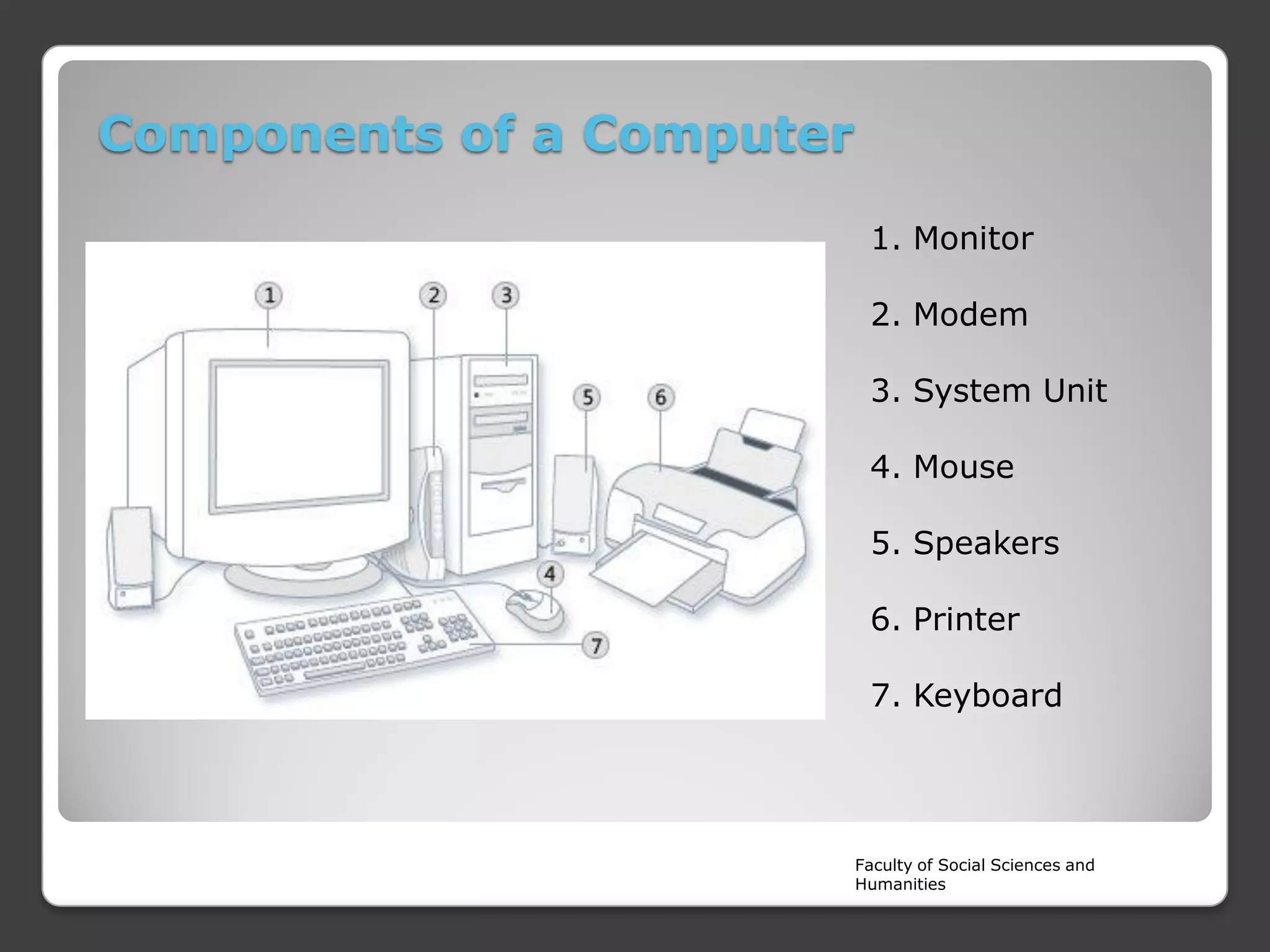
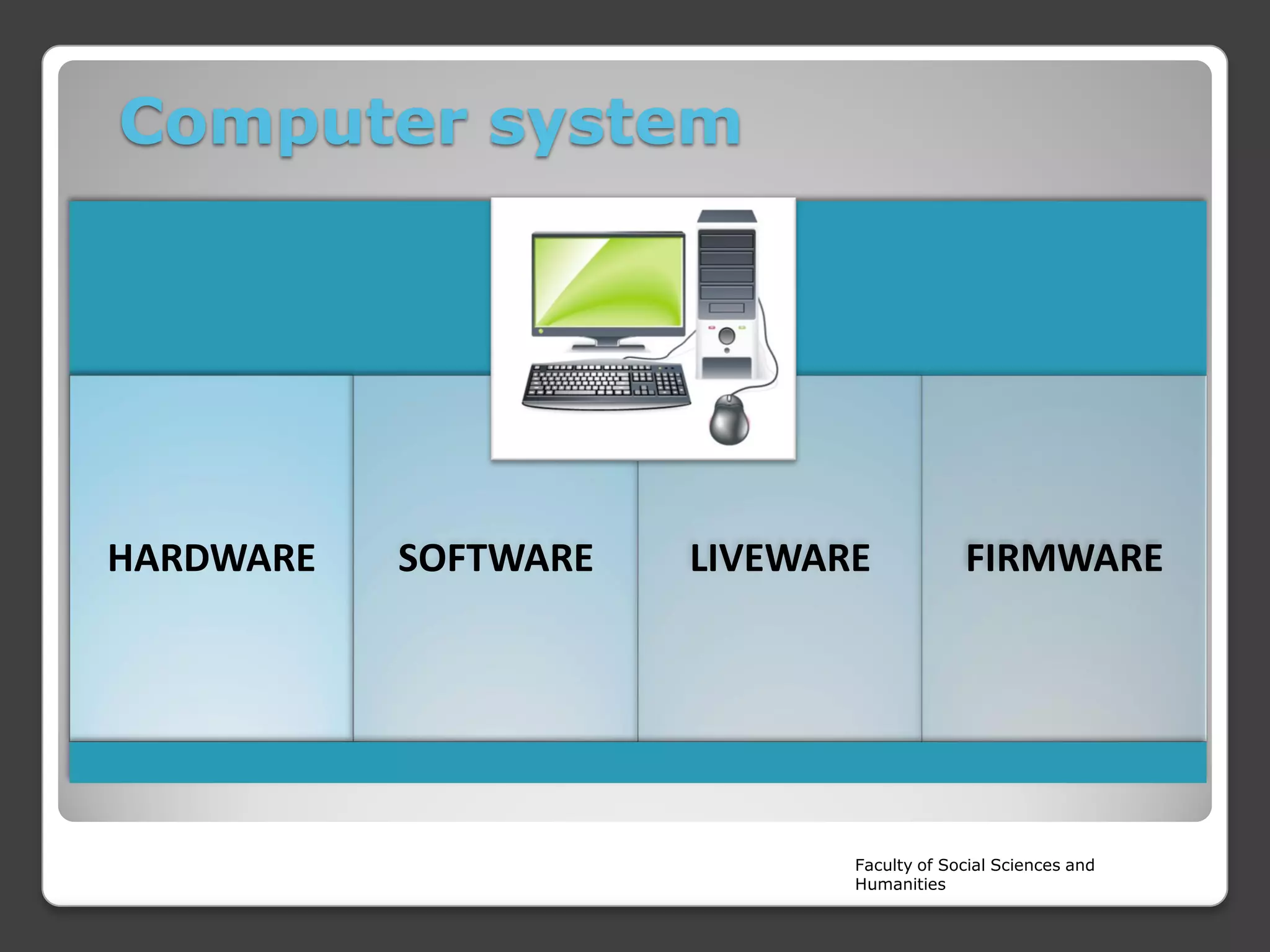
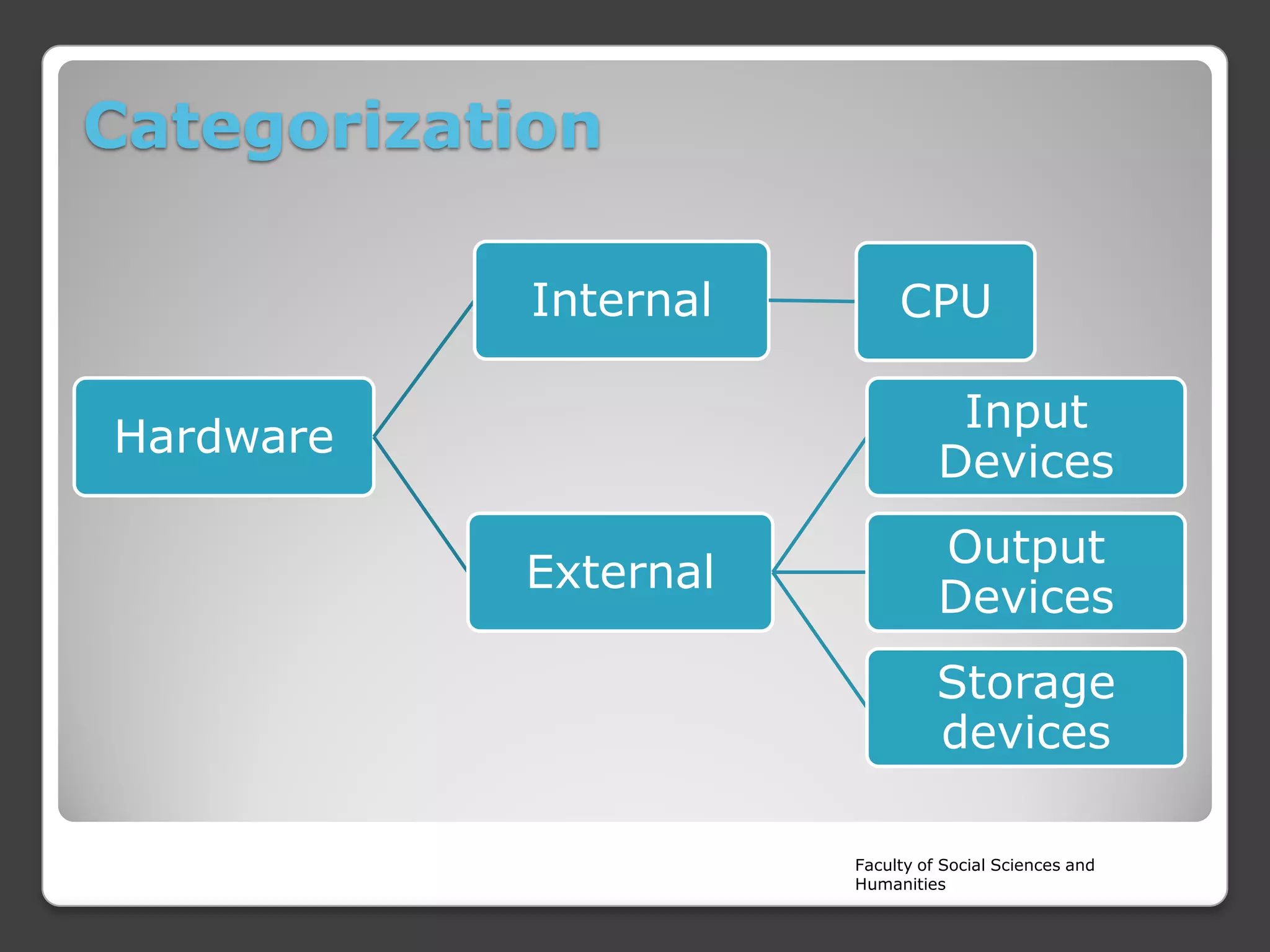
