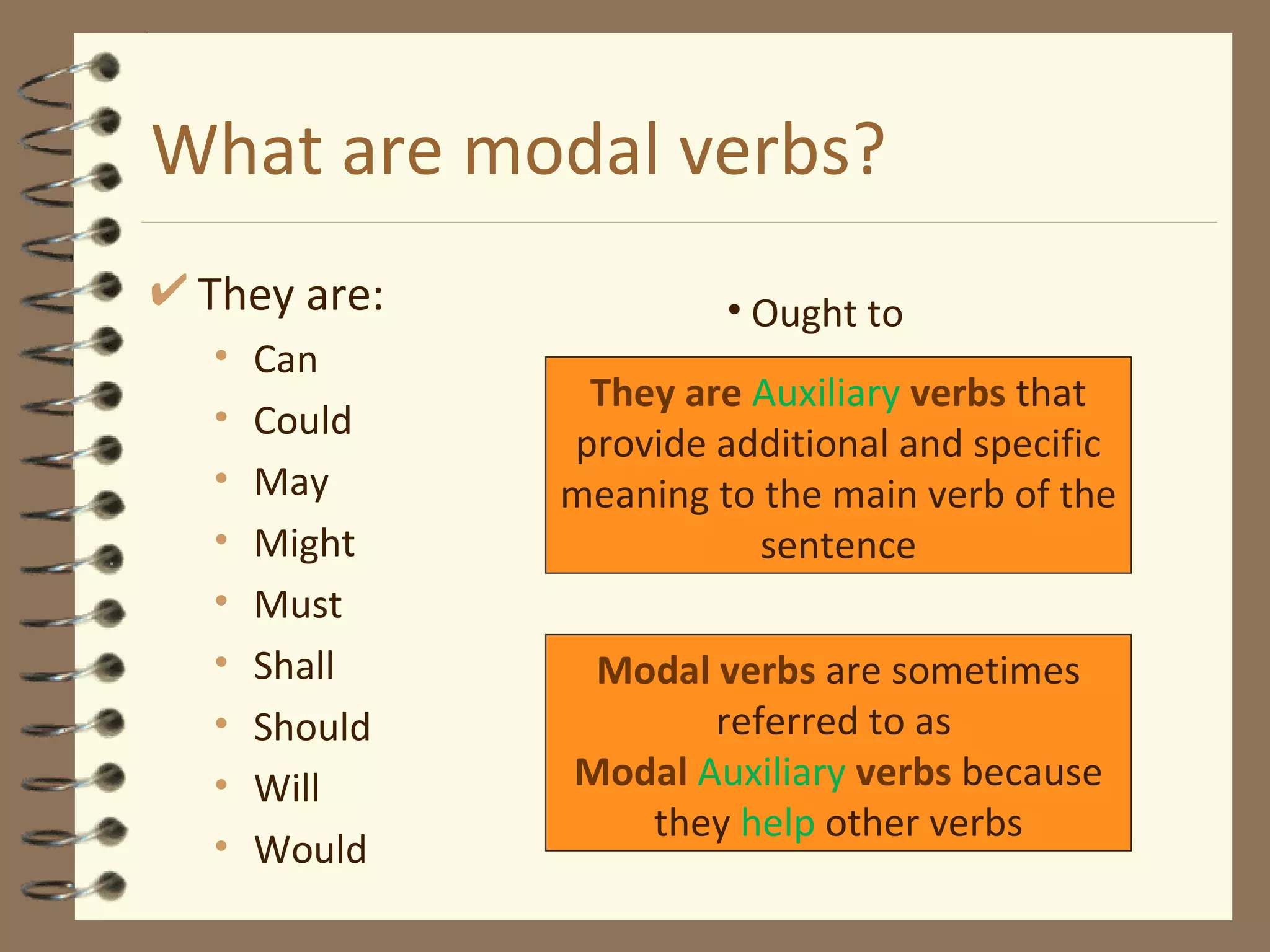
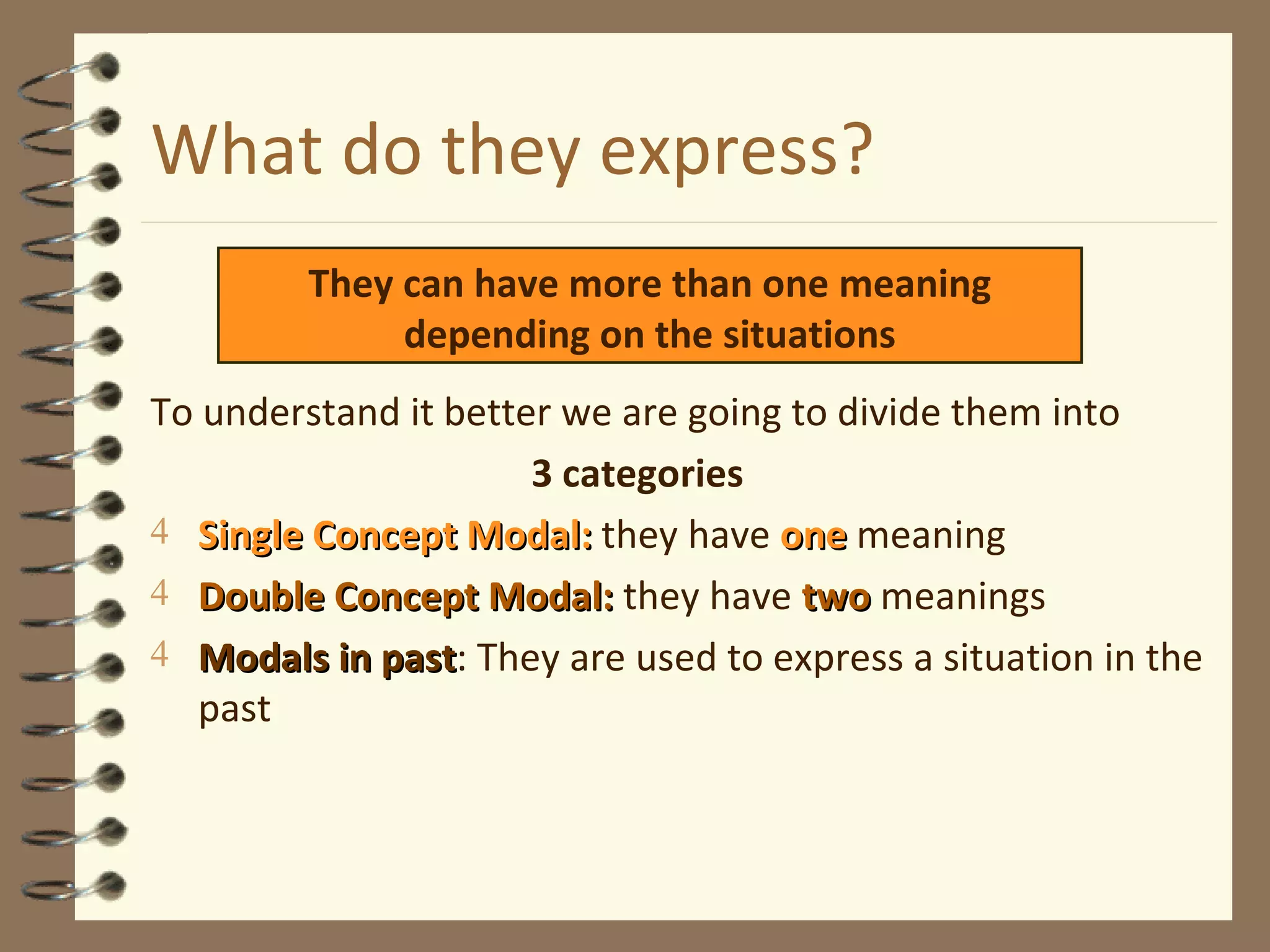
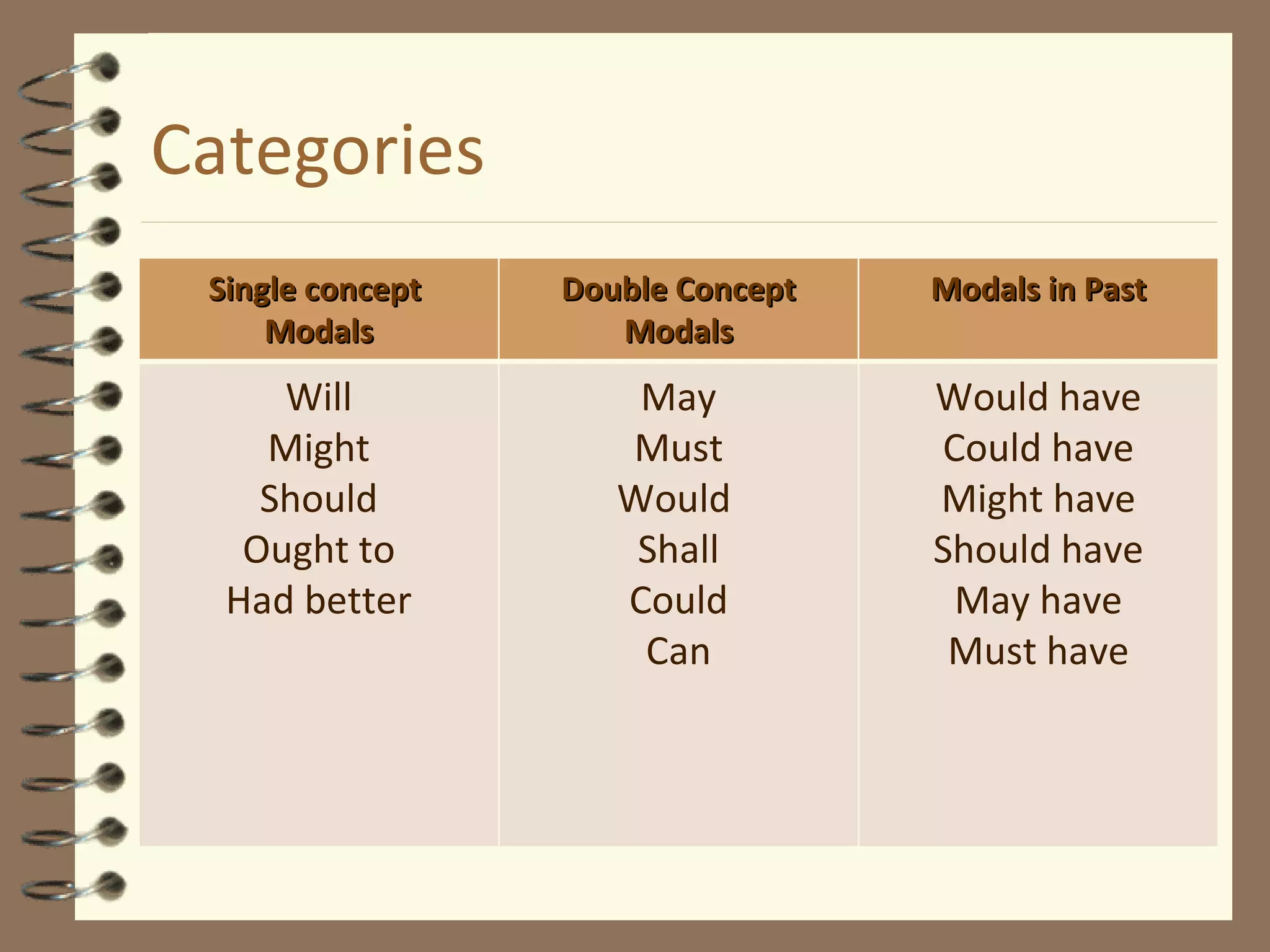
