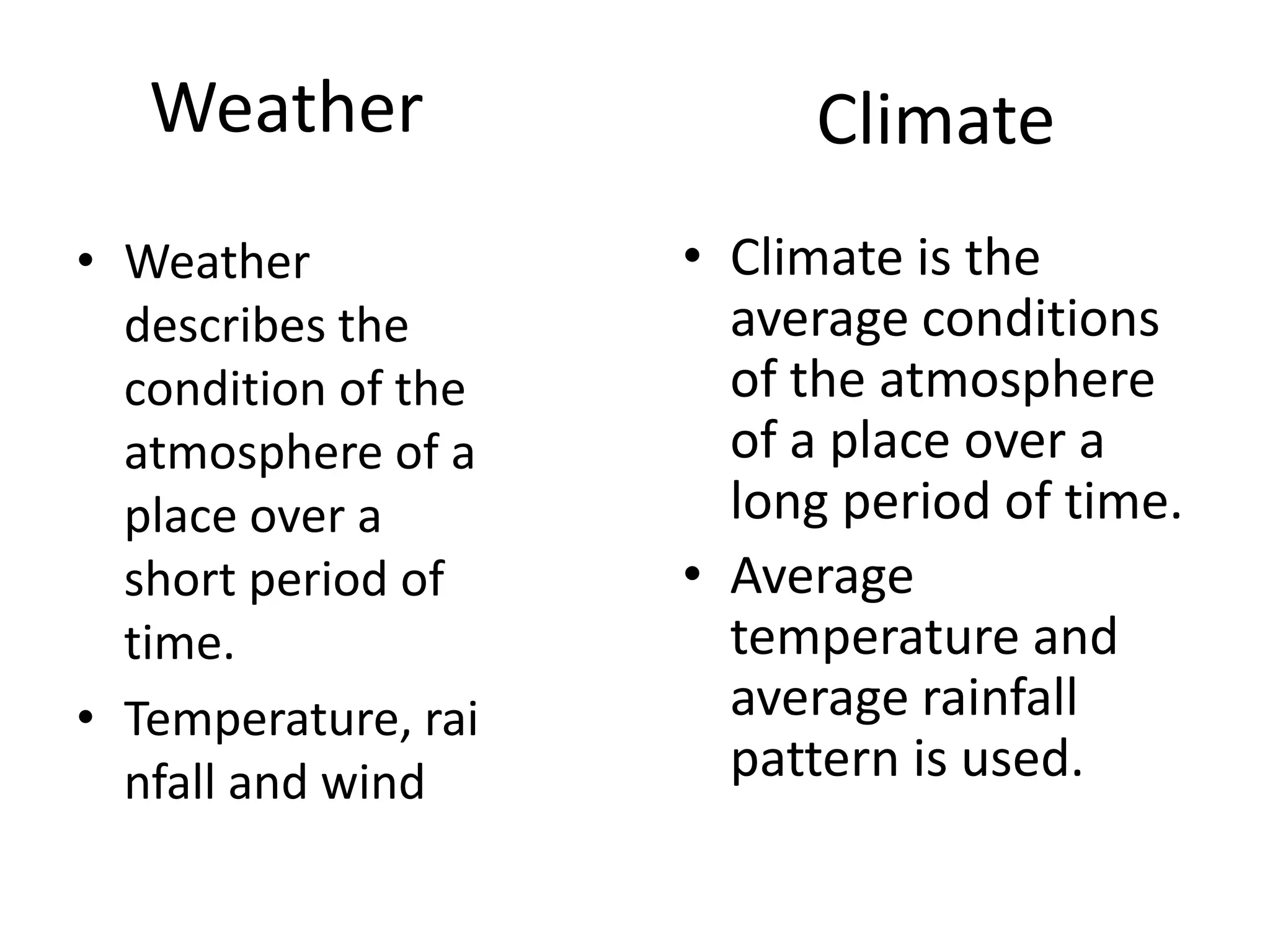
