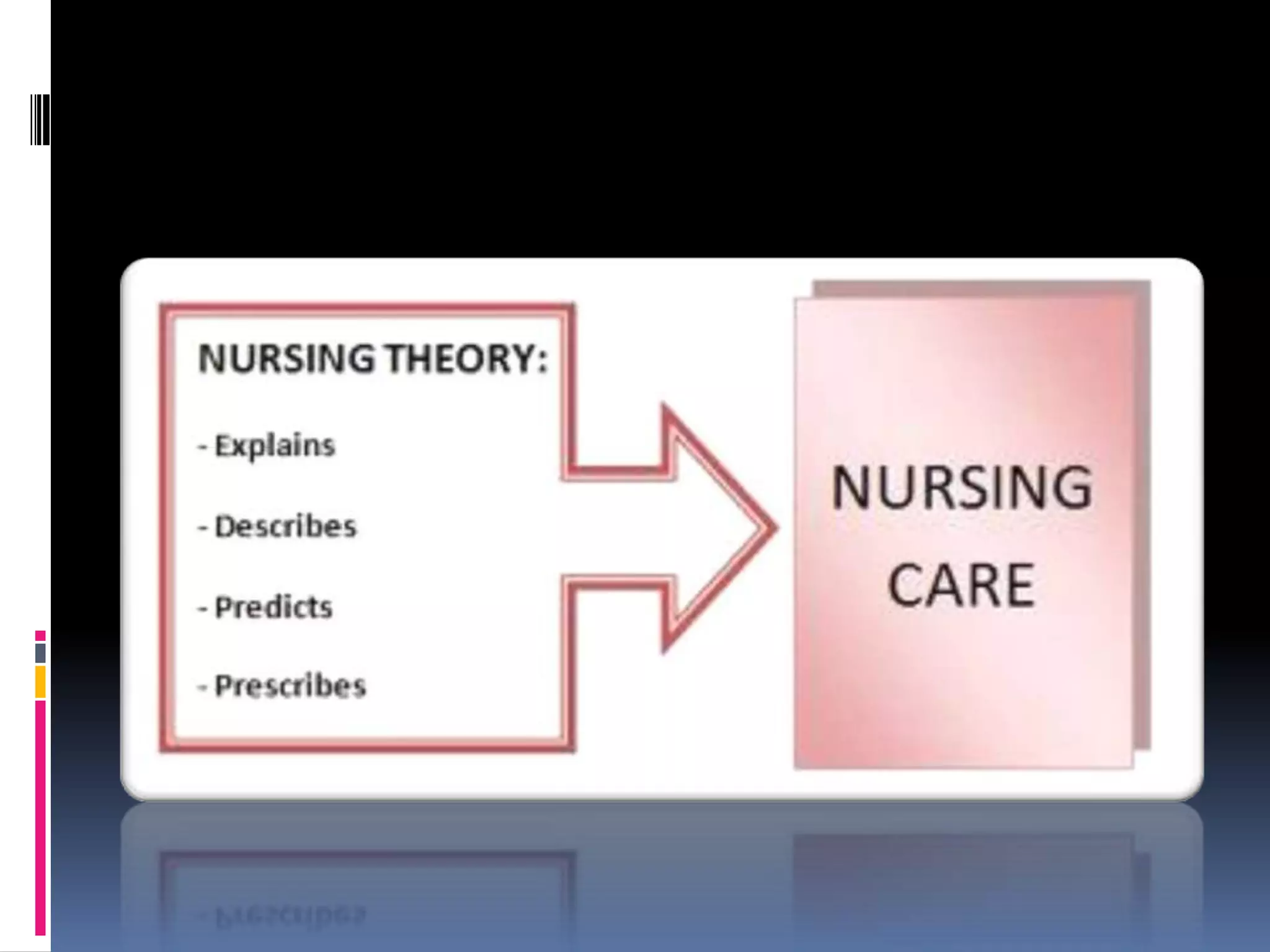
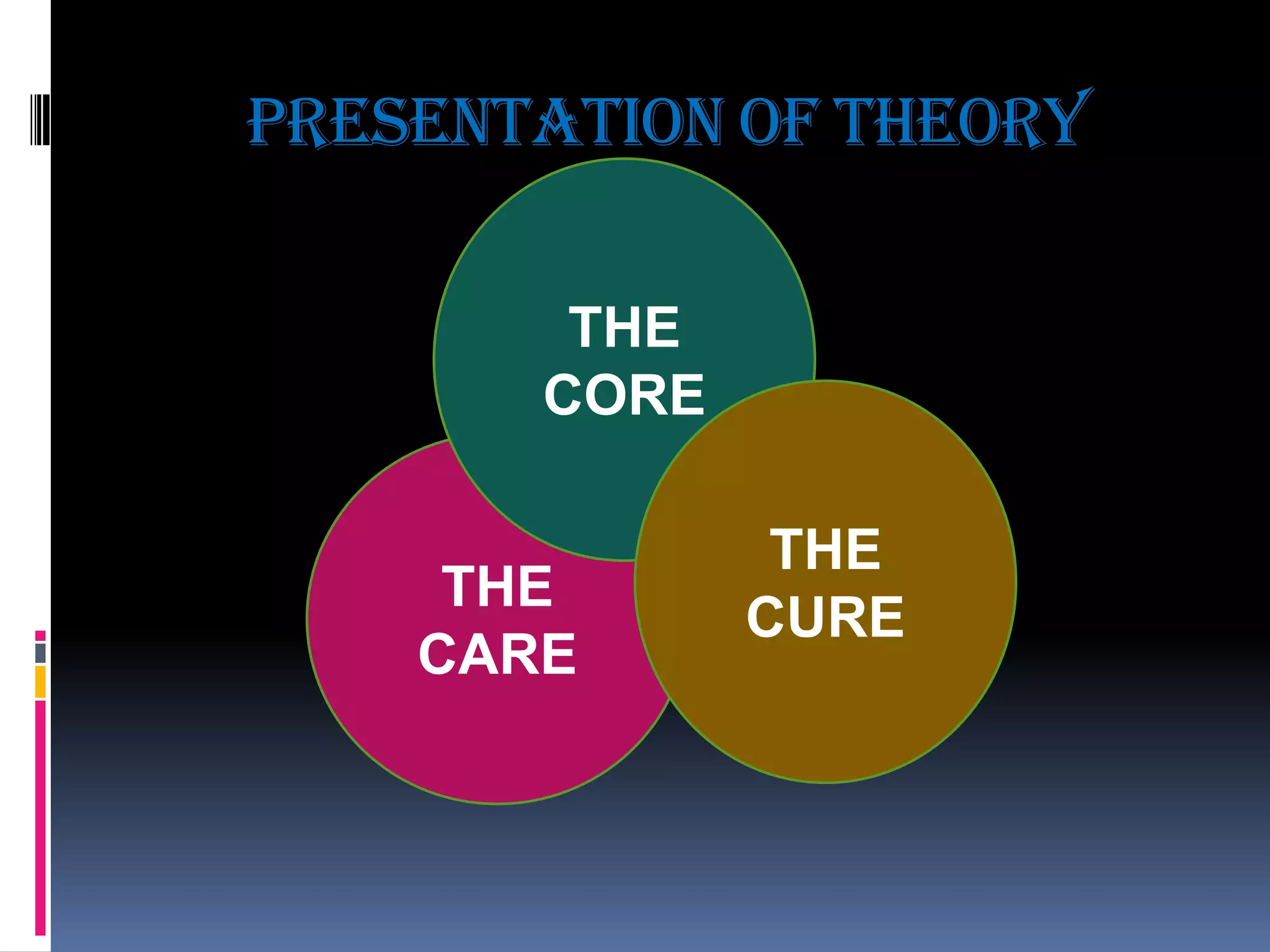
This document provides an overview of Lydia Hall's nursing theory. Hall's theory proposes that nursing care can be delivered on three interlocking levels: care, core, and cure. Care involves hands-on bodily care. Core focuses on using self in relationship to the patient. Cure applies medical knowledge to treat disease. Hall defines nursing as care performed by trained professionals to maintain health and quality of life from birth to death. The theory emphasizes how the three levels interact and change depending on patient needs. It relates to nursing paradigms like individual, health, and environment. The document also outlines Hall's background, limitations of the theory, and examples of its applications.