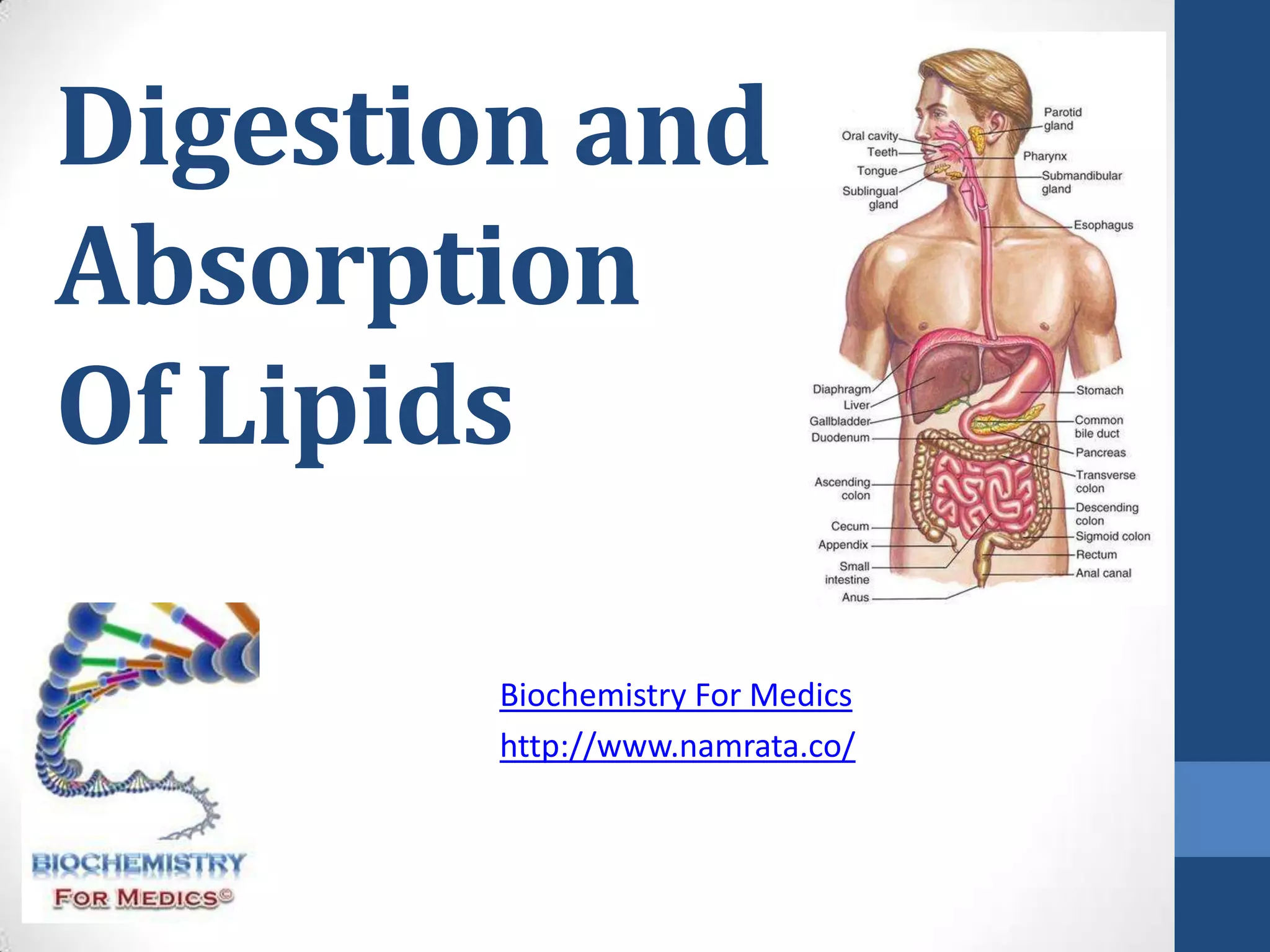
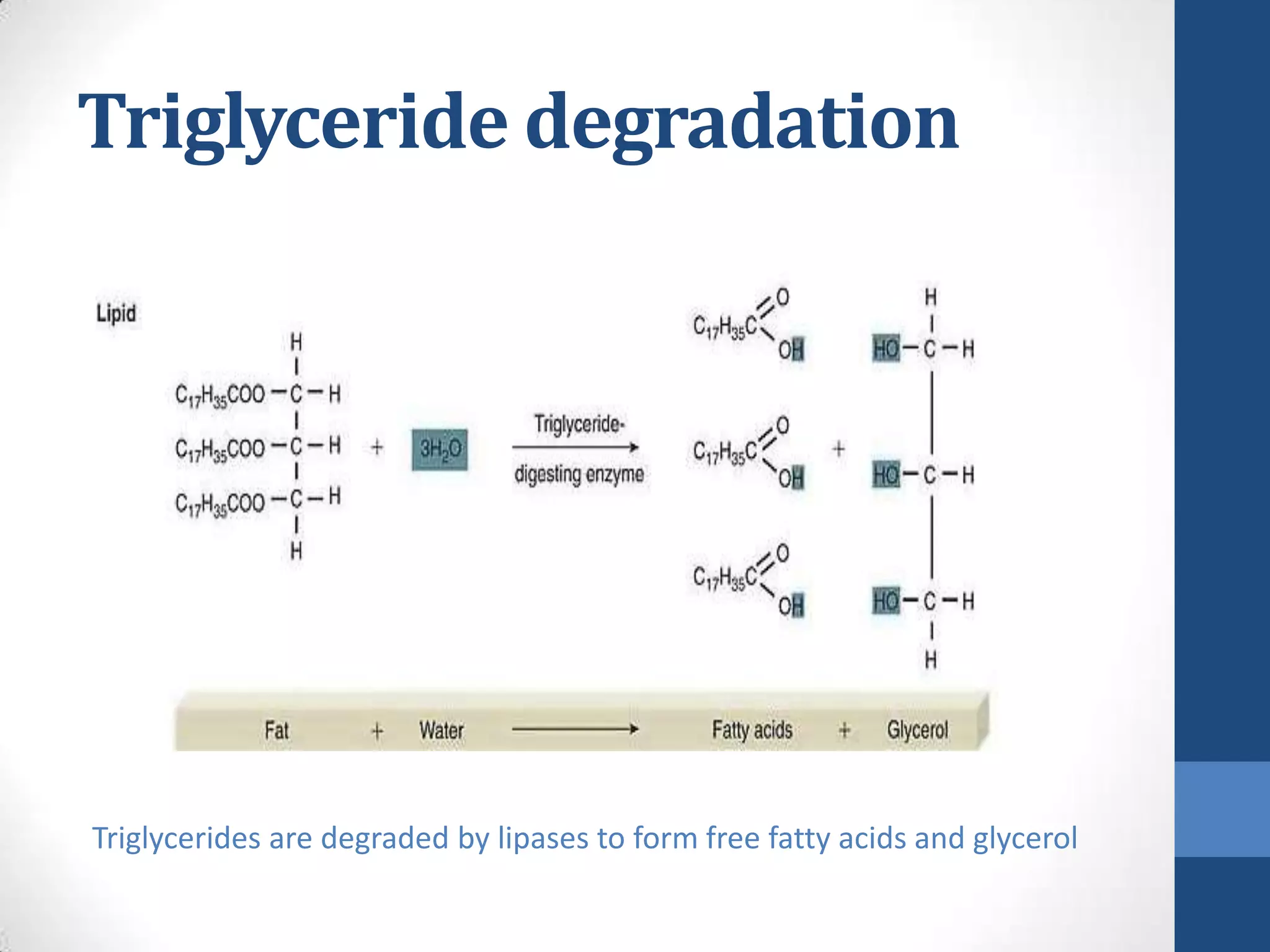
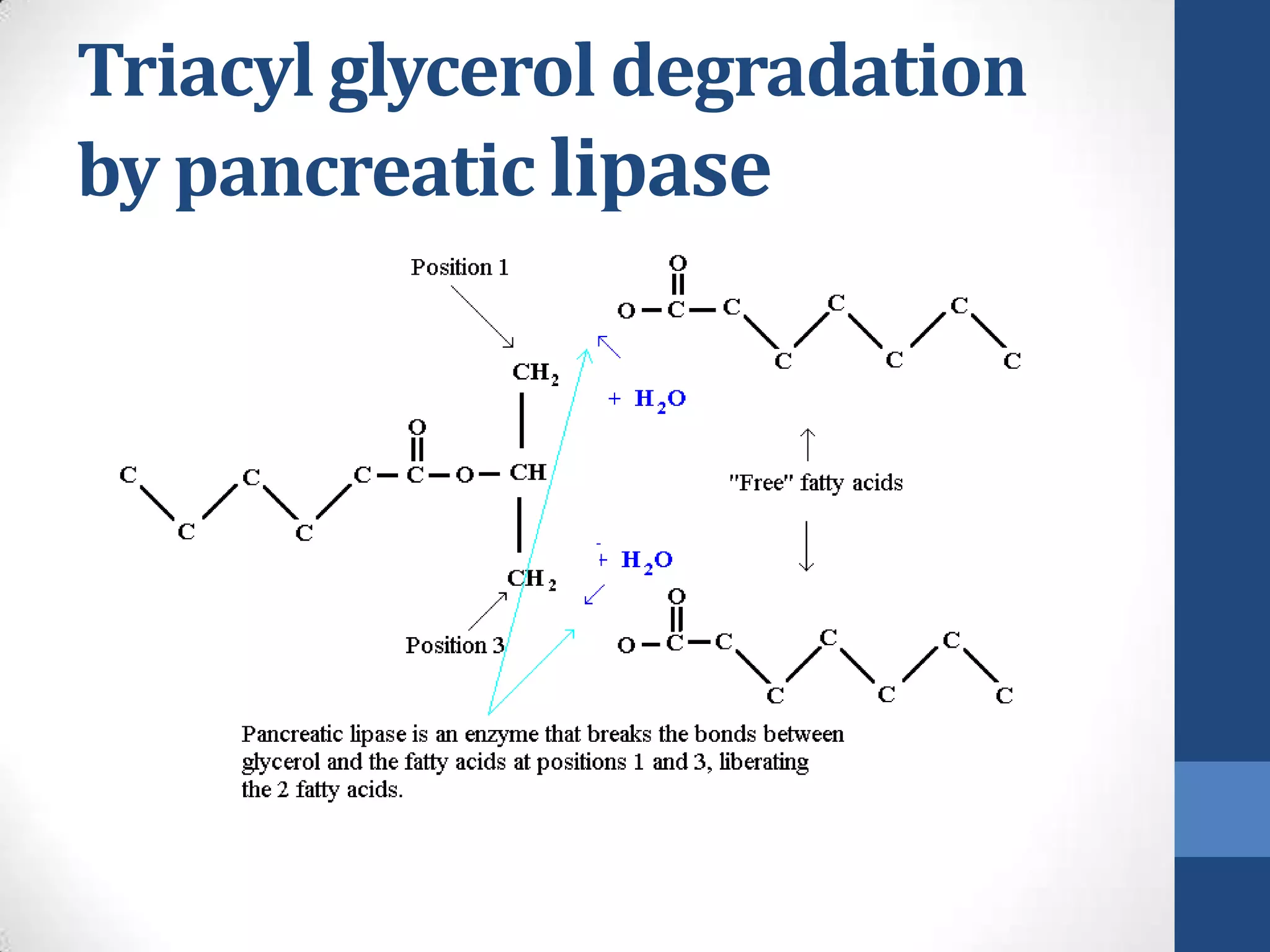
