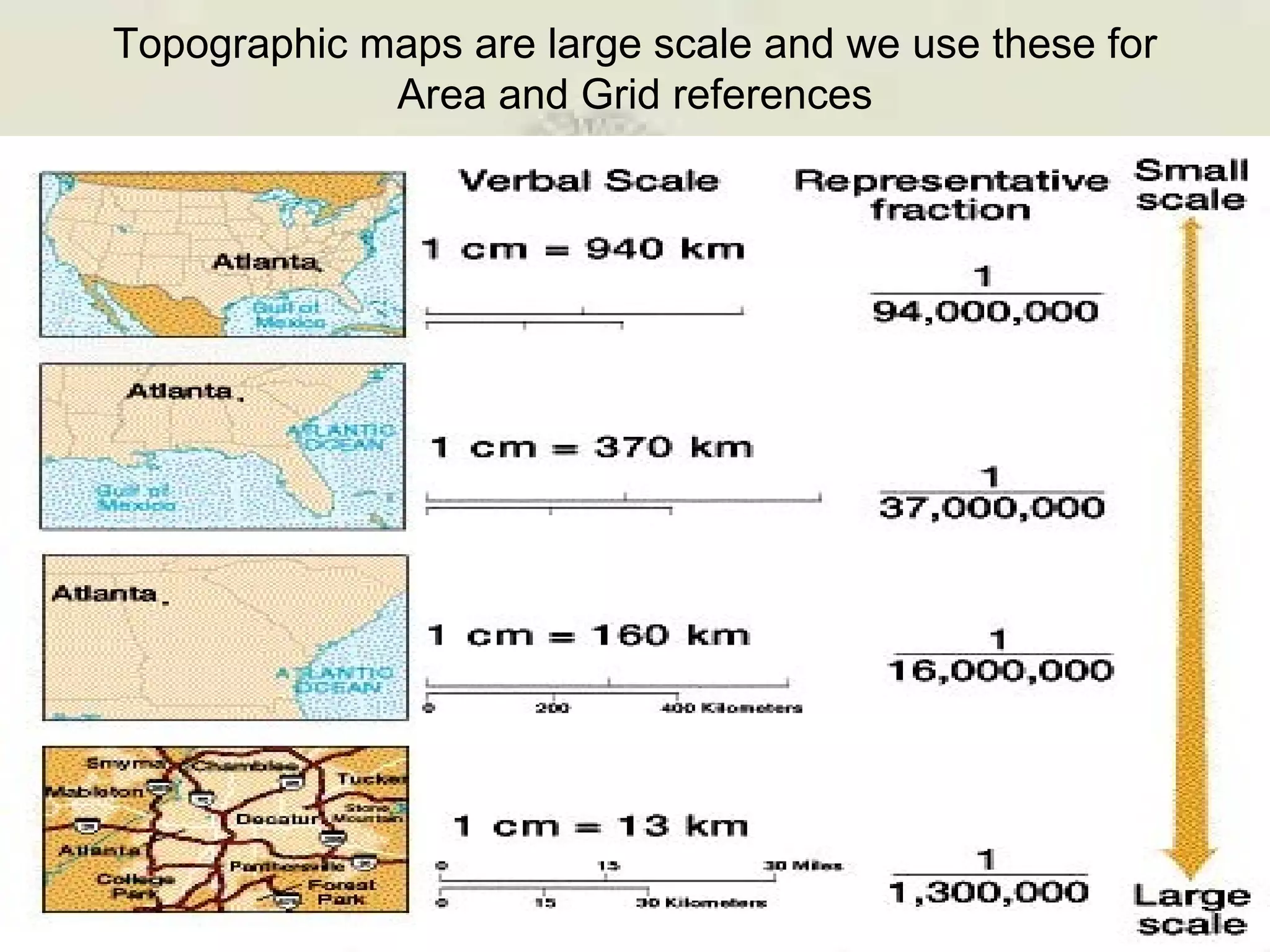
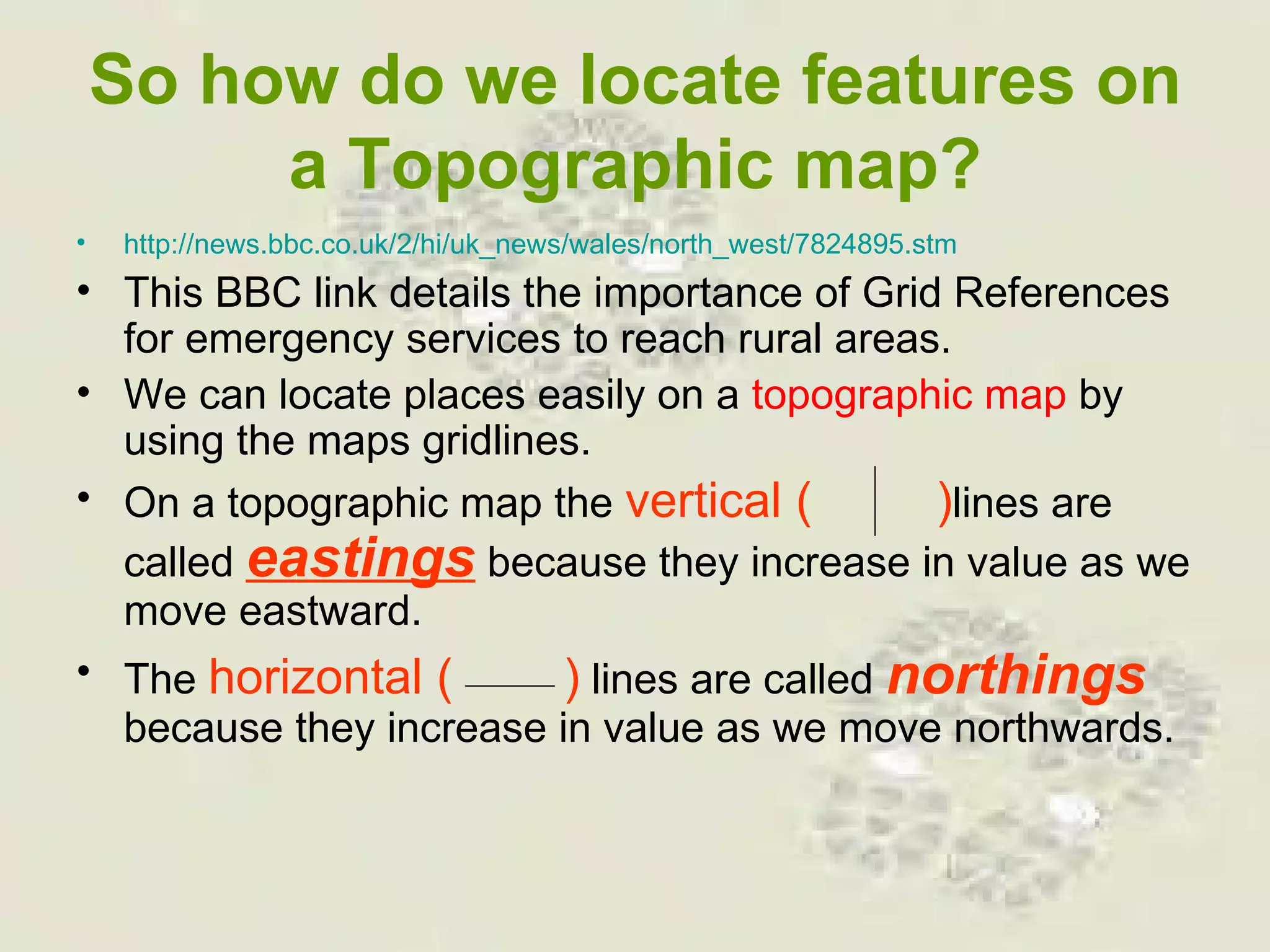
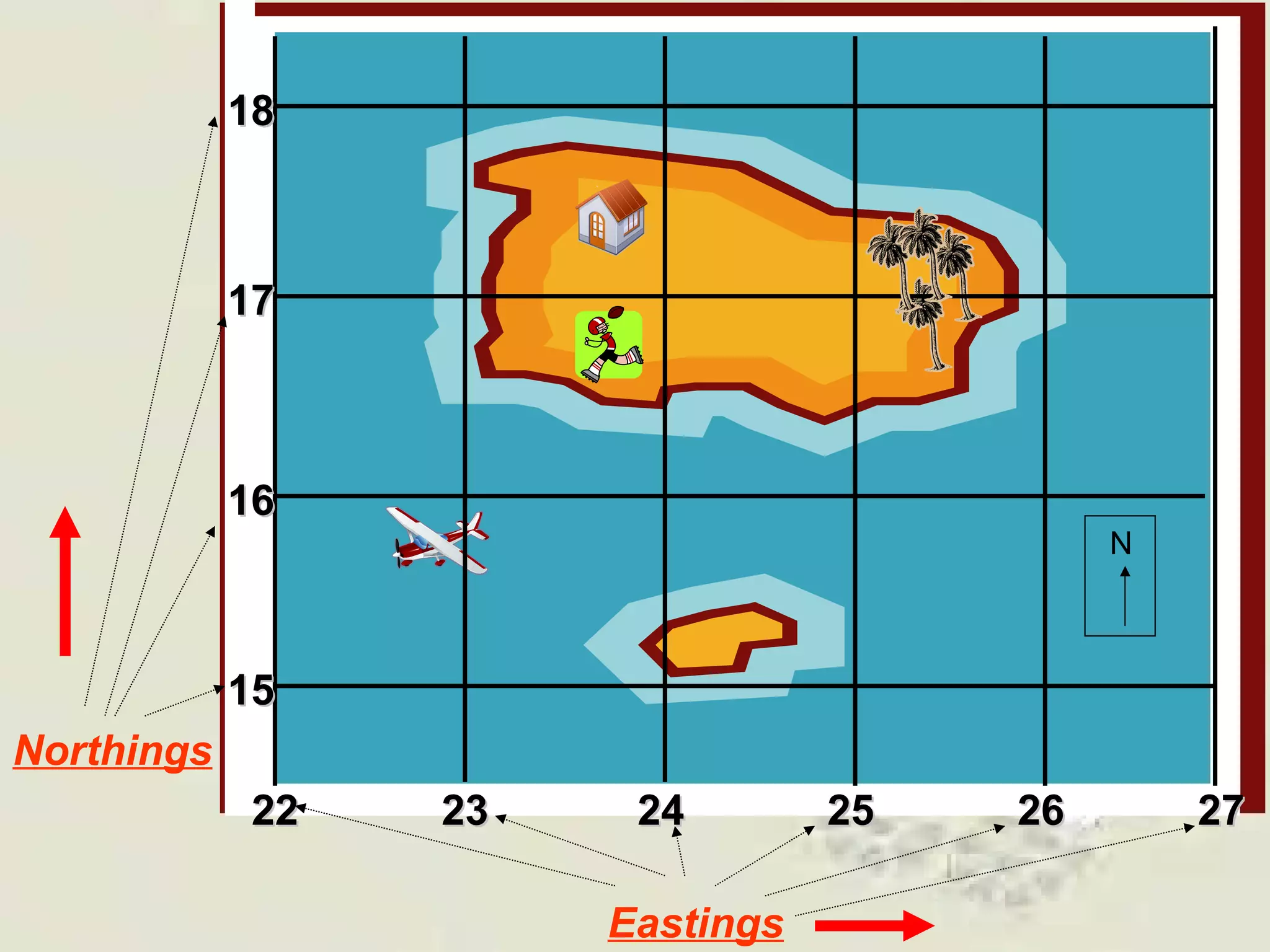
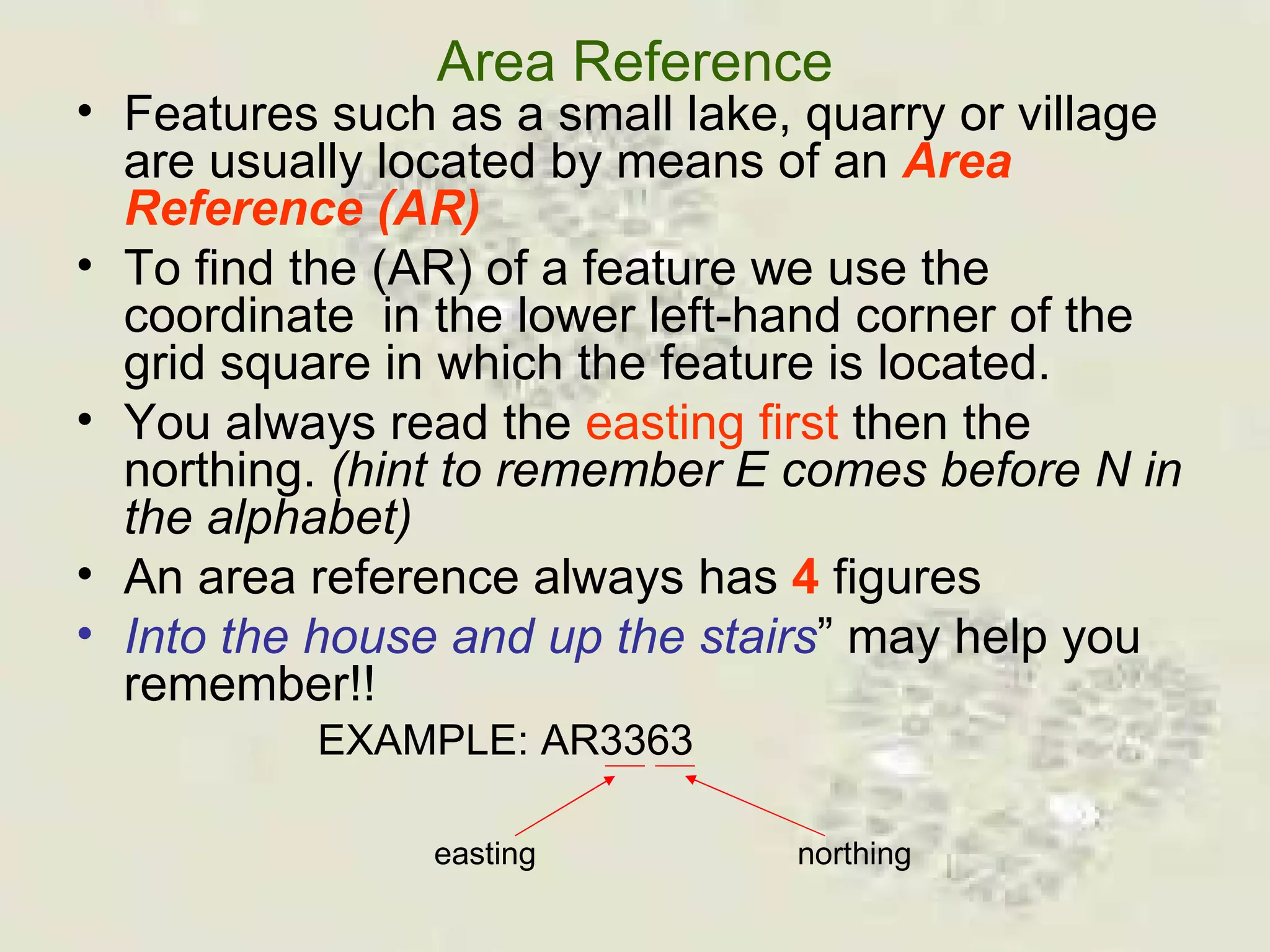