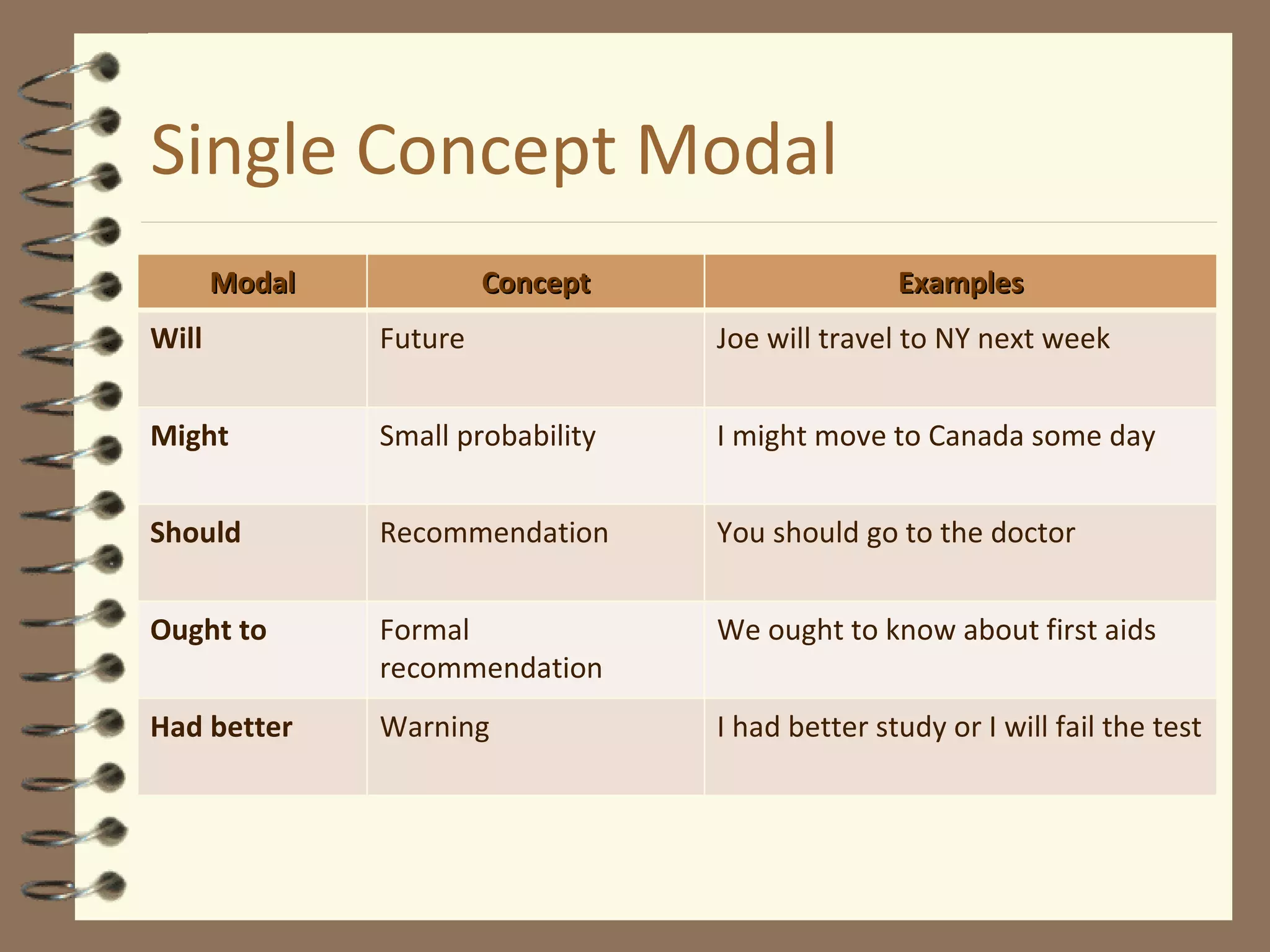
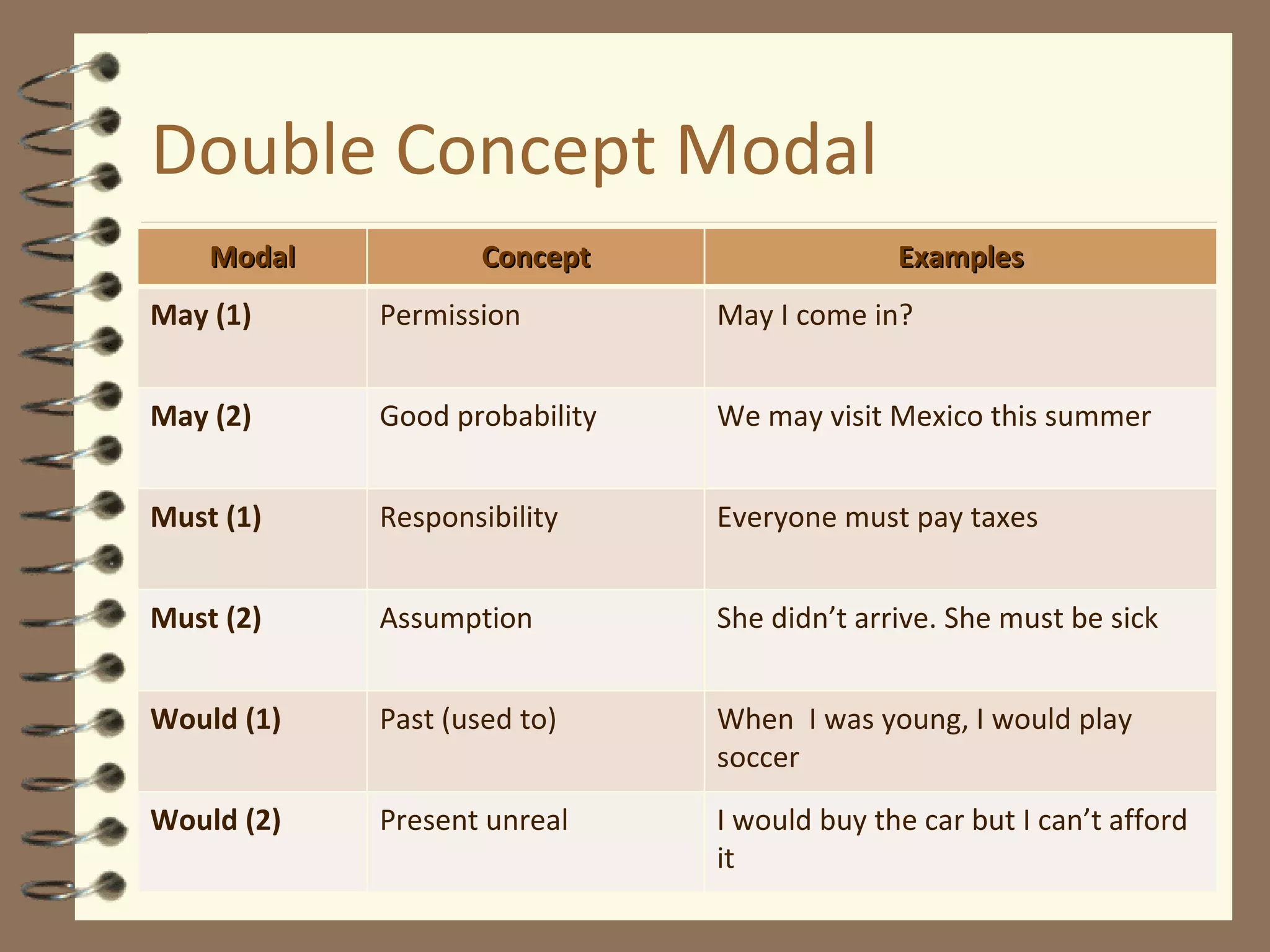