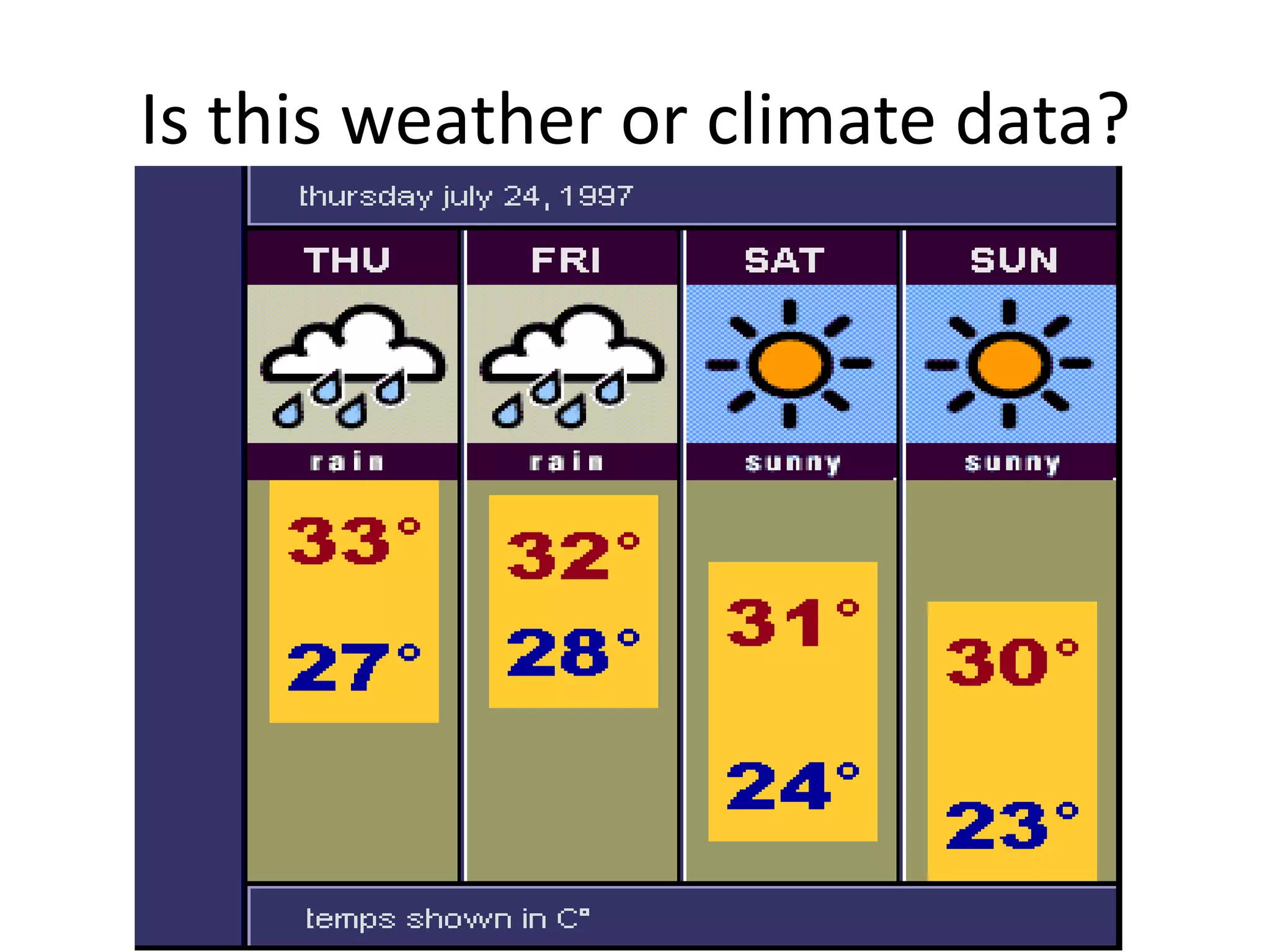