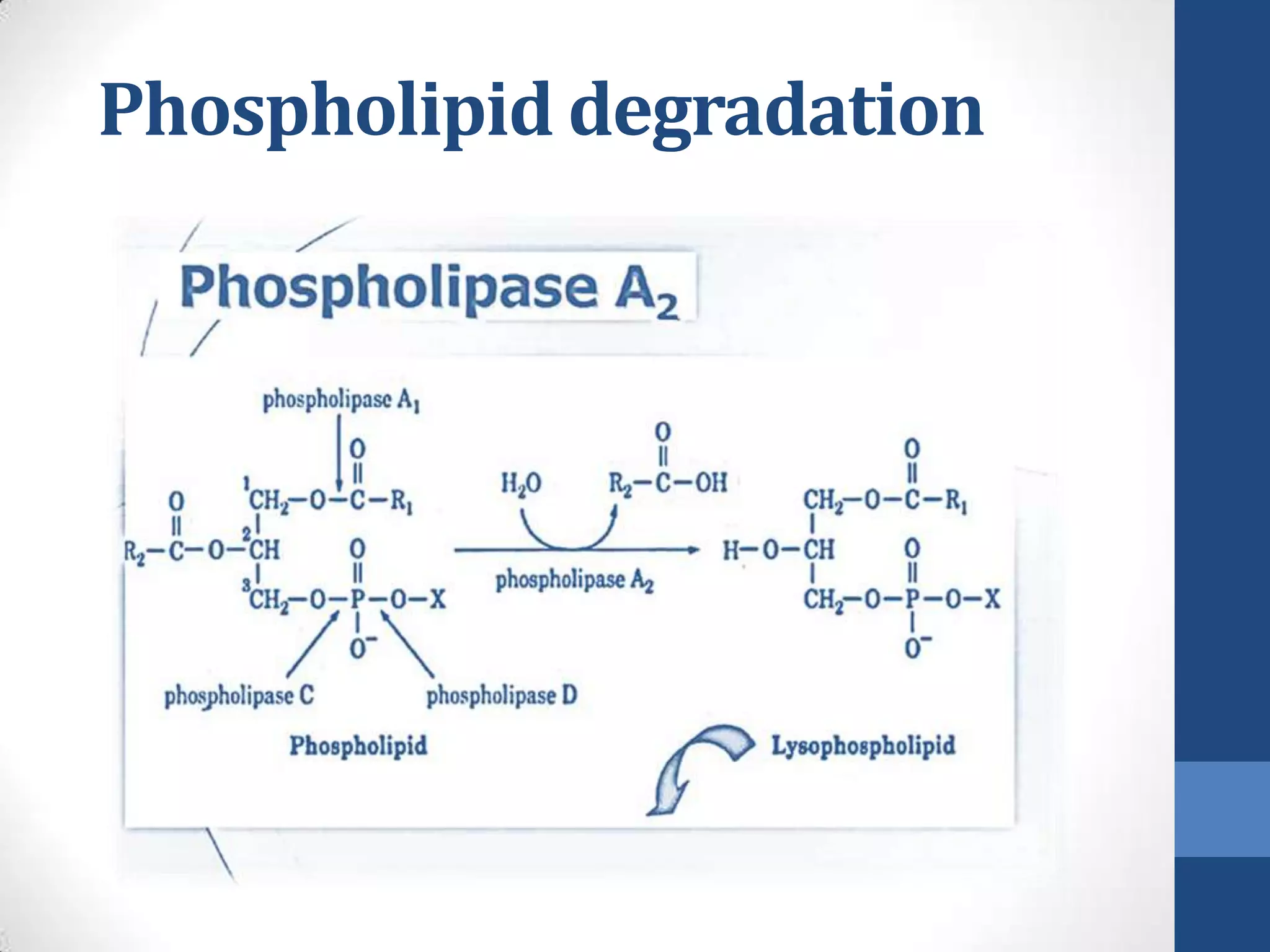
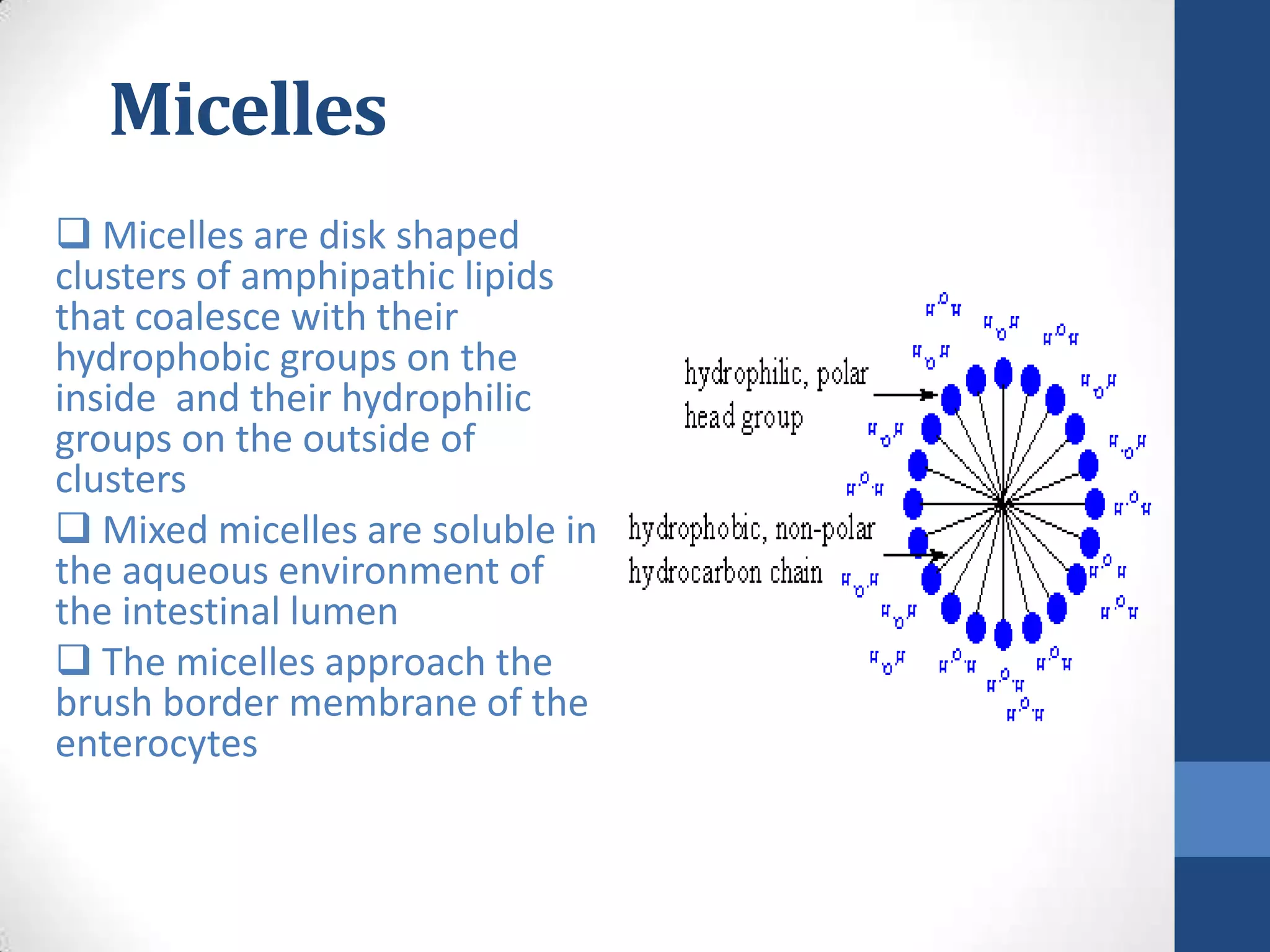
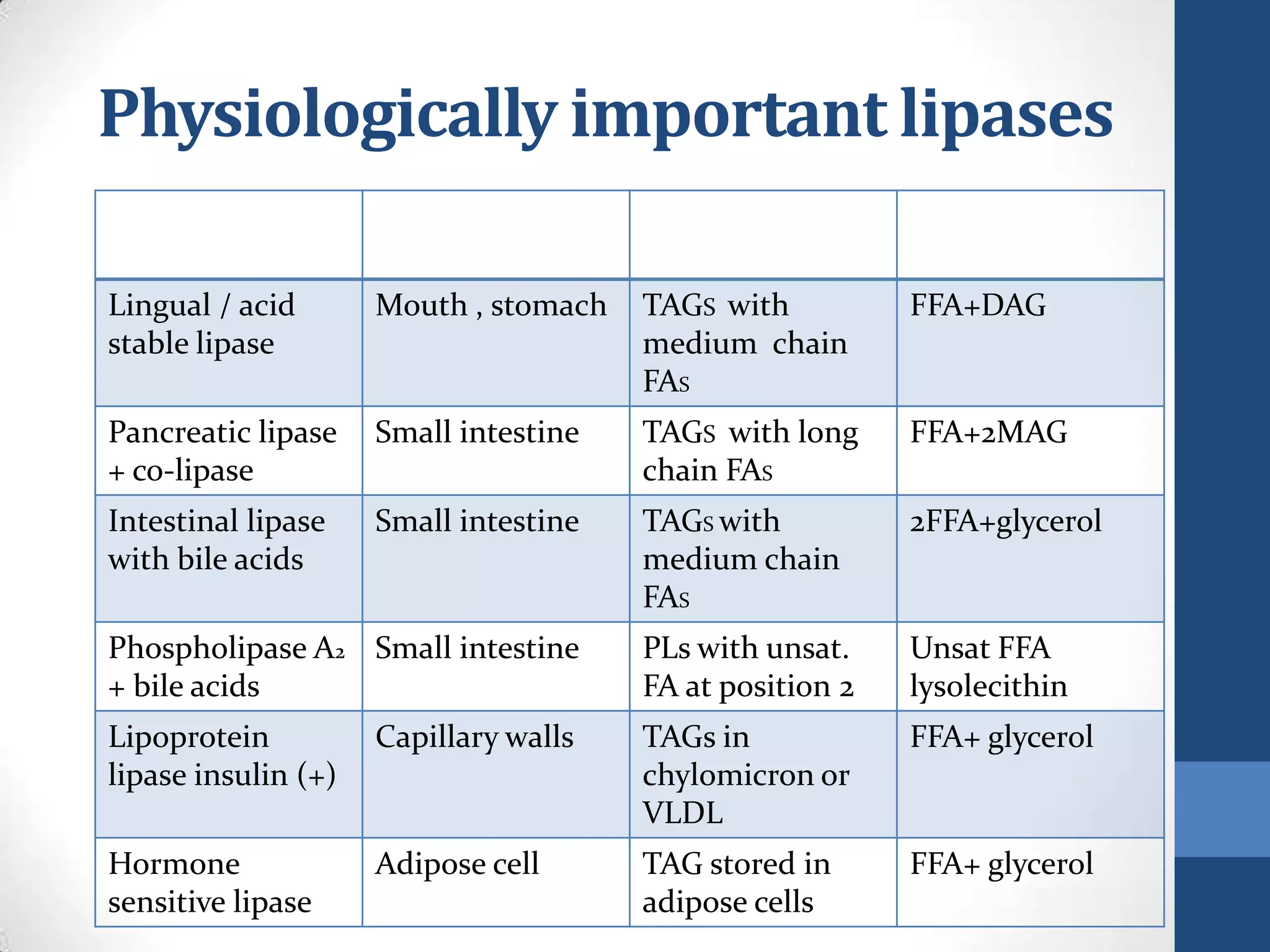
