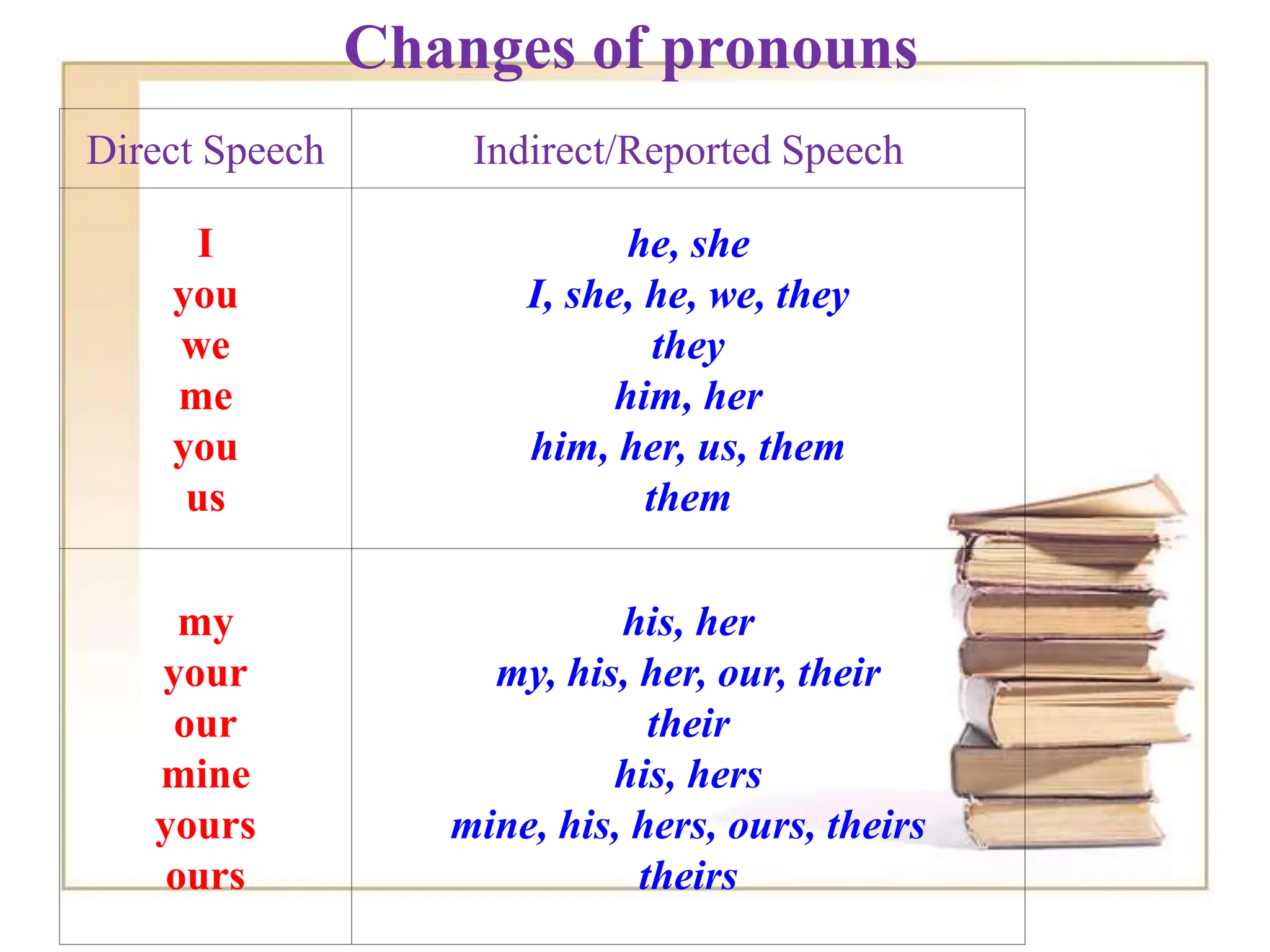
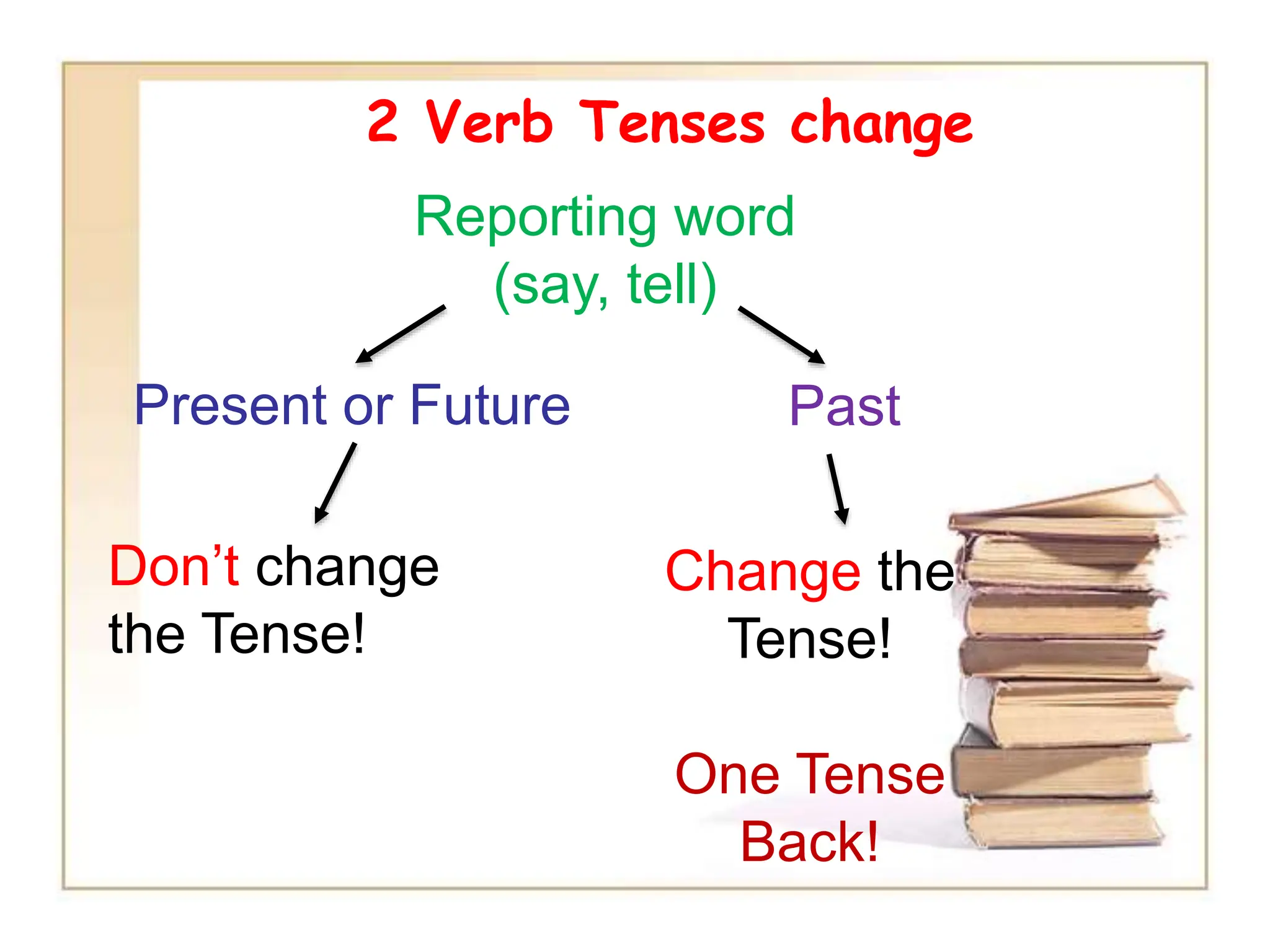