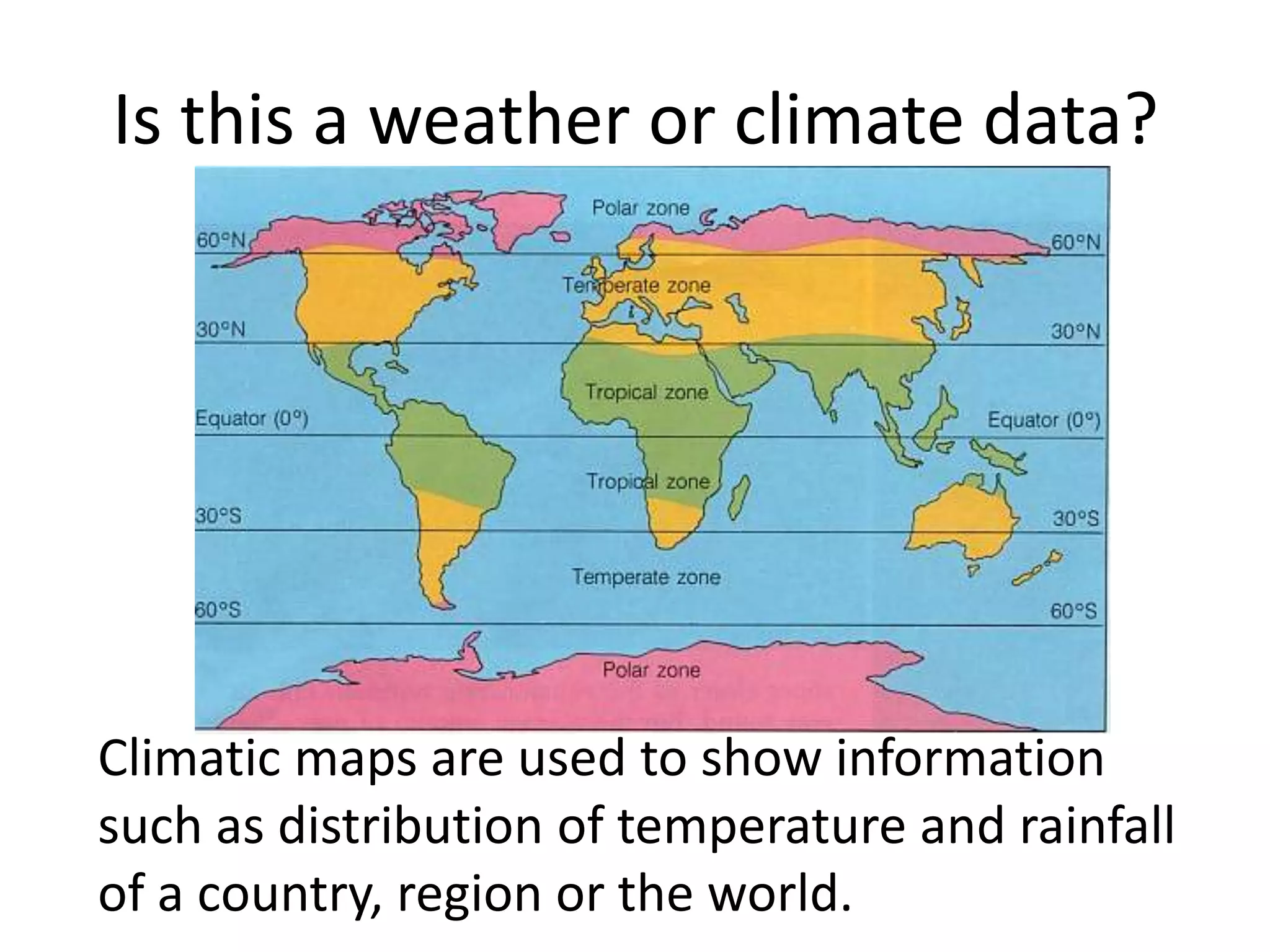
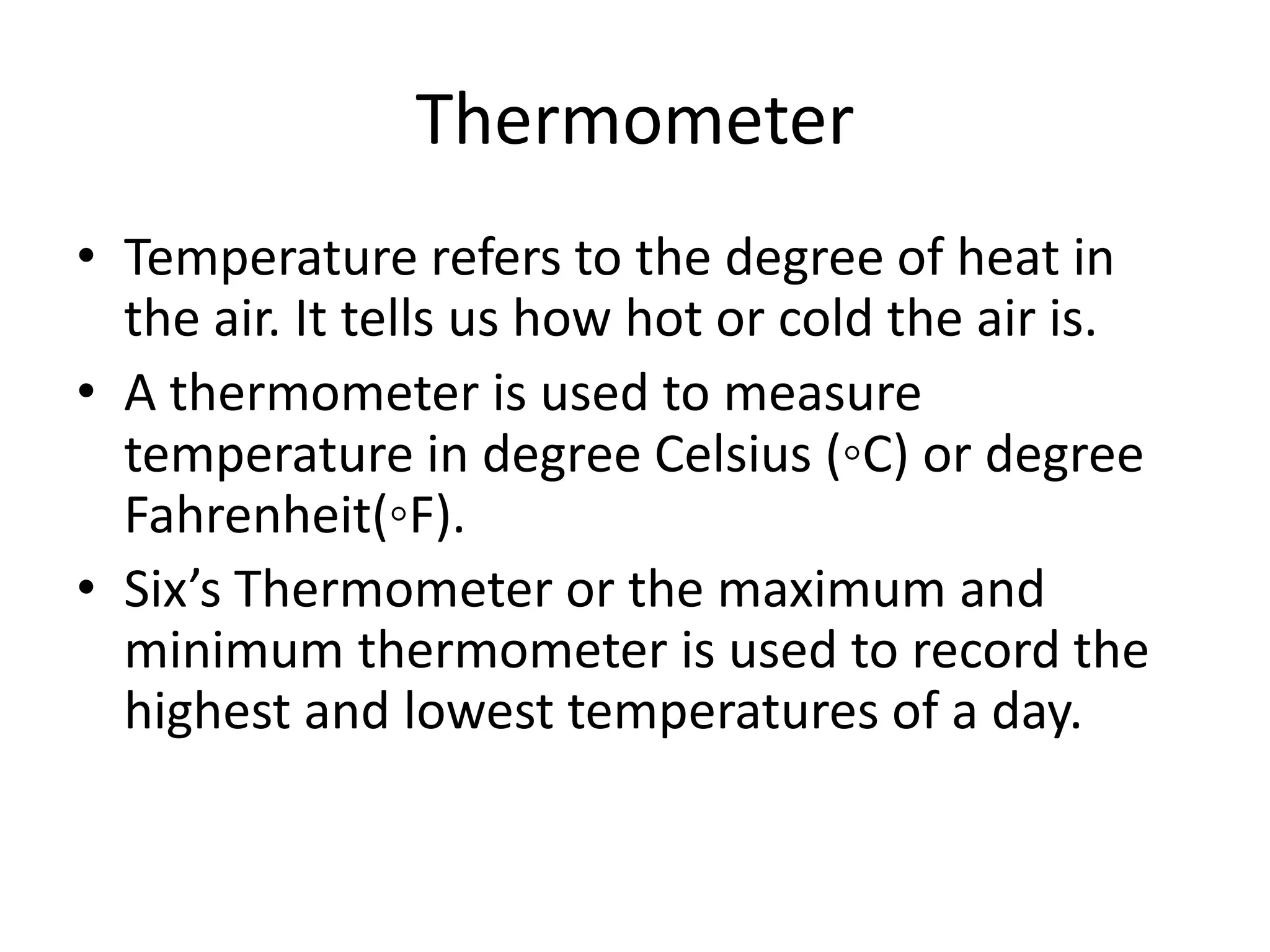