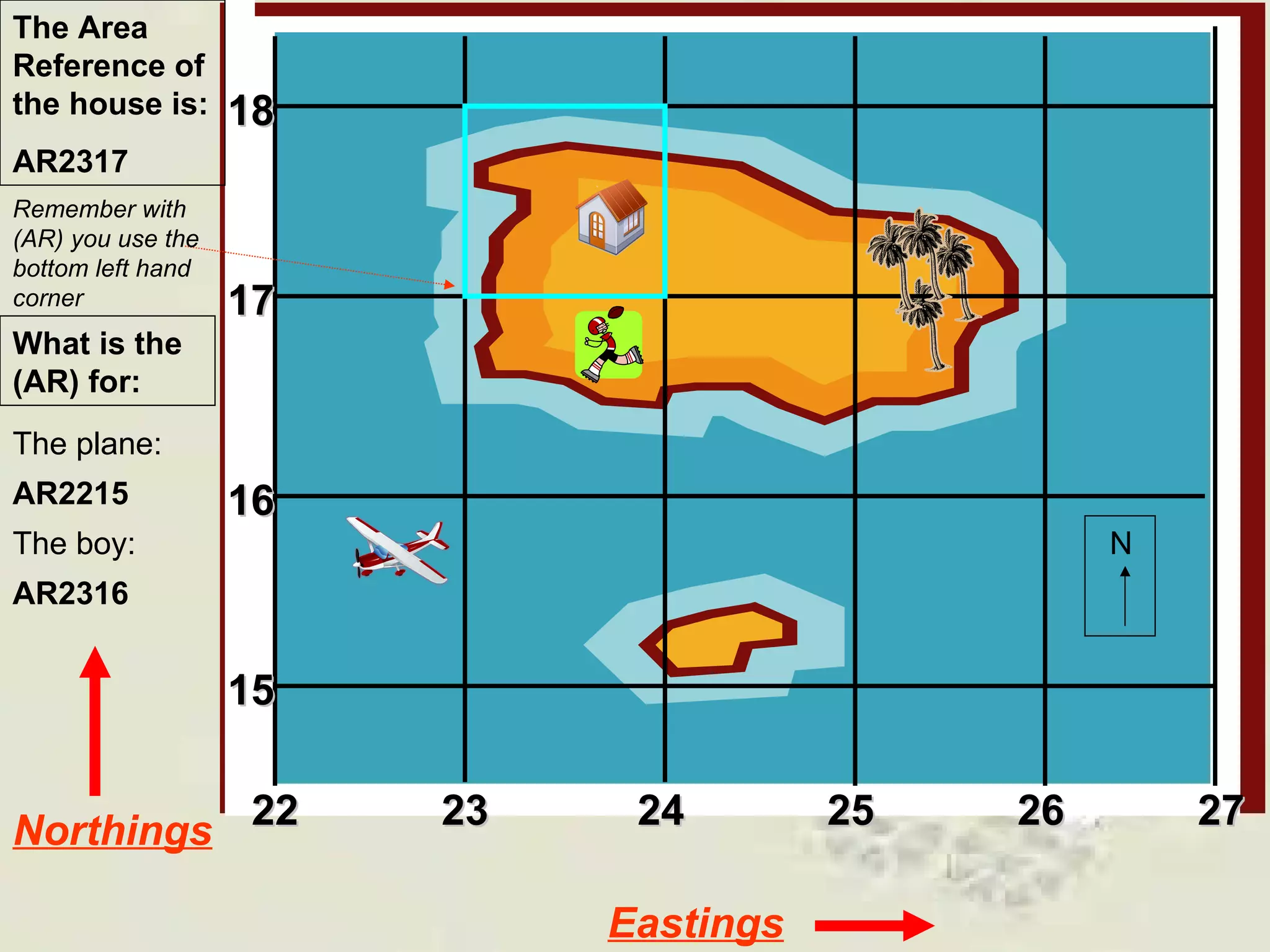
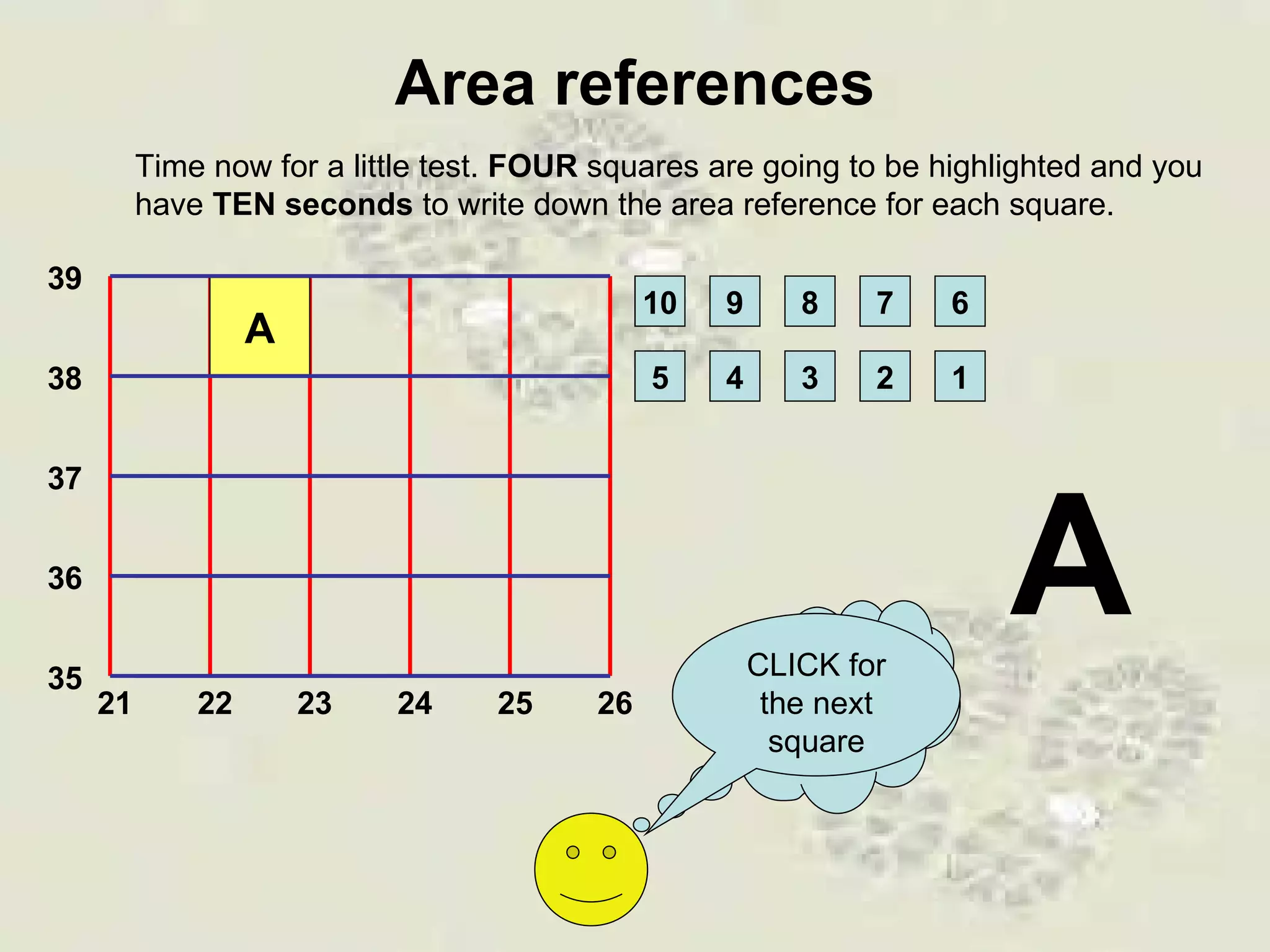
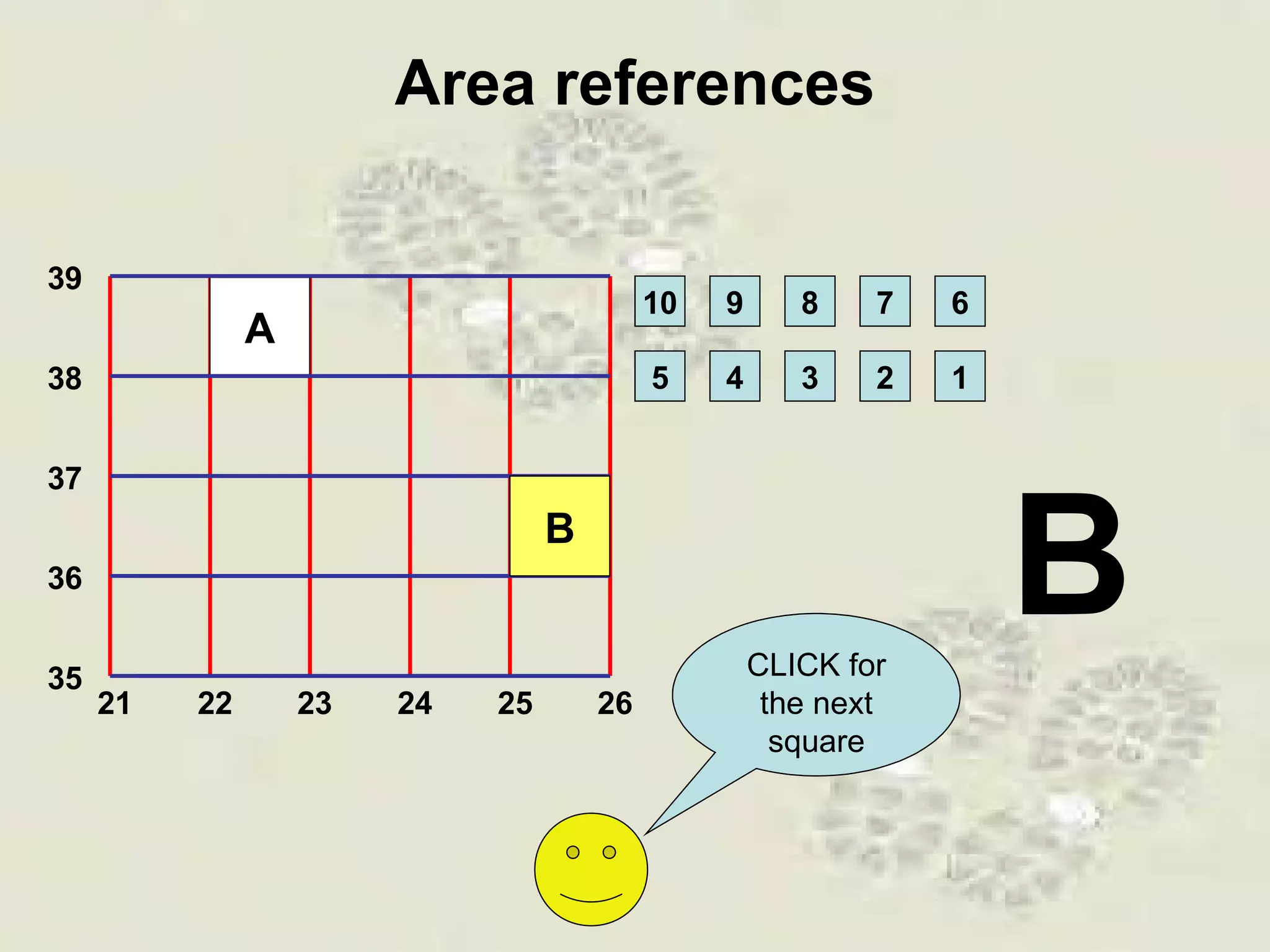