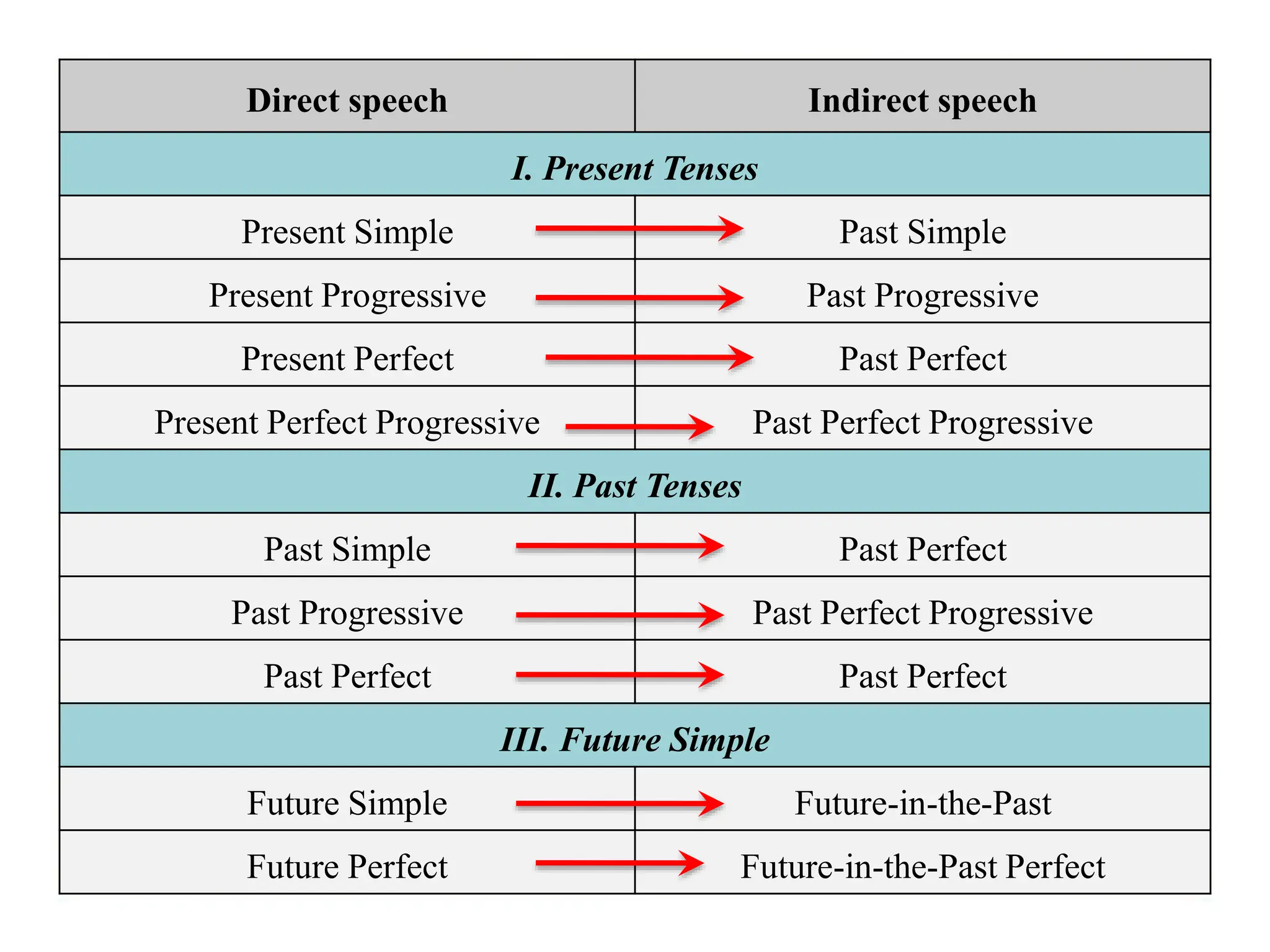
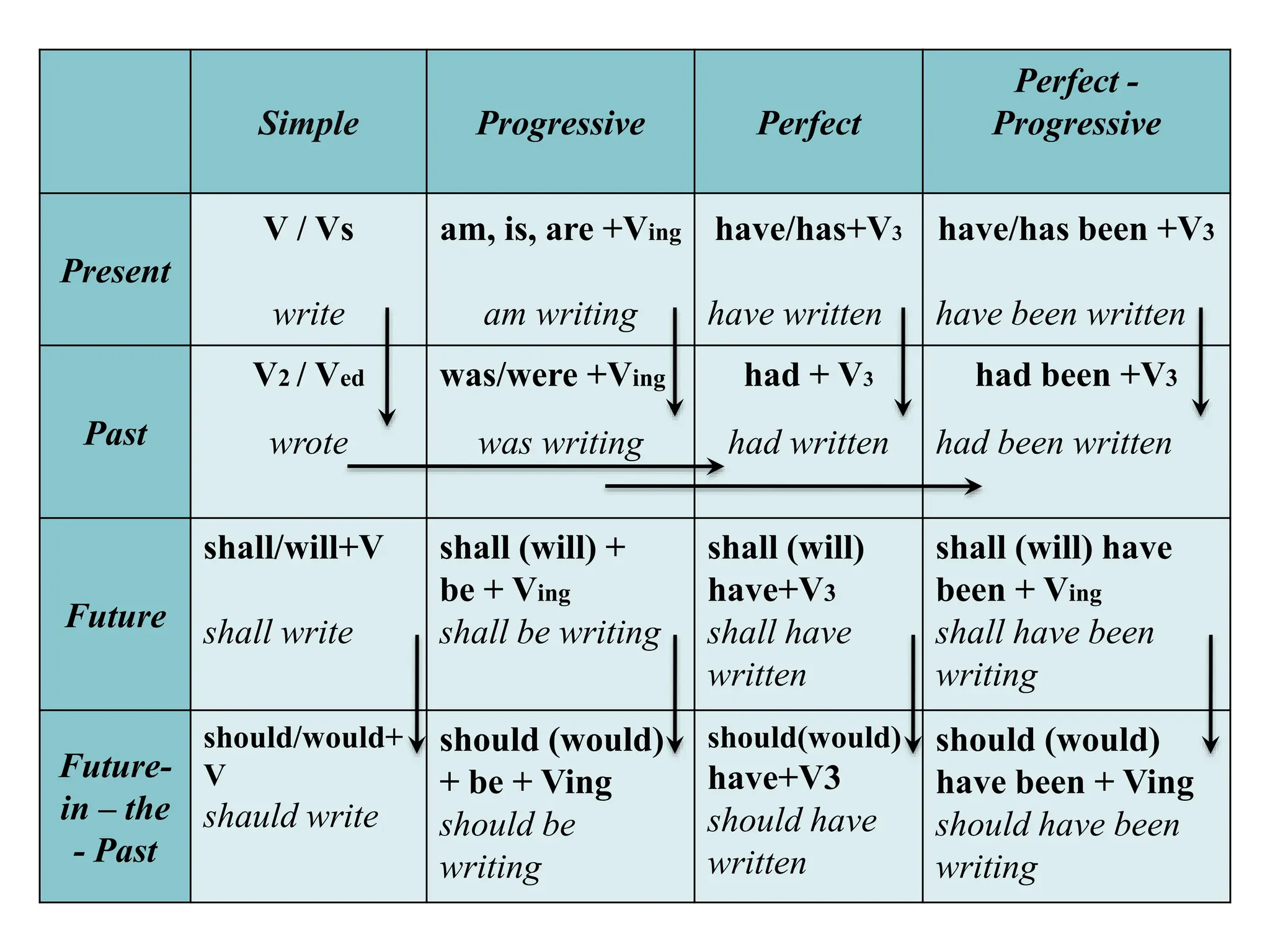
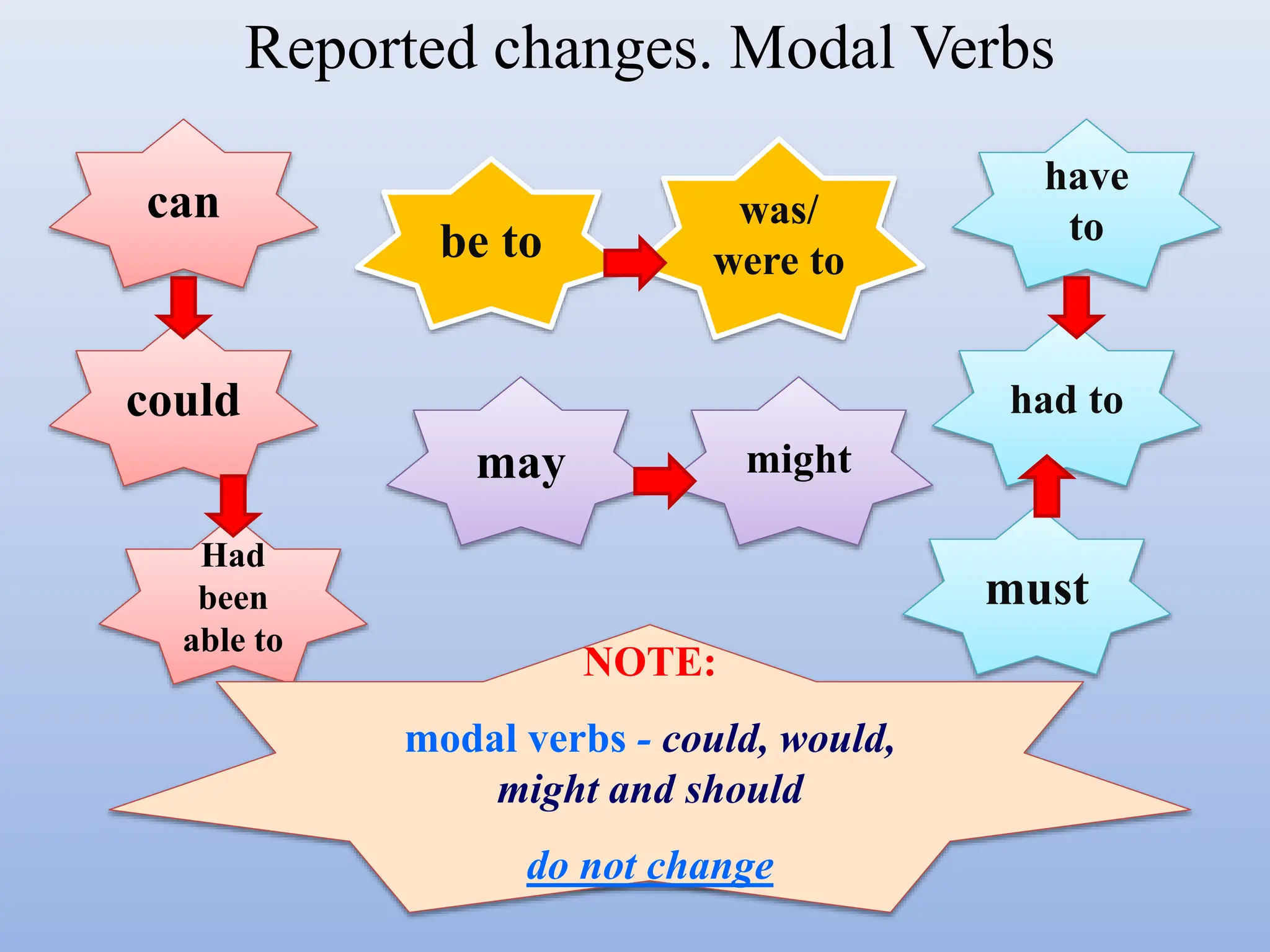
