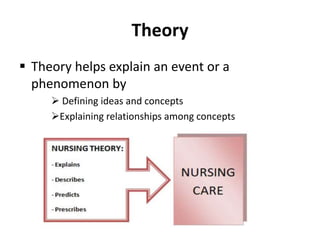
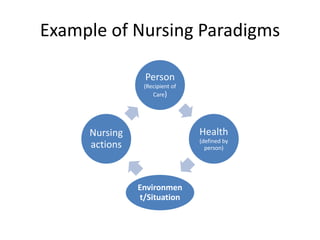
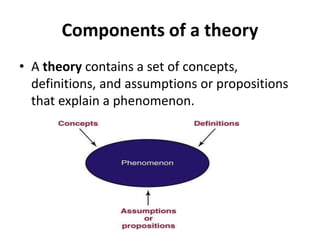
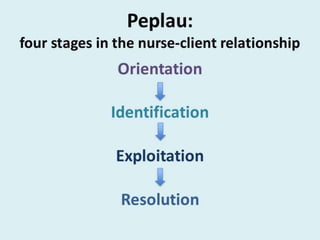
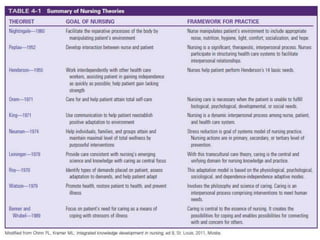
The document discusses the theoretical foundations of nursing practice, emphasizing the importance of nursing theory in defining, explaining, and predicting nursing care. It outlines various types of nursing theories, including grand, middle-range, descriptive, and prescriptive theories, while also presenting selected nursing theories by notable figures like Florence Nightingale and Hildegard Peplau. Additionally, the definition of health as proposed by the World Health Organization and the health belief model are introduced to illustrate the relationship between beliefs and health behaviors.