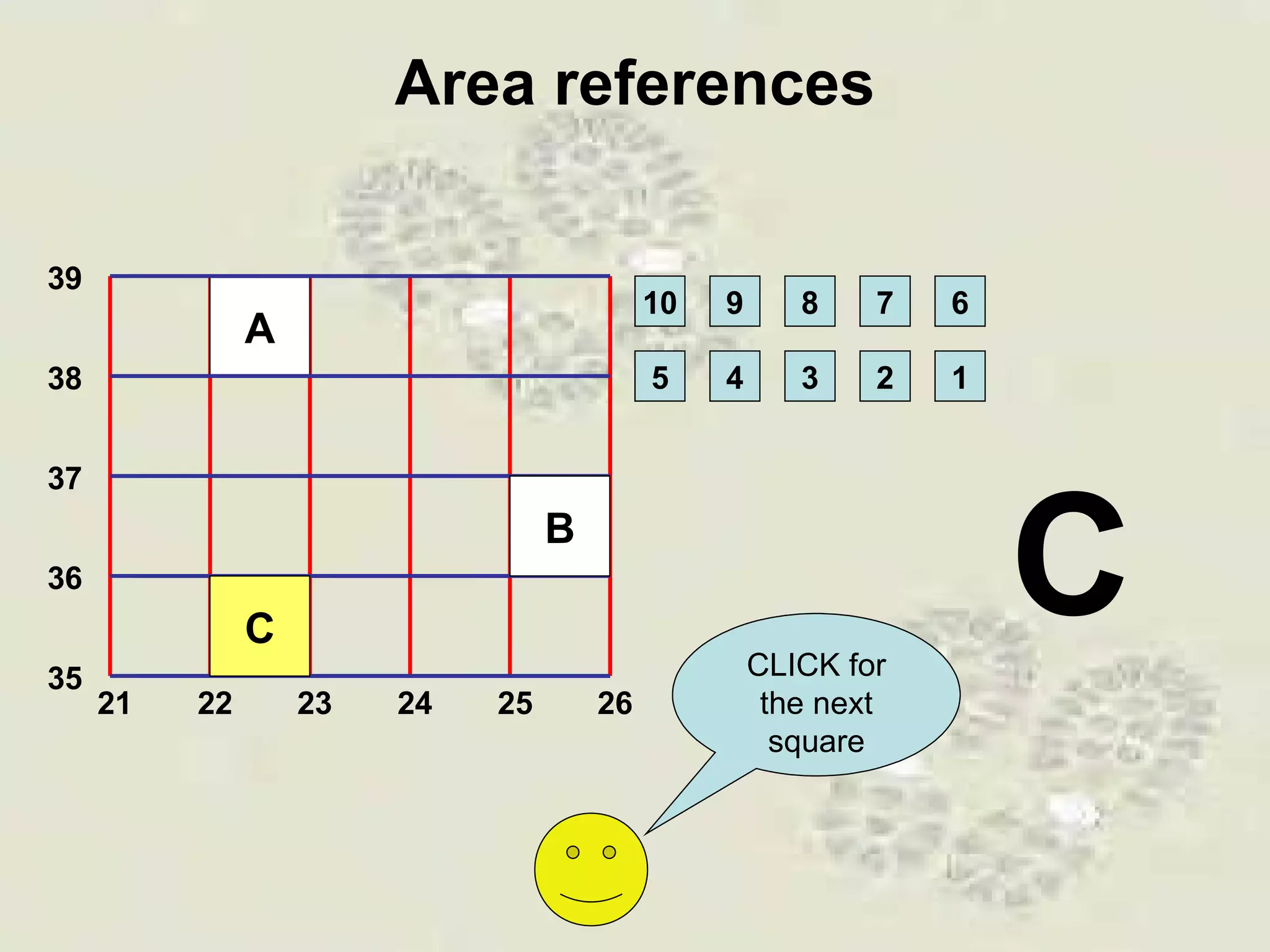
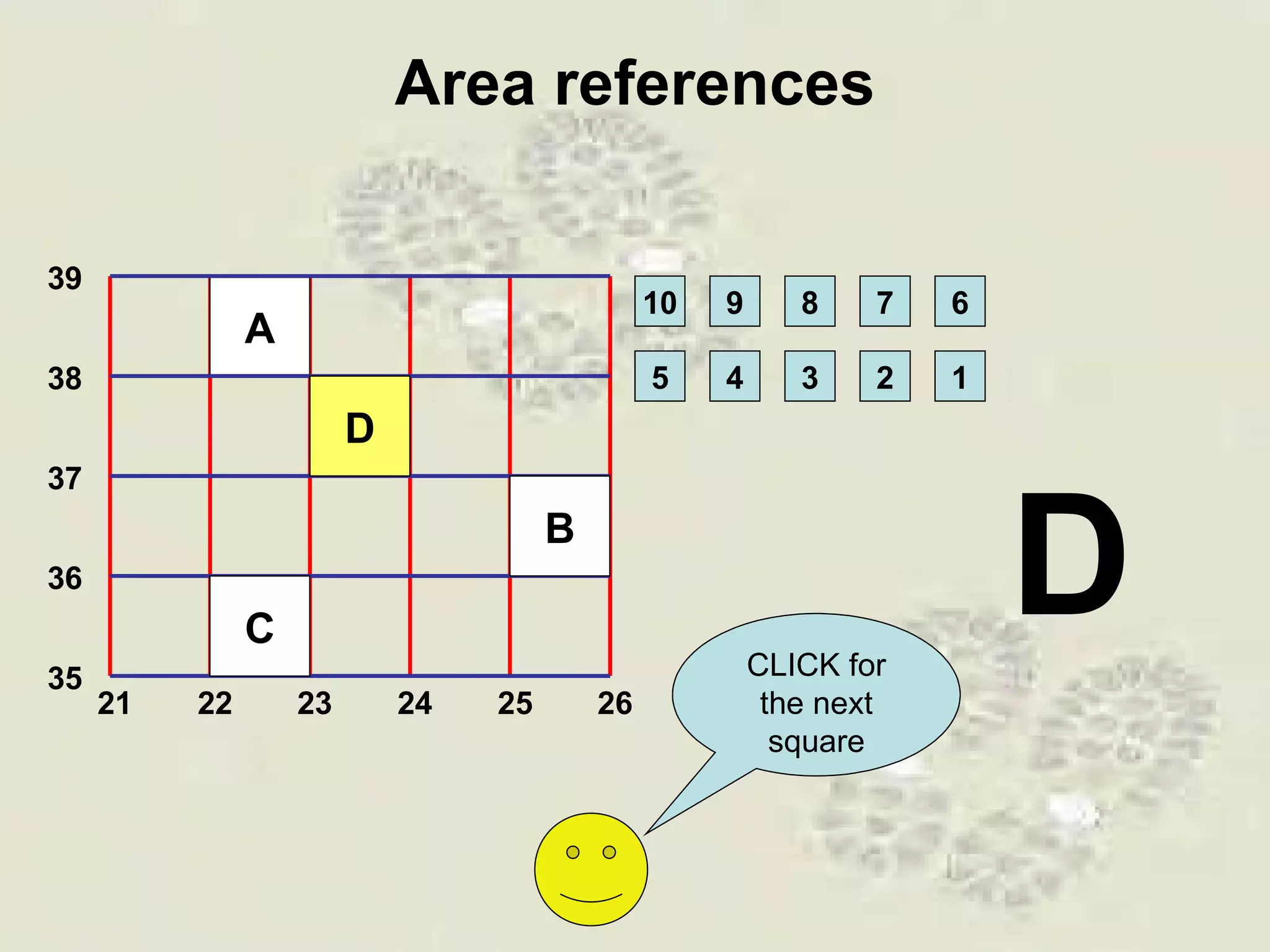
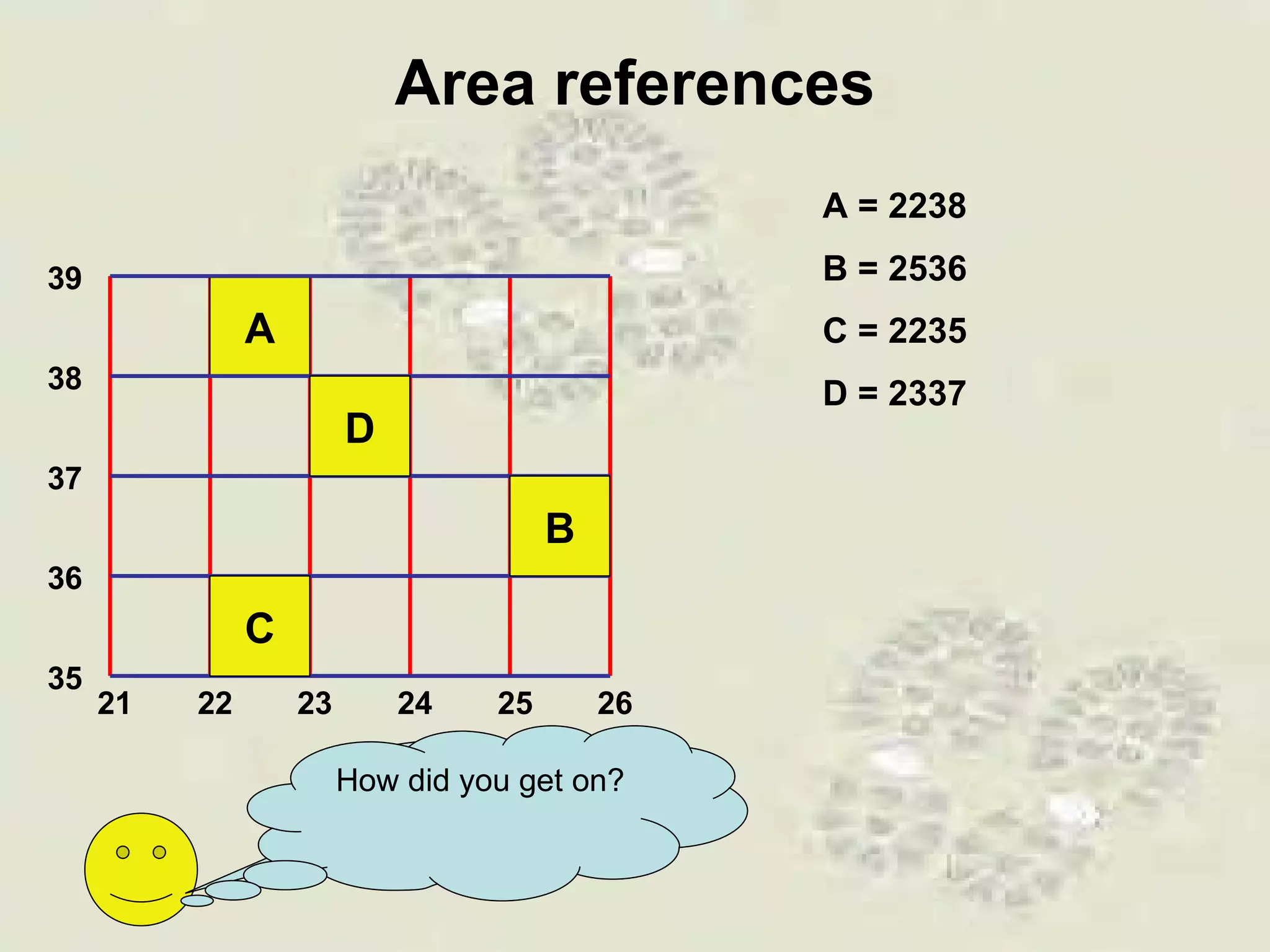
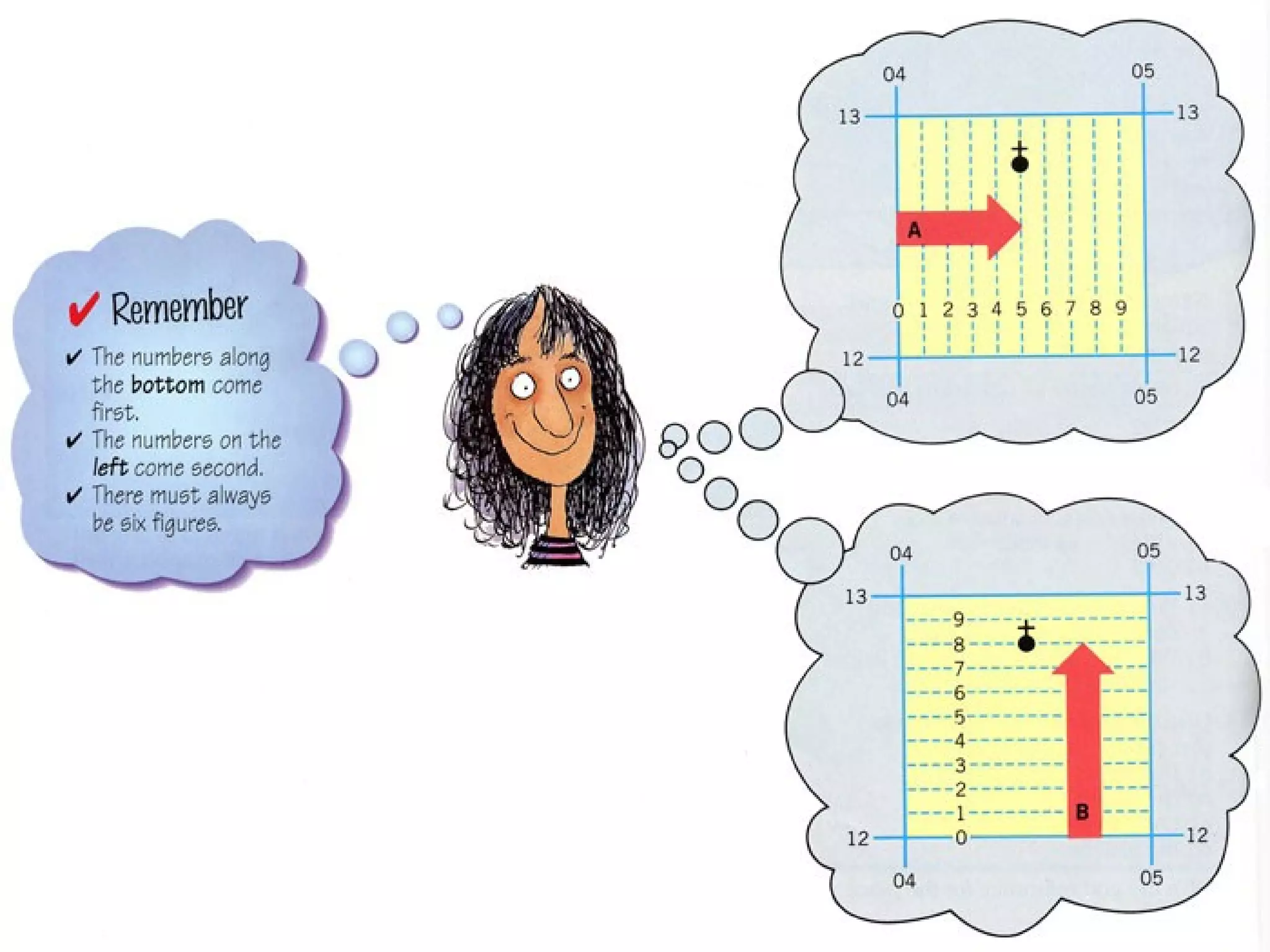