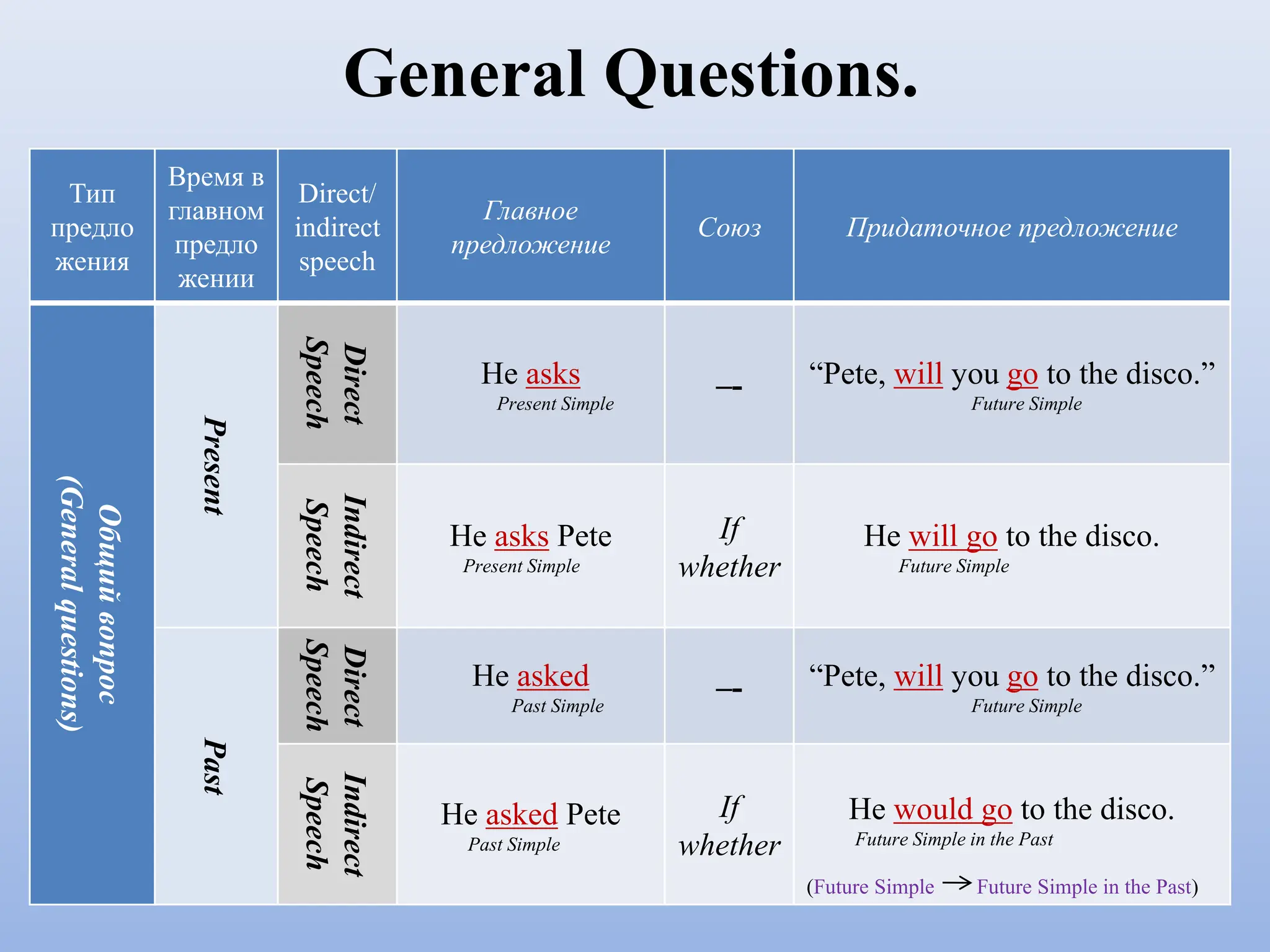
The document discusses reported or indirect speech, which is used to report what other people have said, thought, or believed. It explains that pronouns, verb tenses, time words, and question words may need to change when converting direct quotes into reported speech. Examples are provided to illustrate these changes between direct and reported speech.