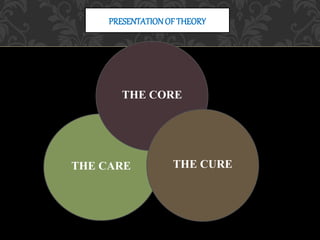
Lydia Hall developed a nursing theory that conceptualized nursing care into three overlapping circles: care, core, and cure. The care circle focuses on nurturing and comforting patients. The core circle emphasizes meeting patients' social, emotional, and intellectual needs to help them understand themselves and solve problems. The cure circle involves applying medical knowledge and cooperating with doctors and families on patients' medical, surgical, and rehabilitative needs. Hall believed all three aspects interact and change based on patients' individual, health, environmental, and nursing needs, with the overall emphasis being on caring for the whole person. The theory focused heavily on the care and core roles of nurses with limited discussion of other nursing roles.