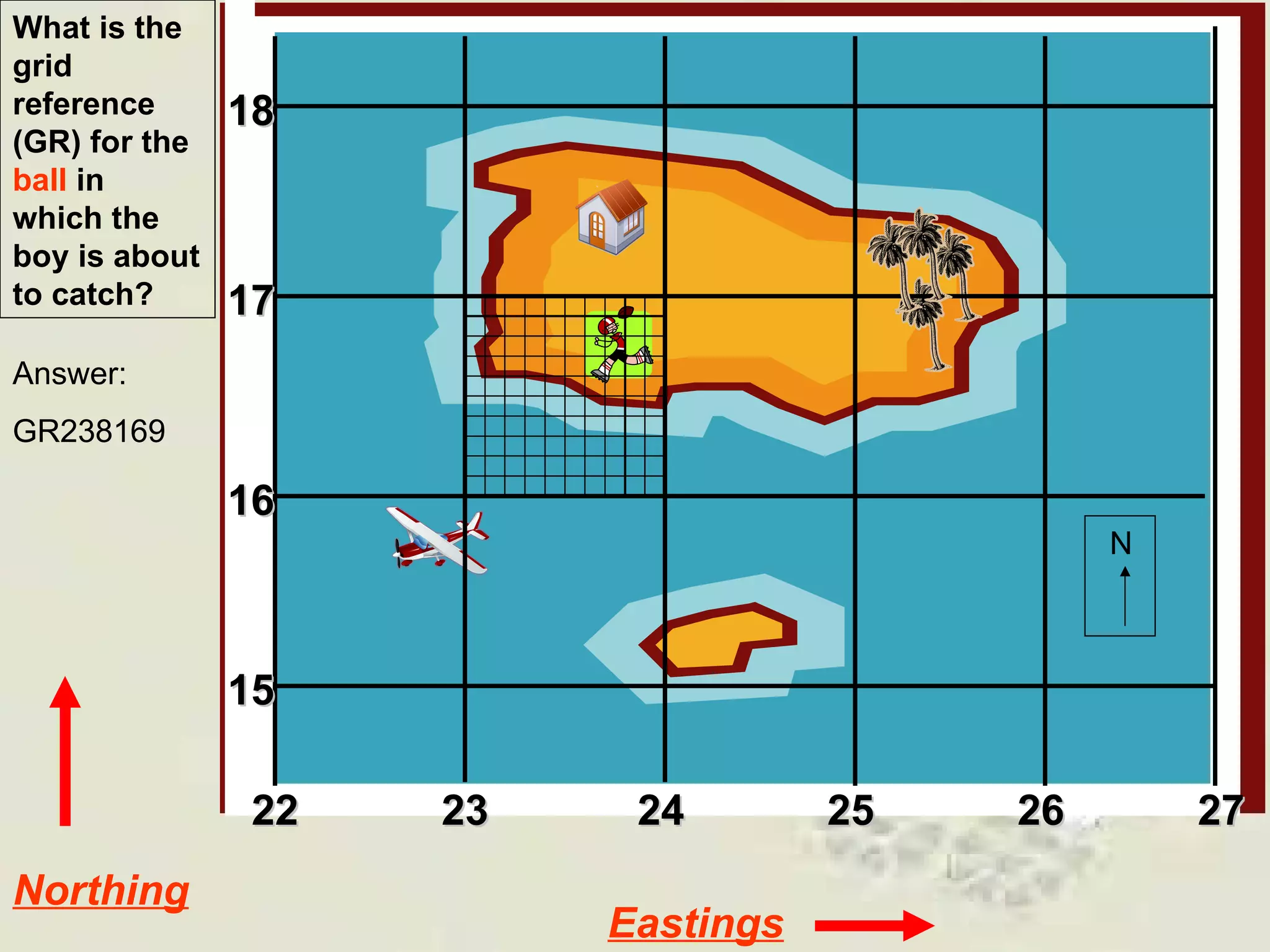
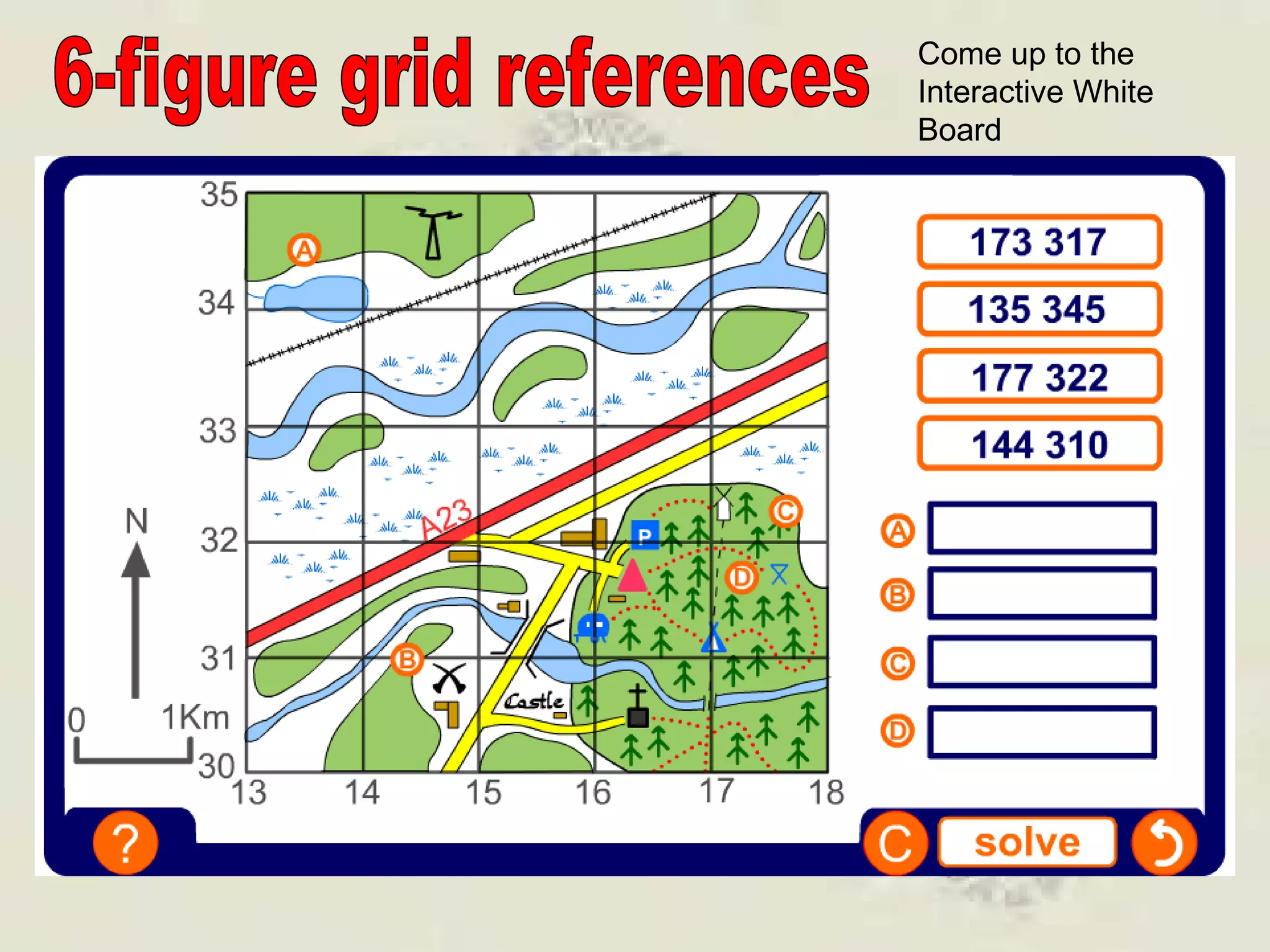
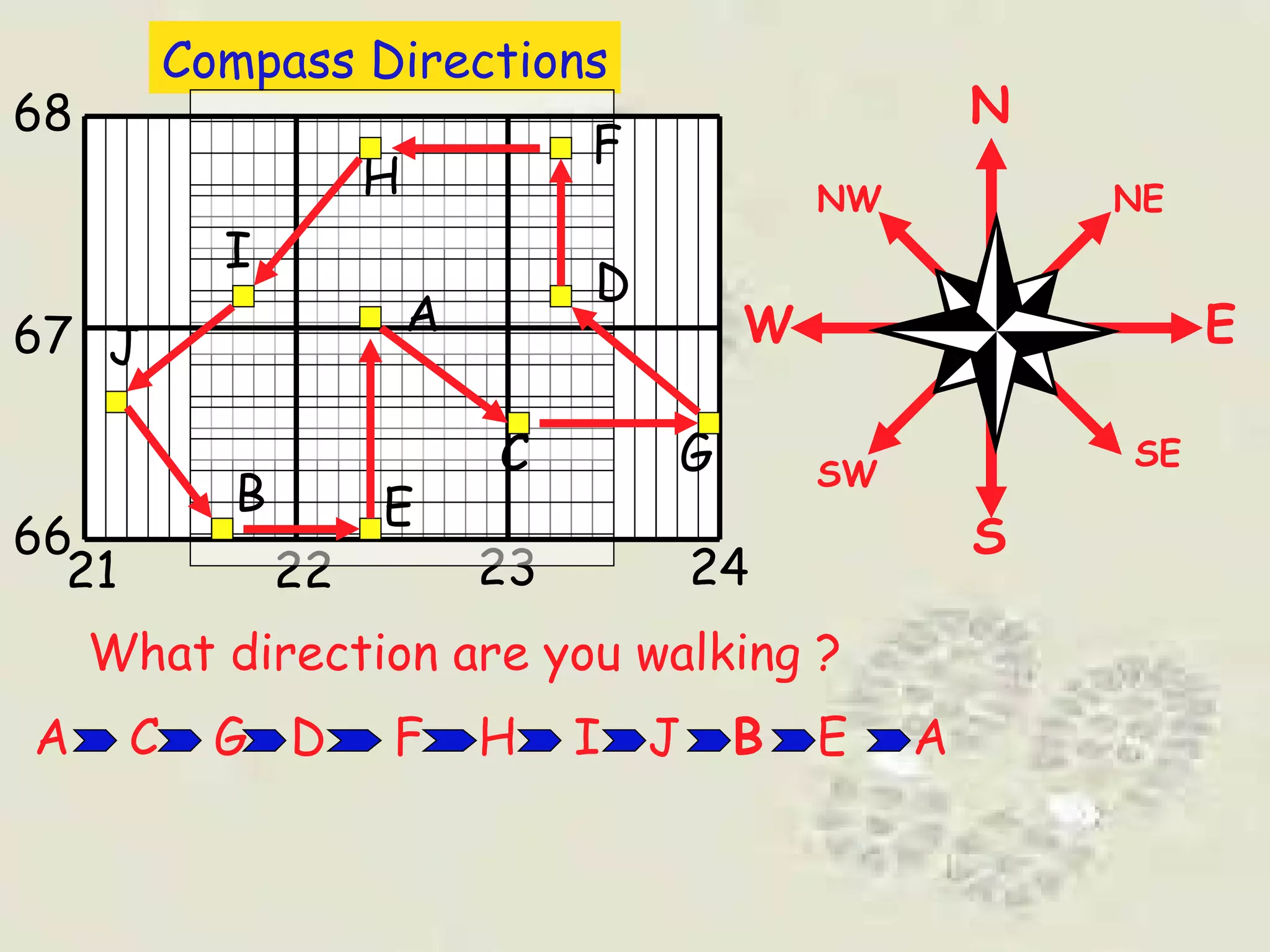