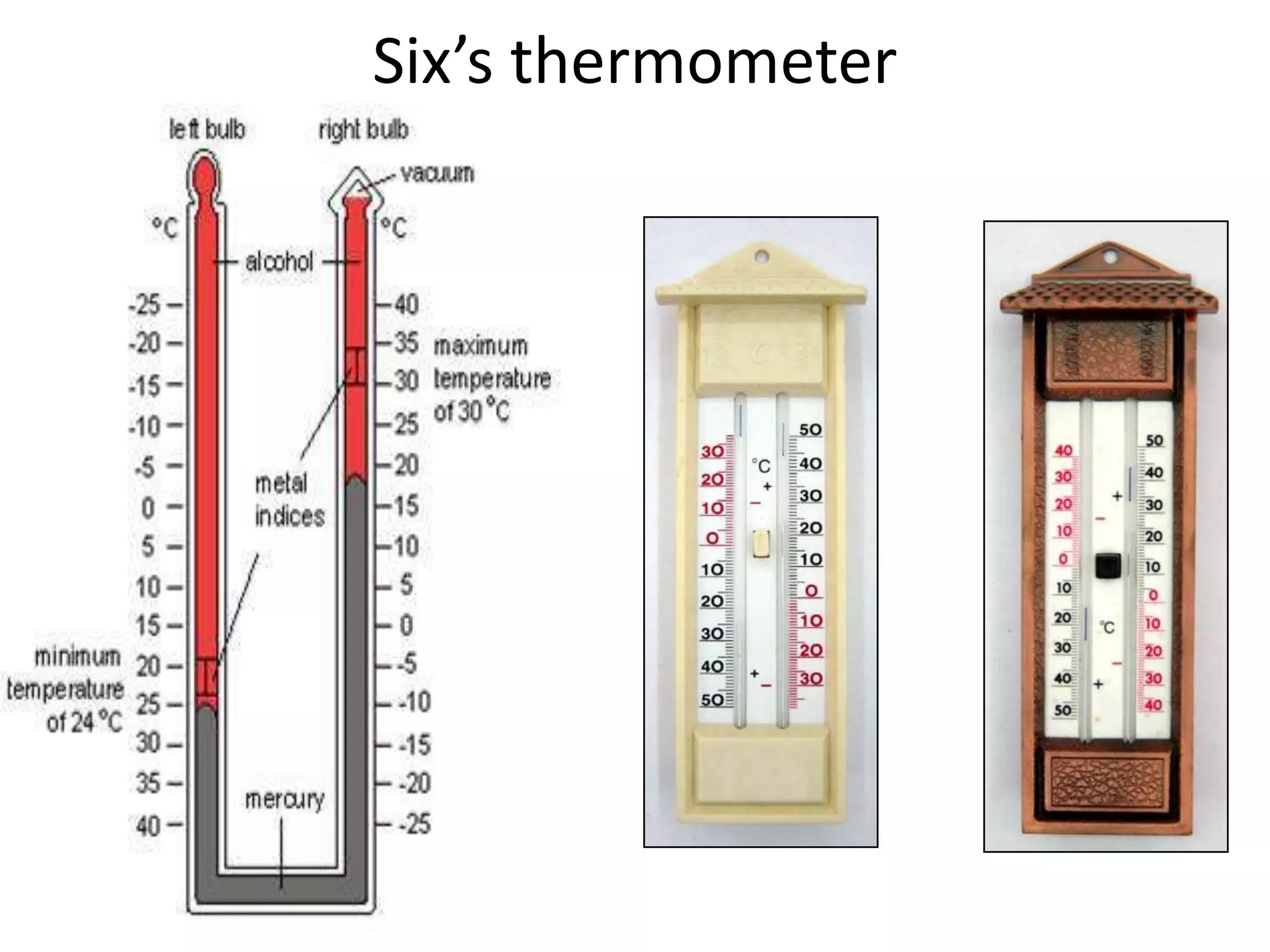
