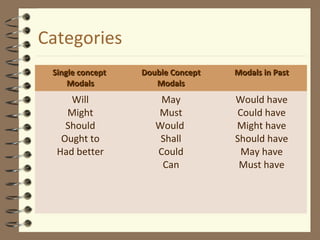
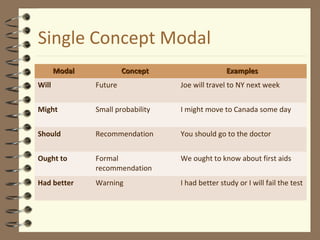
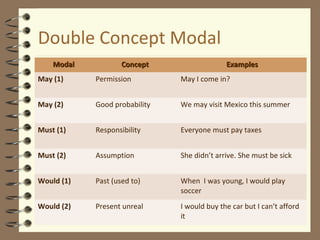
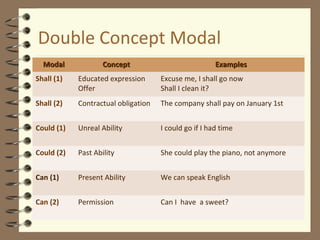
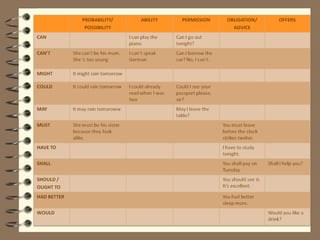
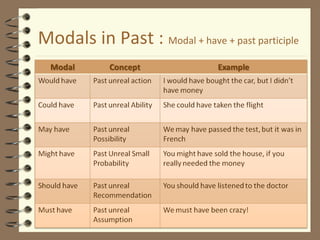
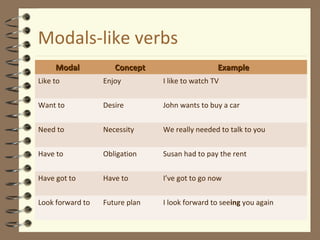
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that provide additional meaning to the main verb of a sentence. They express concepts like ability, permission, obligation, possibility, recommendation and future events. Some modal verbs have a single meaning while others have double meanings depending on context. Modal verbs do not conjugate or take tense and are followed by the base form of the main verb. They are categorized as single concept, double concept, or past tense modals. Examples are provided to illustrate the meanings and uses of different modal verbs.