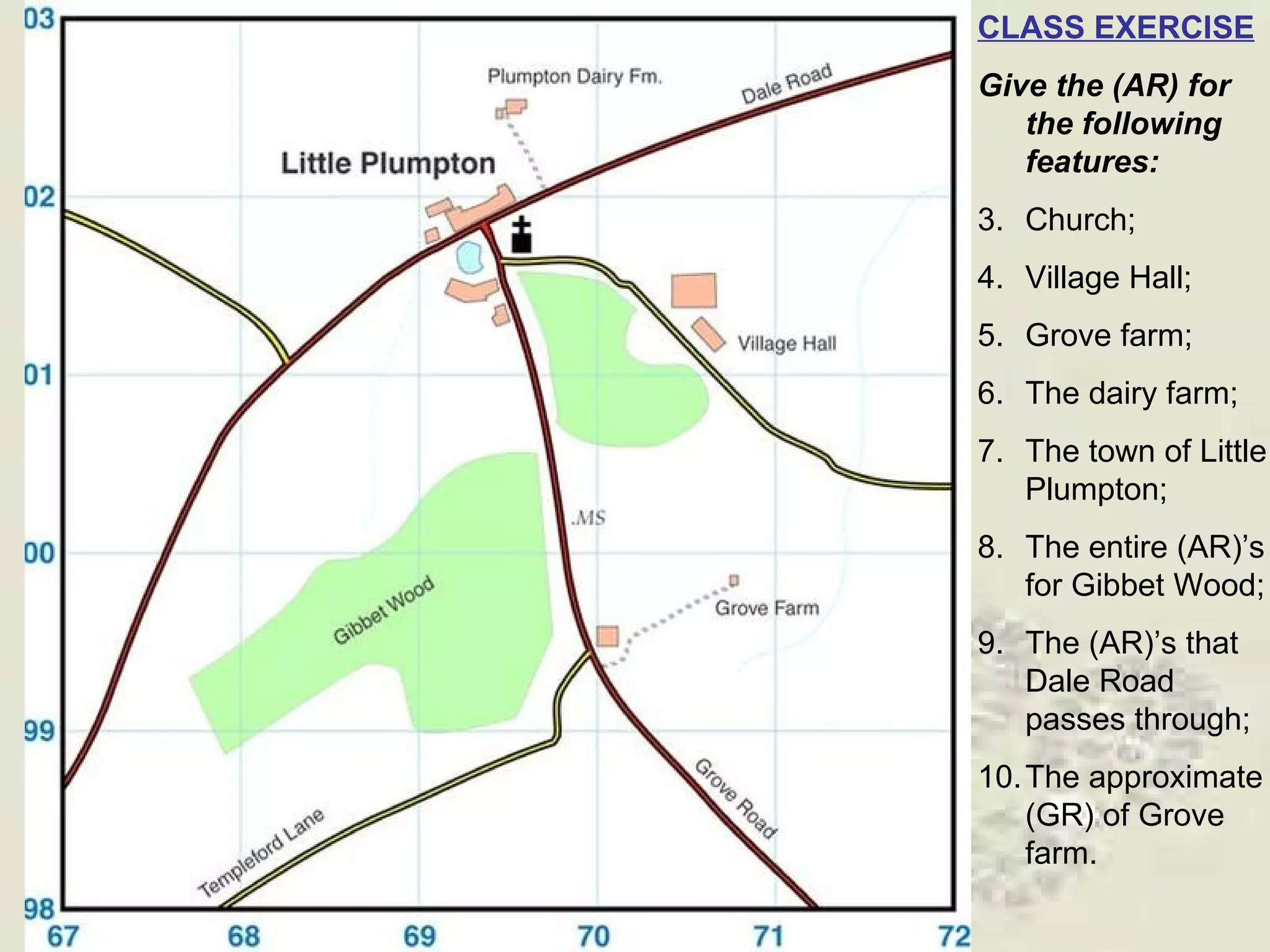
This document discusses grid references and how they are used to locate features on maps. It explains that topographic maps use a grid system of eastings and northings to specify locations, and that area references use a four-digit code to indicate a specific grid square. It also introduces six-figure grid references which can pinpoint an exact location within a grid square down to the tenth of the easting and northing. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to read and use both area references and more precise grid references.