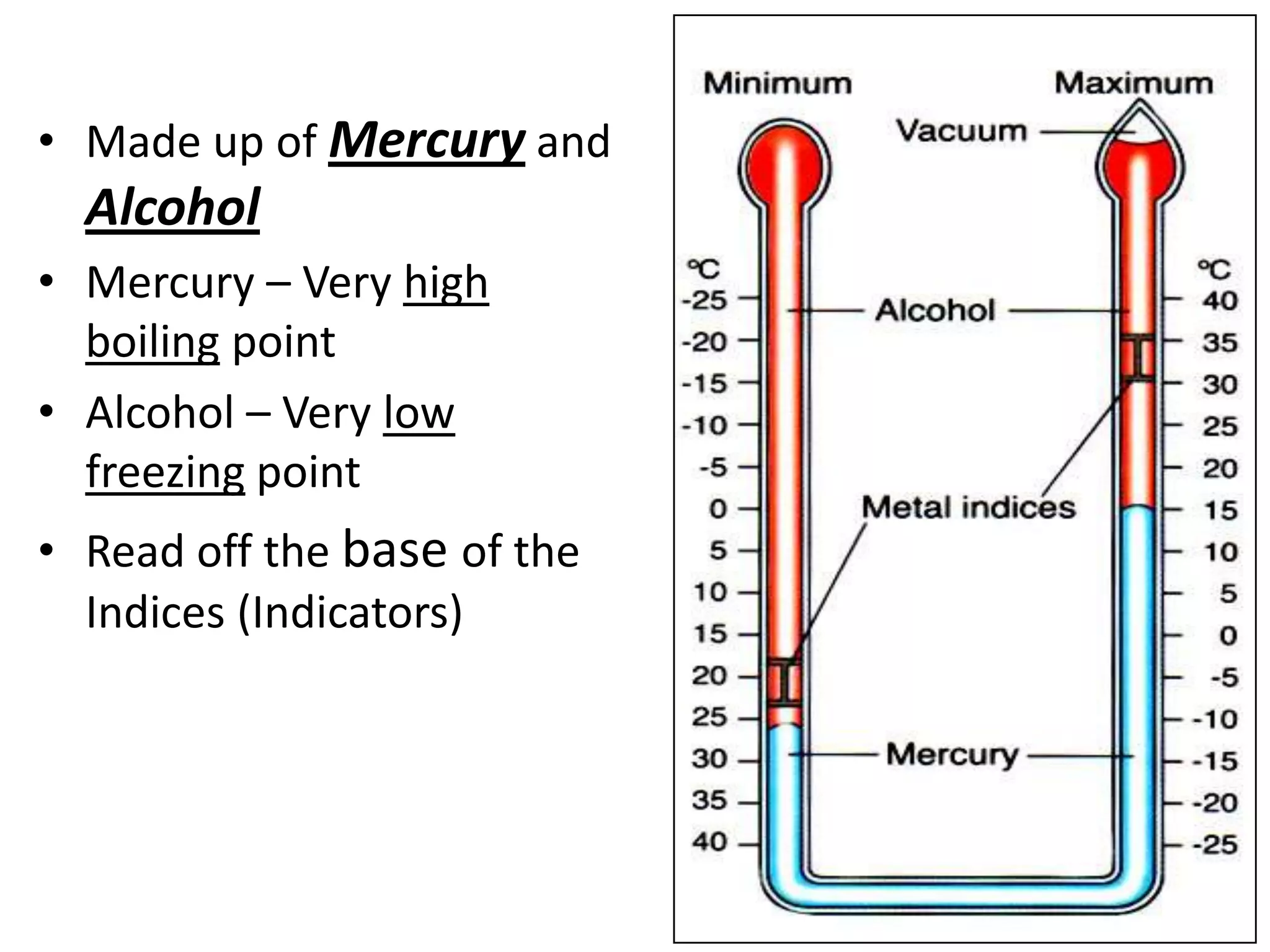
