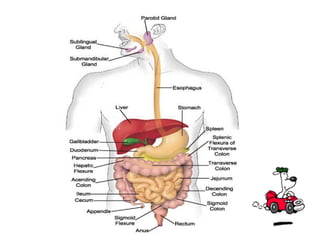
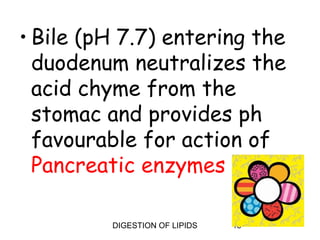
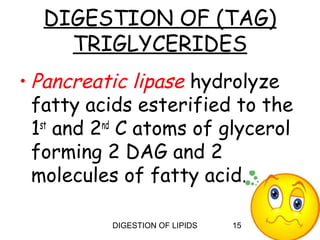
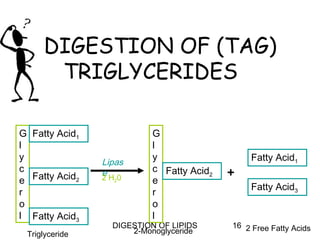
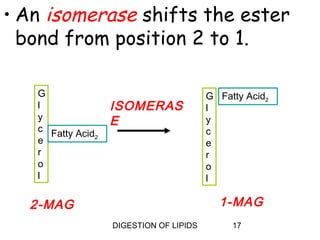
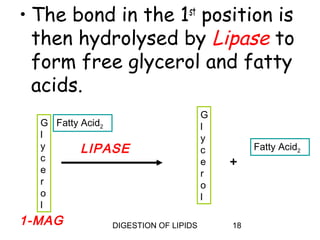
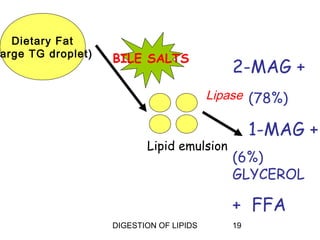
The document summarizes the digestion of lipids in the human body. It discusses that lipids provide energy and fat-soluble vitamins. The major dietary lipids are triglycerides, cholesterol, and phospholipids. Lipid digestion begins in the mouth through the action of lingual lipase, and continues in the stomach with gastric lipase. In the small intestine, lipids are emulsified by bile salts and the actions of pancreatic lipases further break down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoacylglycerols through a multi-step process. Digestion of lipids is only partial, with some triglycerides and cholesterol esters remaining undigested.