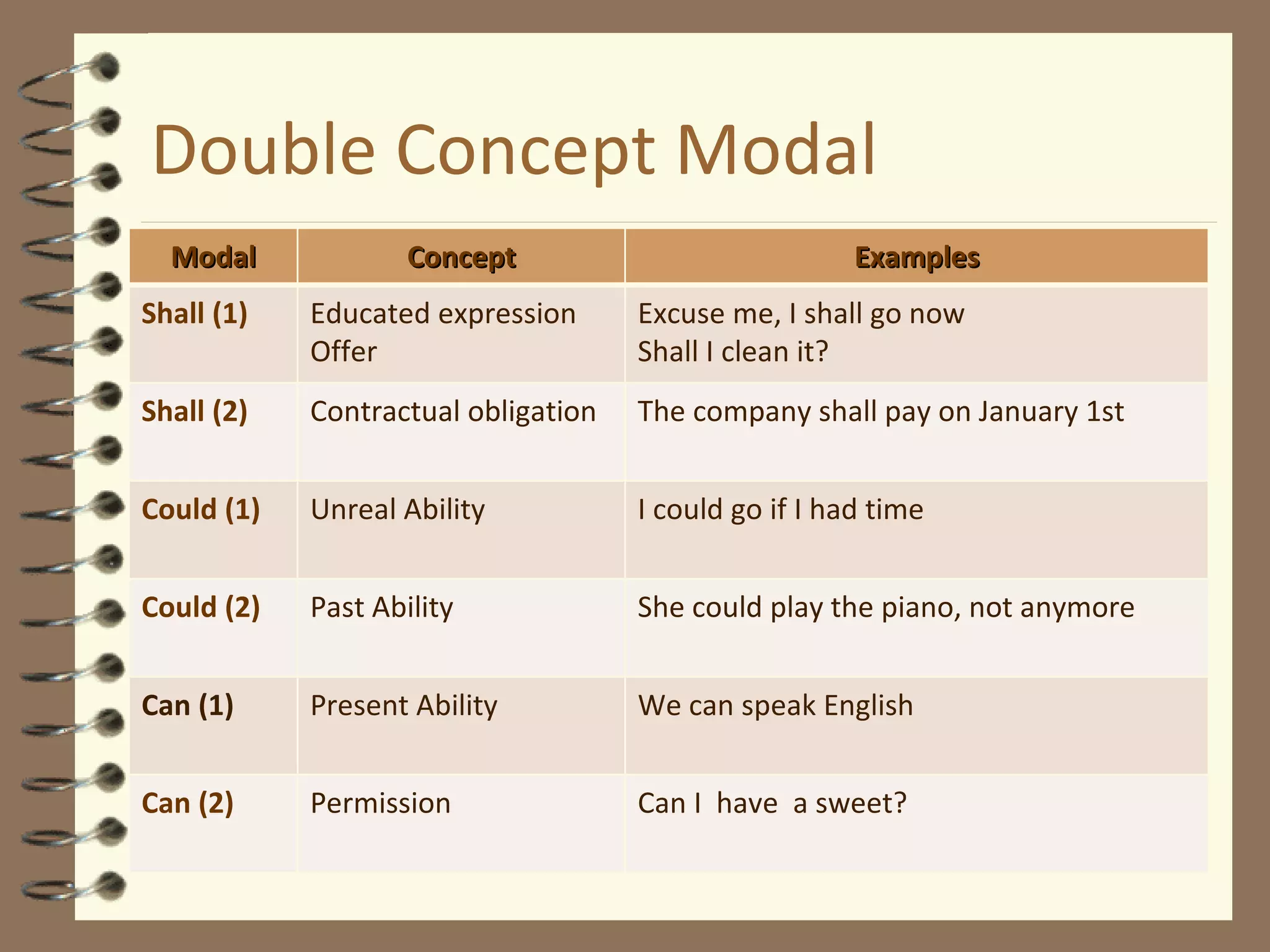
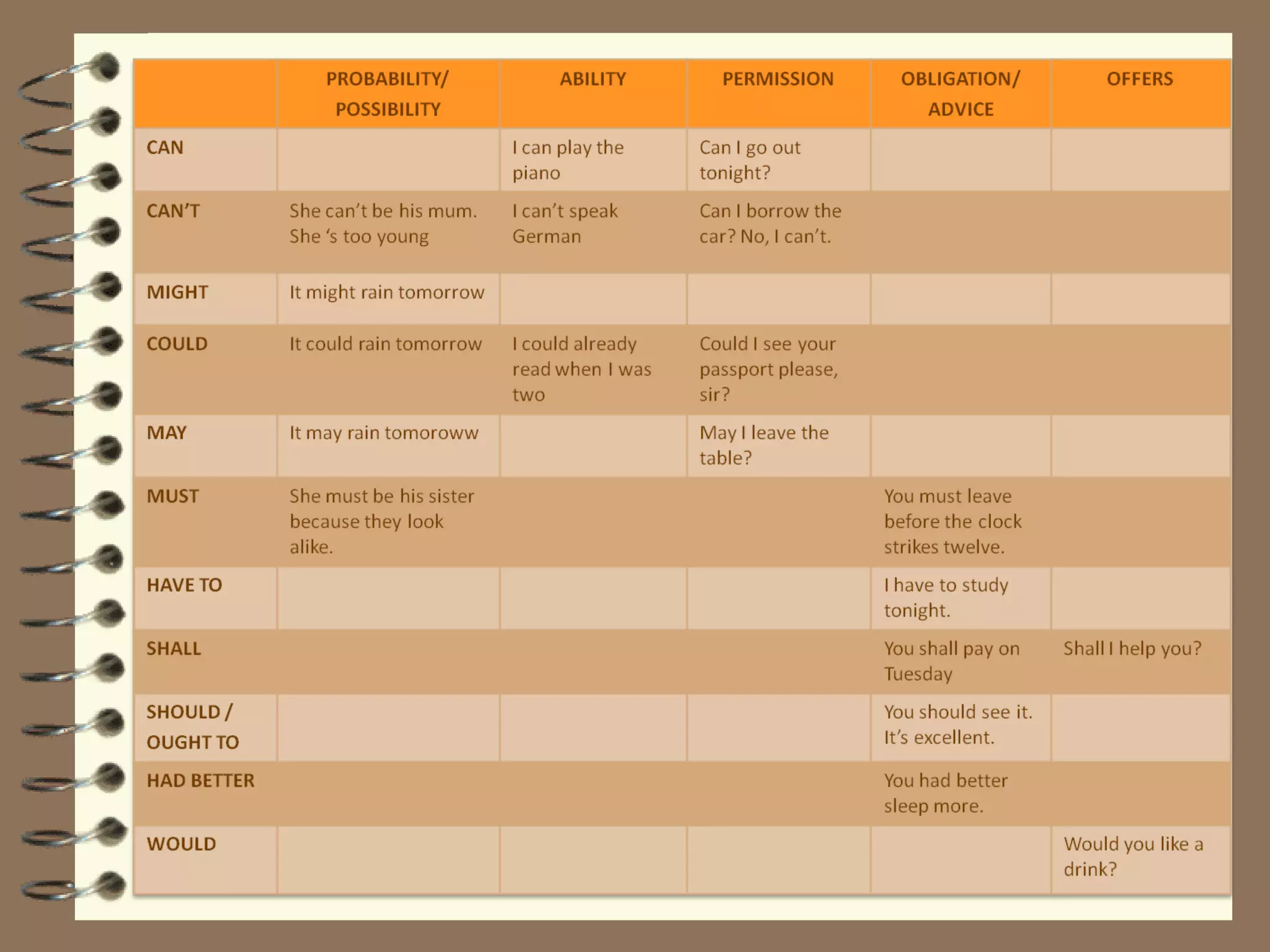
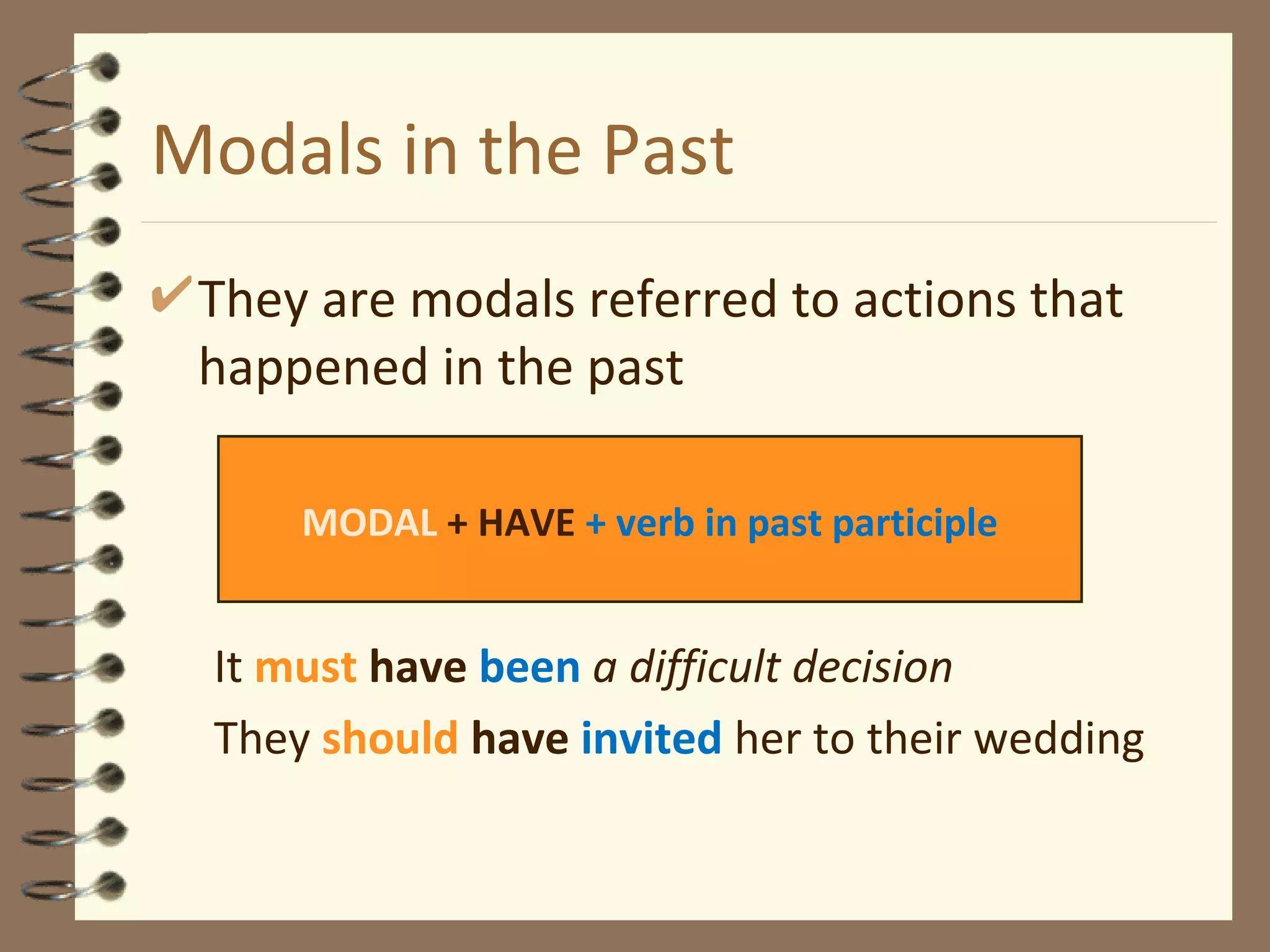