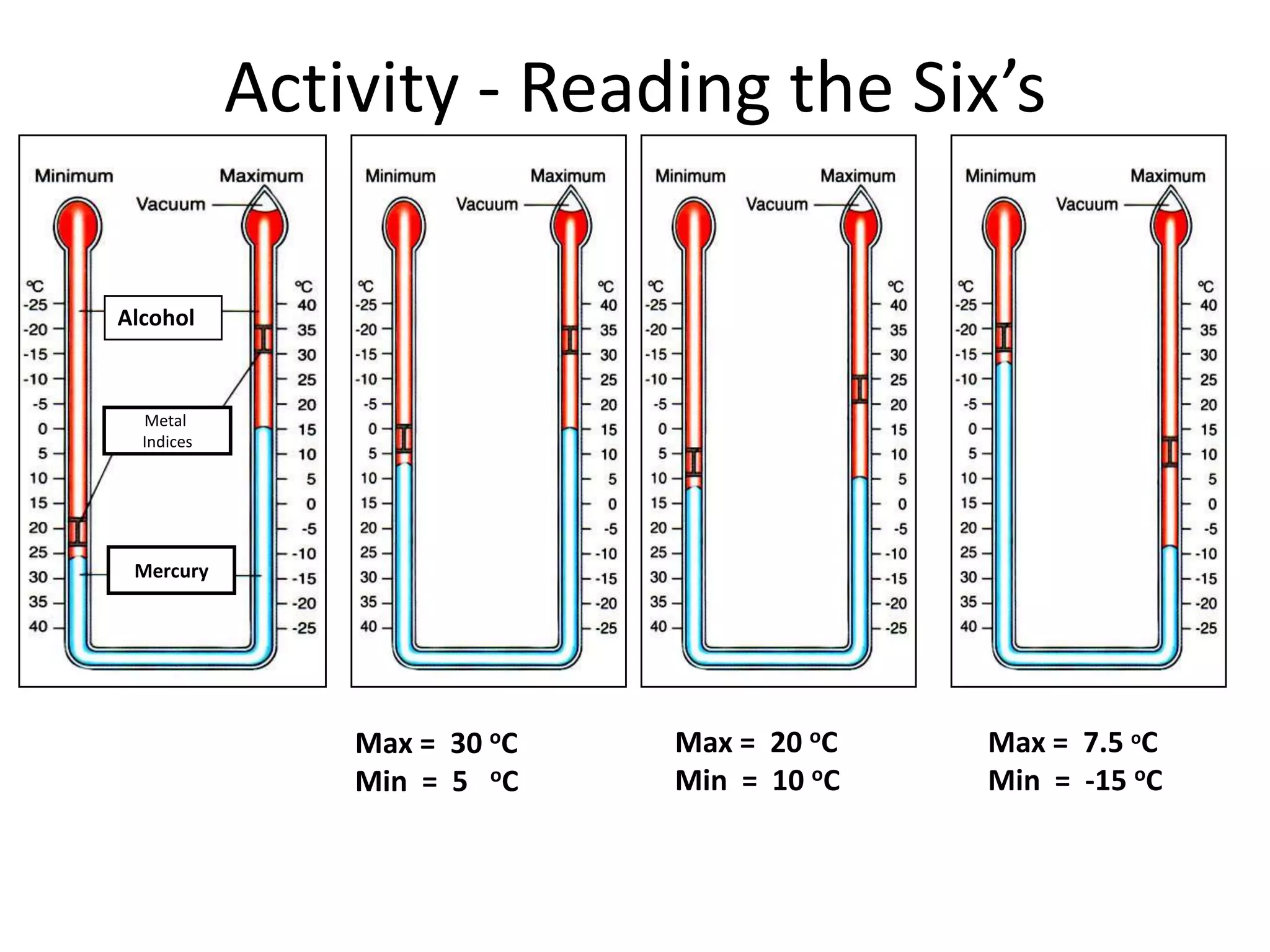
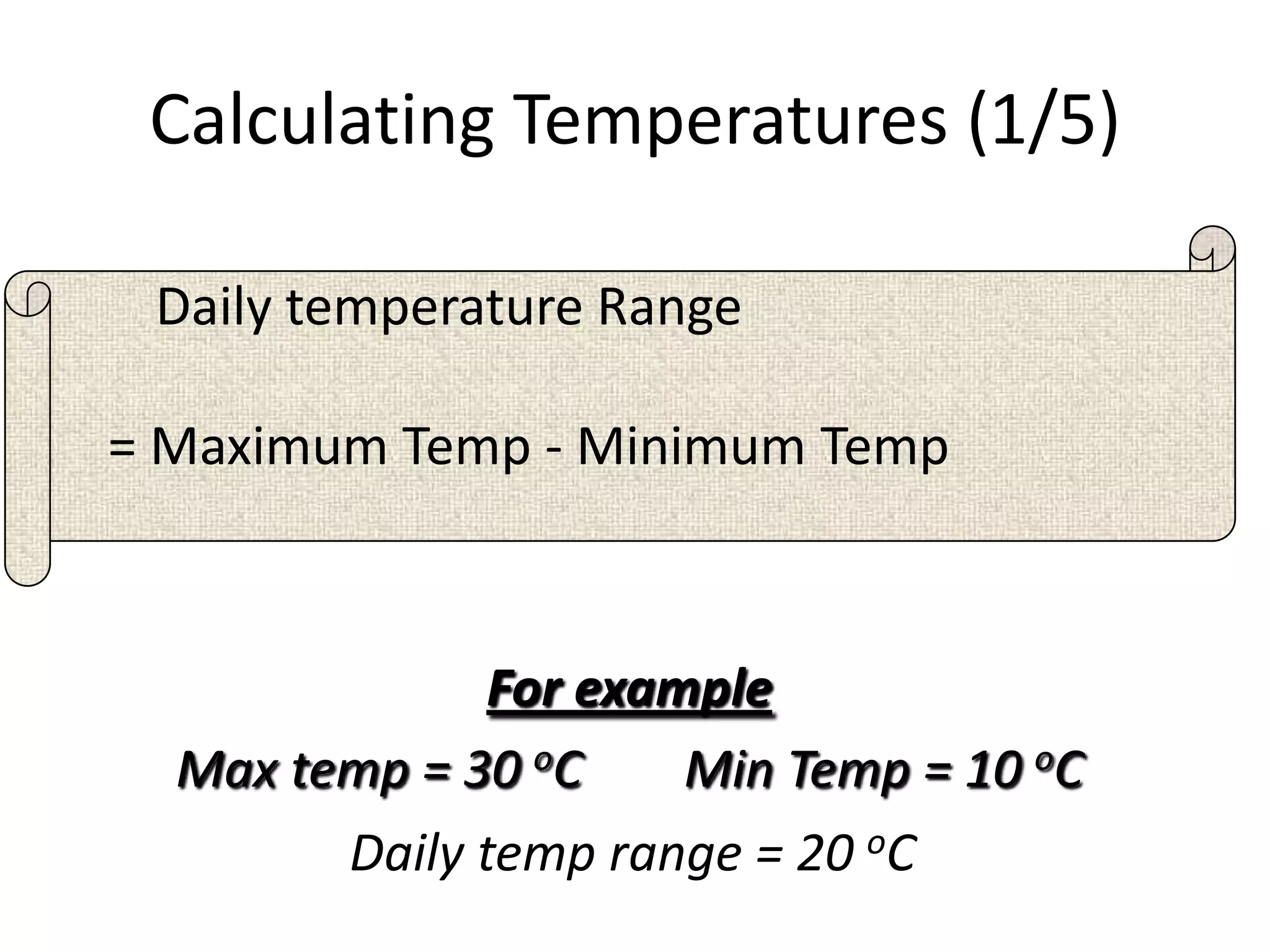