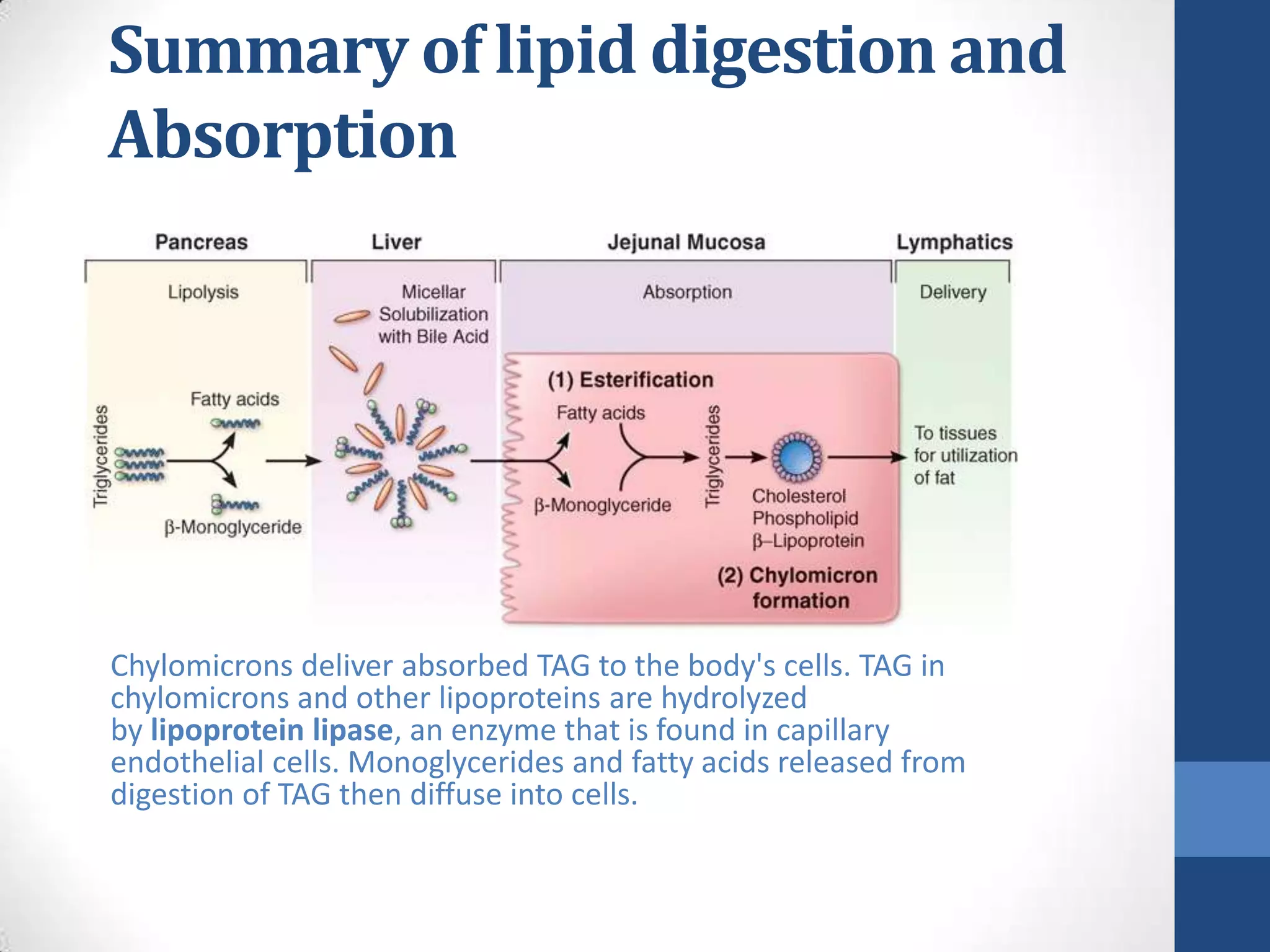
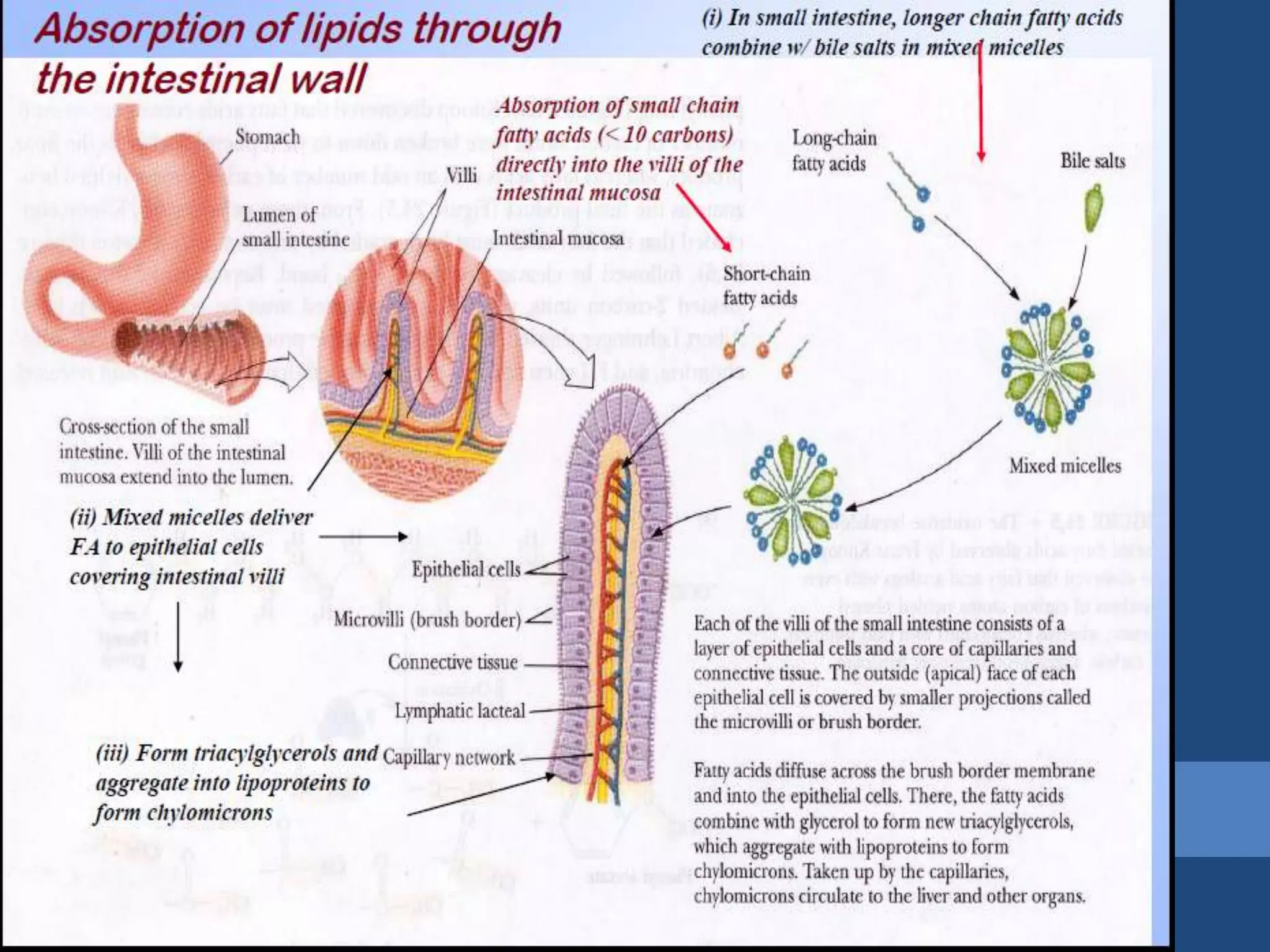
Lipids are digested and absorbed in a multi-step process involving enzymes in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. In the mouth, lingual lipase begins hydrolysis of triglycerides. In the stomach, gastric lipase continues this process. In the small intestine, pancreatic lipase works with bile salts to further digest triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides. Bile salts emulsify lipids and facilitate absorption. Fatty acids and monoglycerides are absorbed into intestinal cells and re-esterified into triglycerides. These triglycerides are packaged into chylomicrons and enter the lymphatic system for transport.