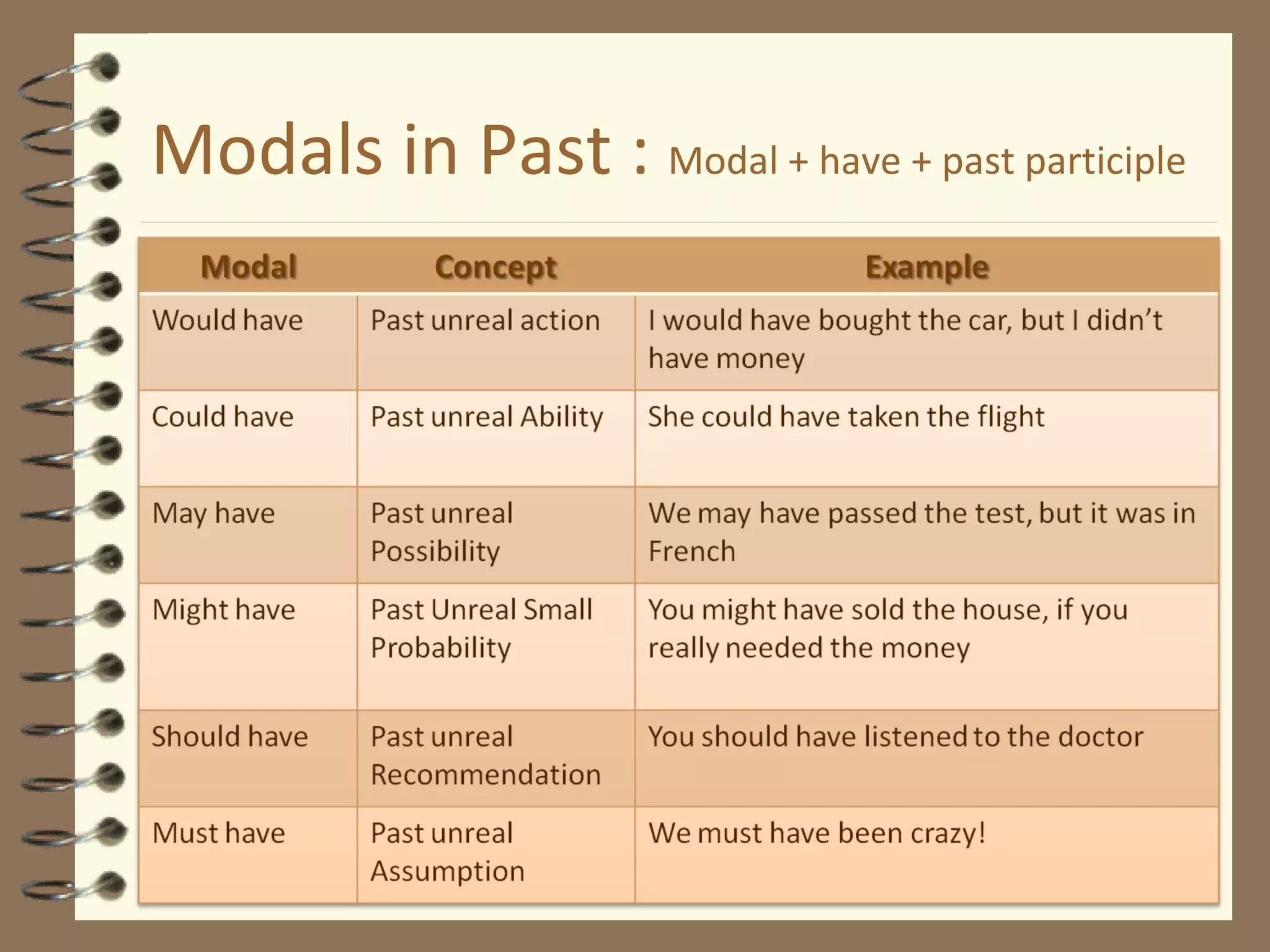
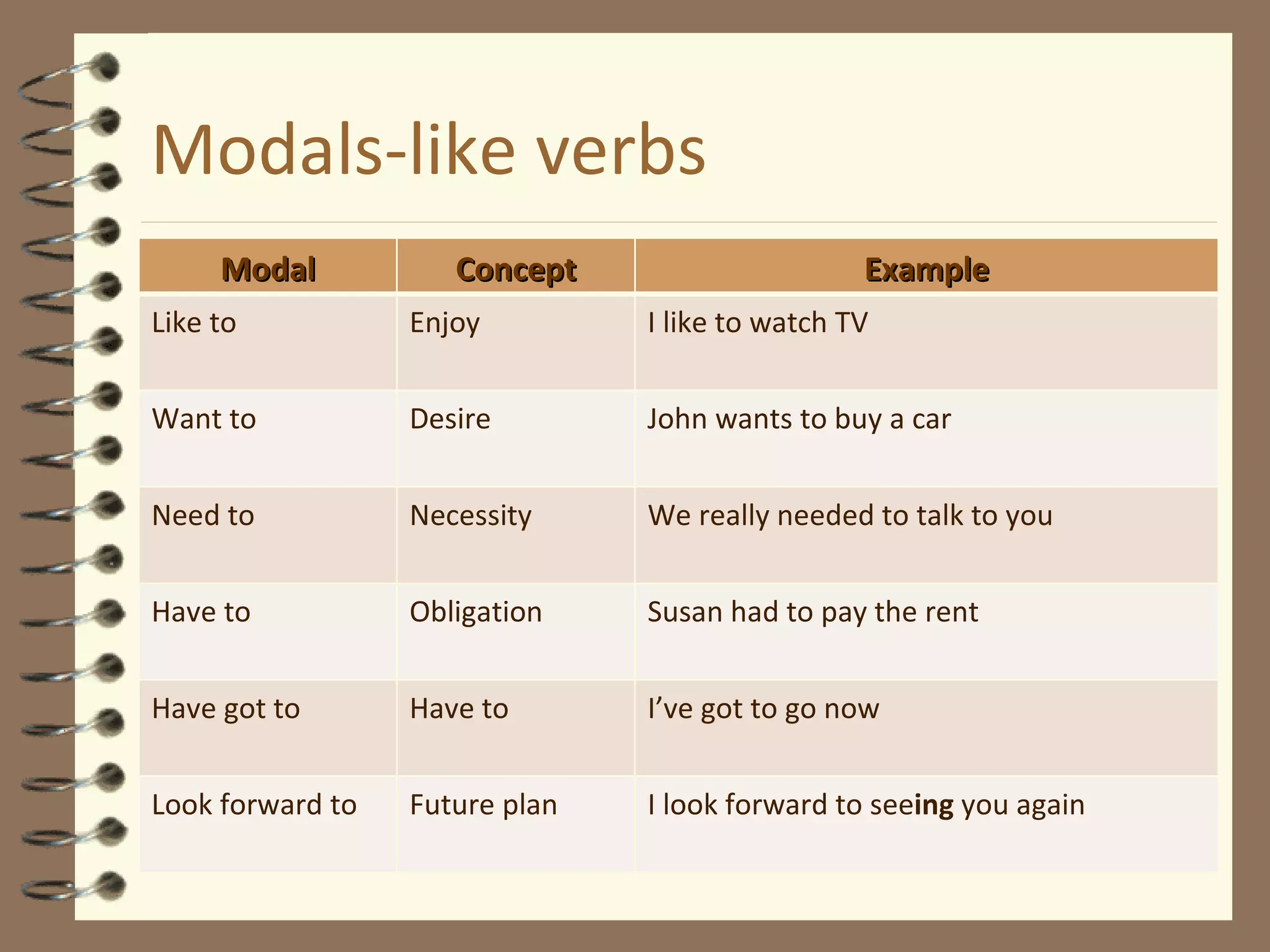
Modal verbs are sometimes called auxiliary verbs that provide additional meaning to the main verb. They express ideas like ability, permission, obligation, possibility, advice and suggestions. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, and ought to. Modal verbs are not conjugated and are followed by the base form of the main verb without "to." They do not have present participle or infinitive forms.