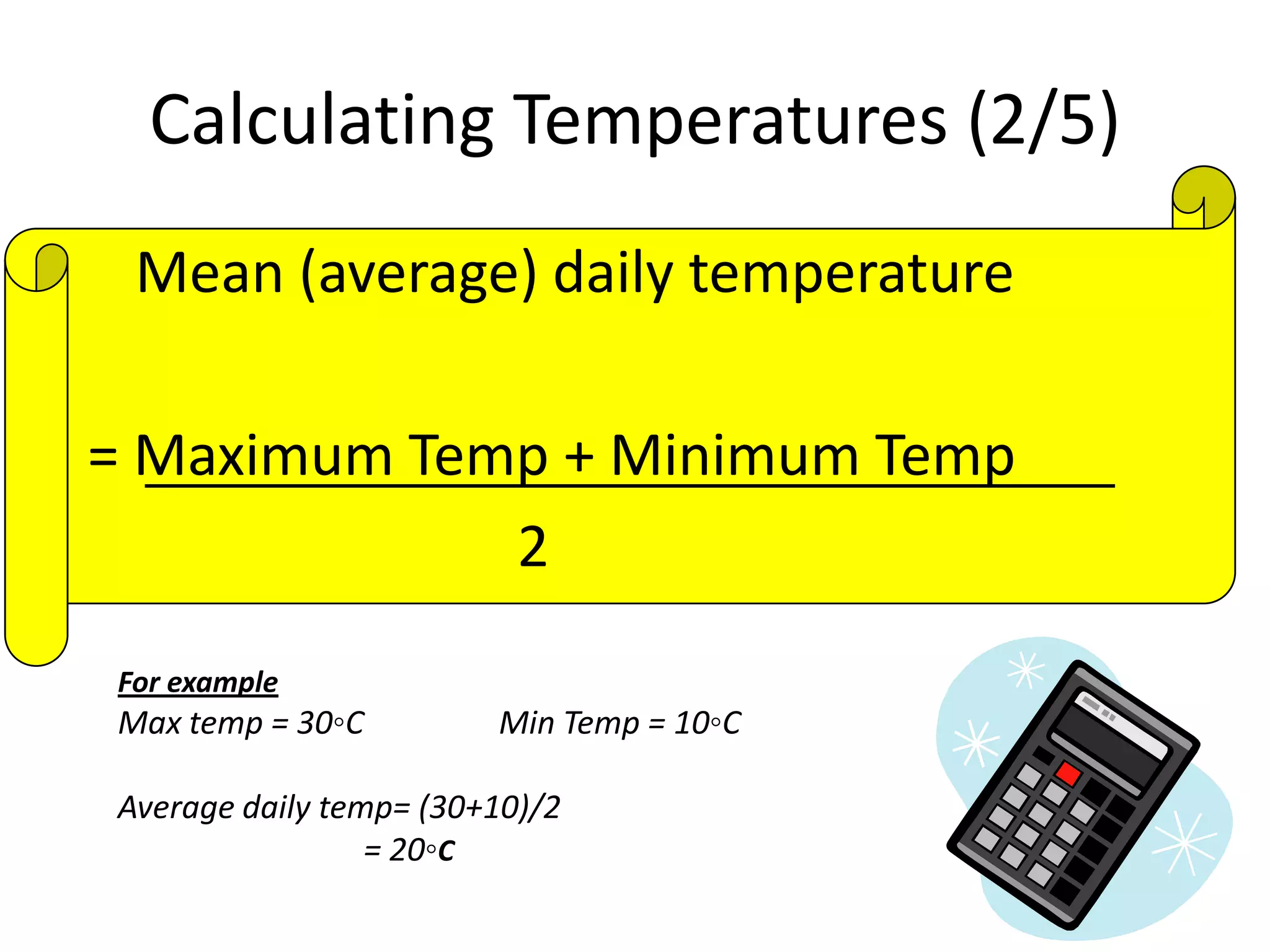