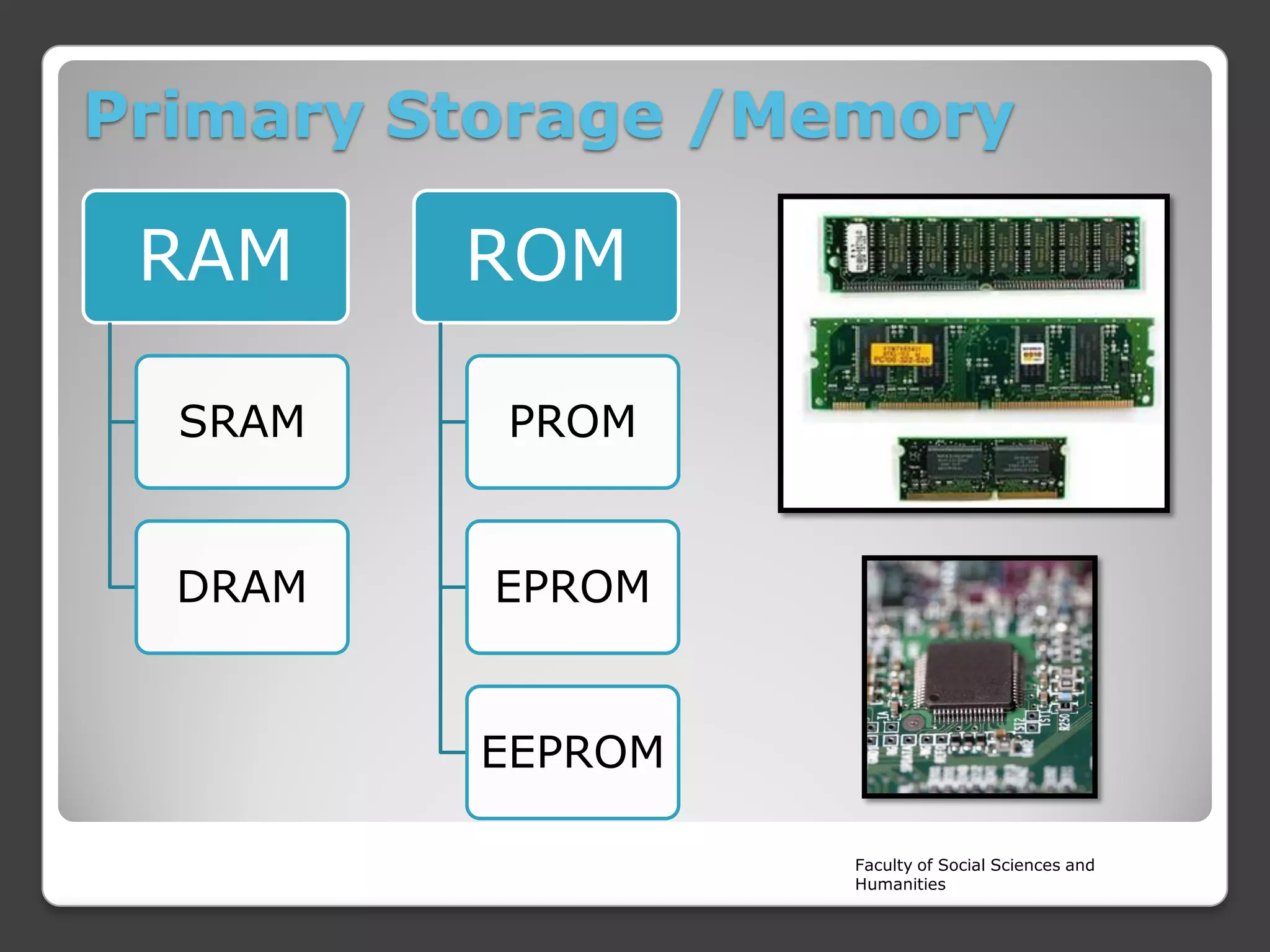
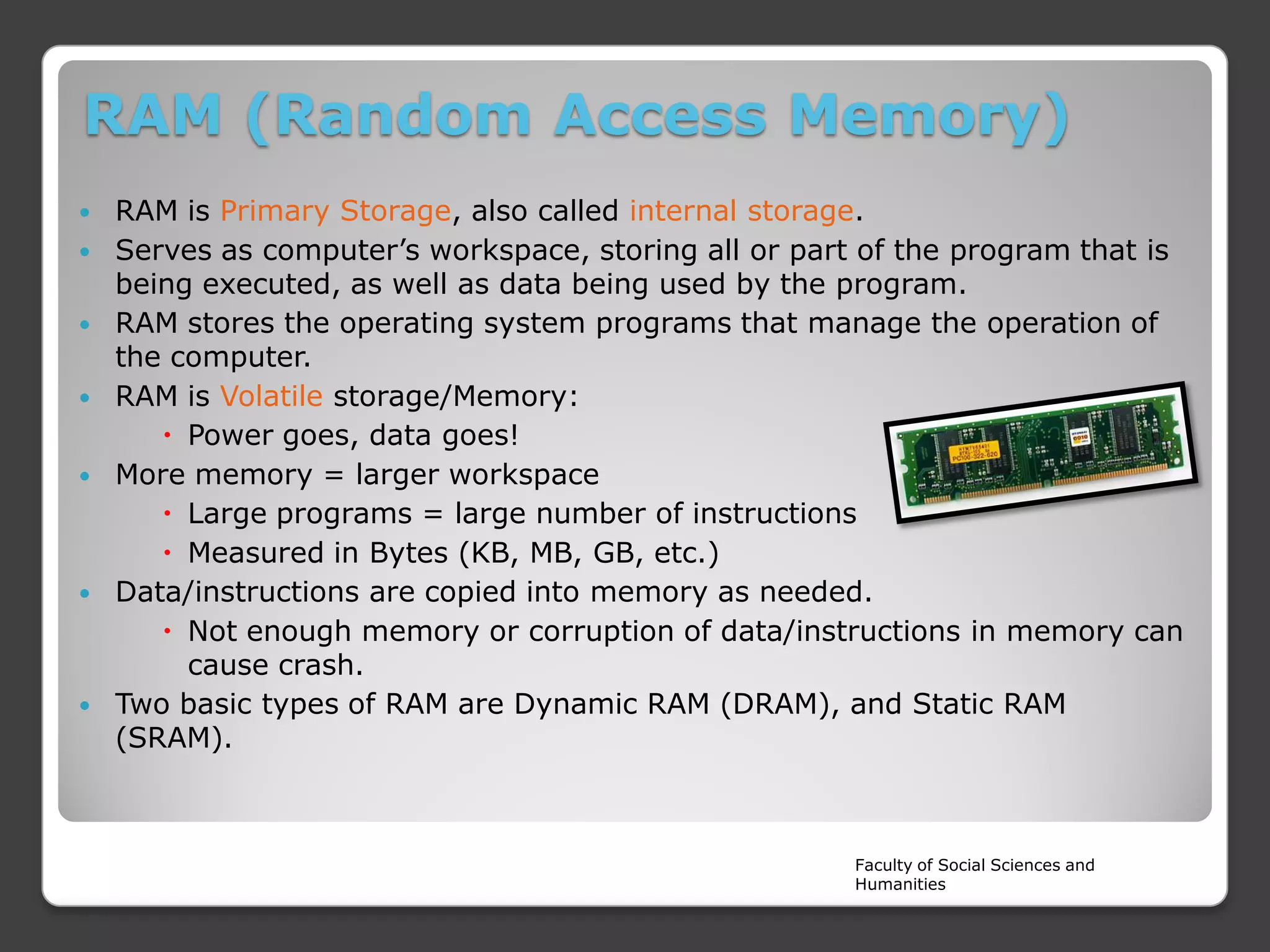
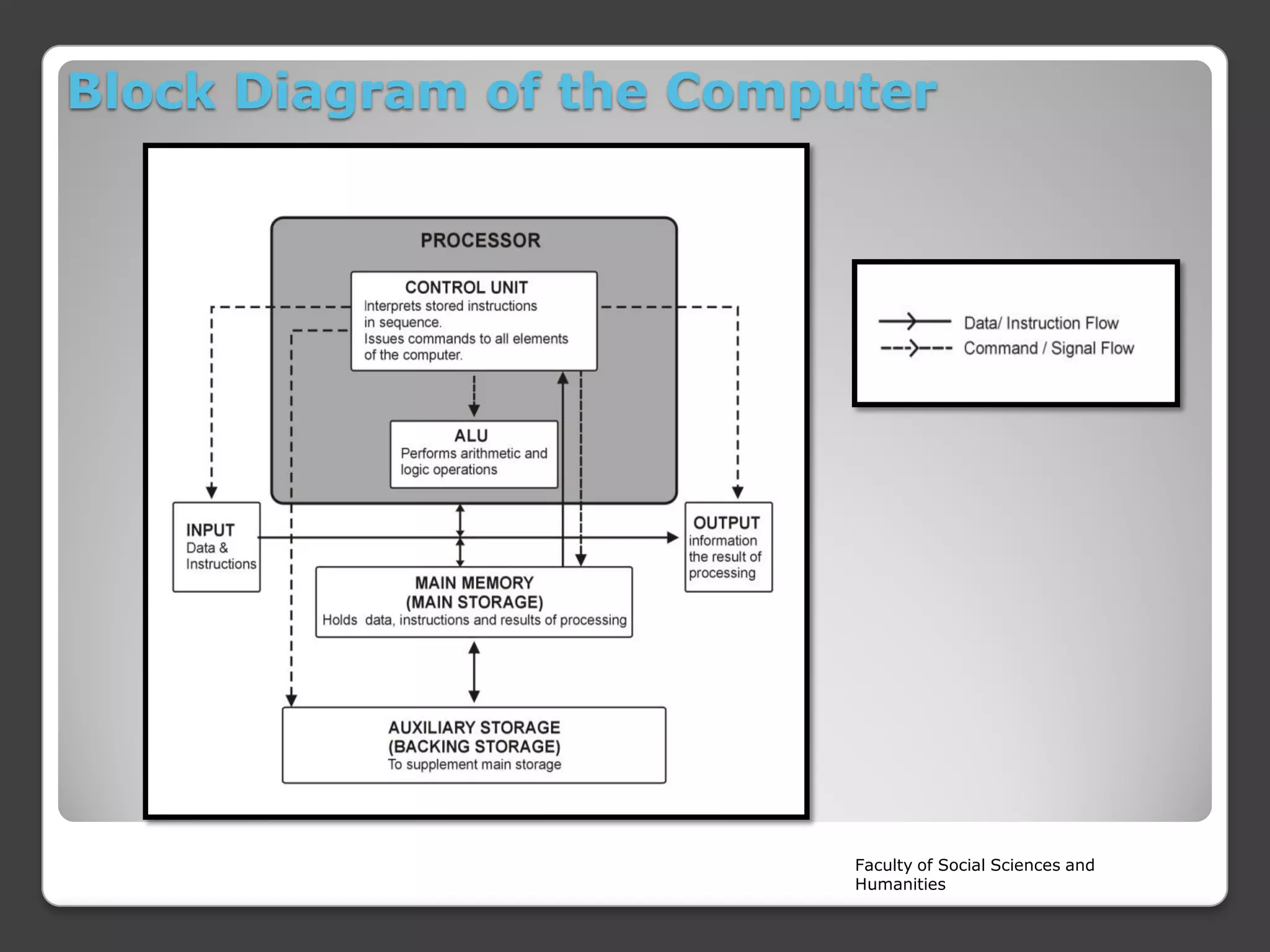
The document is a lecture on the components of a computer system from Rajarata University of Sri Lanka's Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities. It discusses the main internal and external hardware components, including the monitor, modem, system unit, mouse, speakers, printer, and keyboard. It also covers the software, liveware, and firmware that make up a computer system. The key hardware components discussed in more detail are the CPU, motherboard, input devices, output devices, storage devices, and RAM.