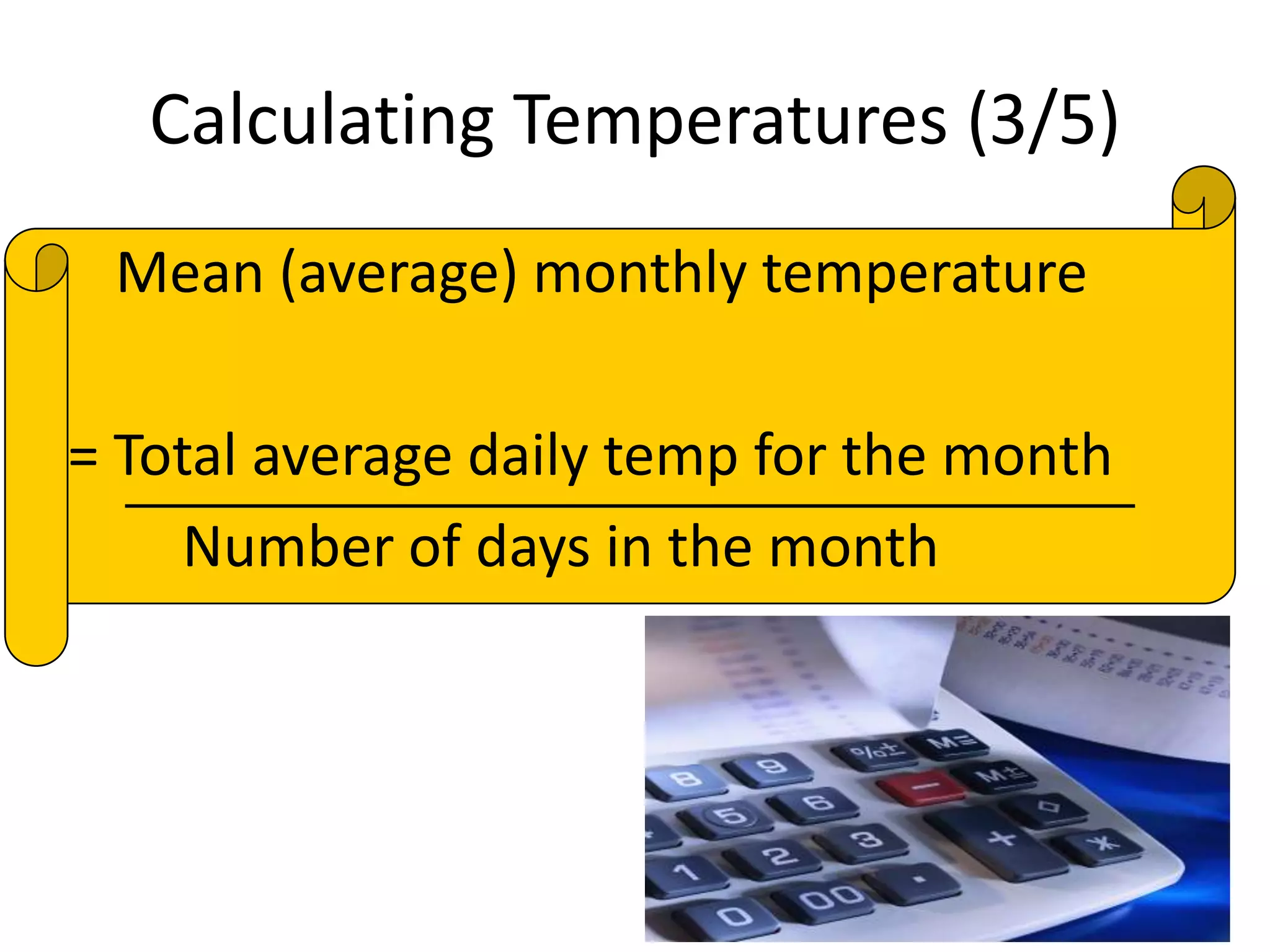
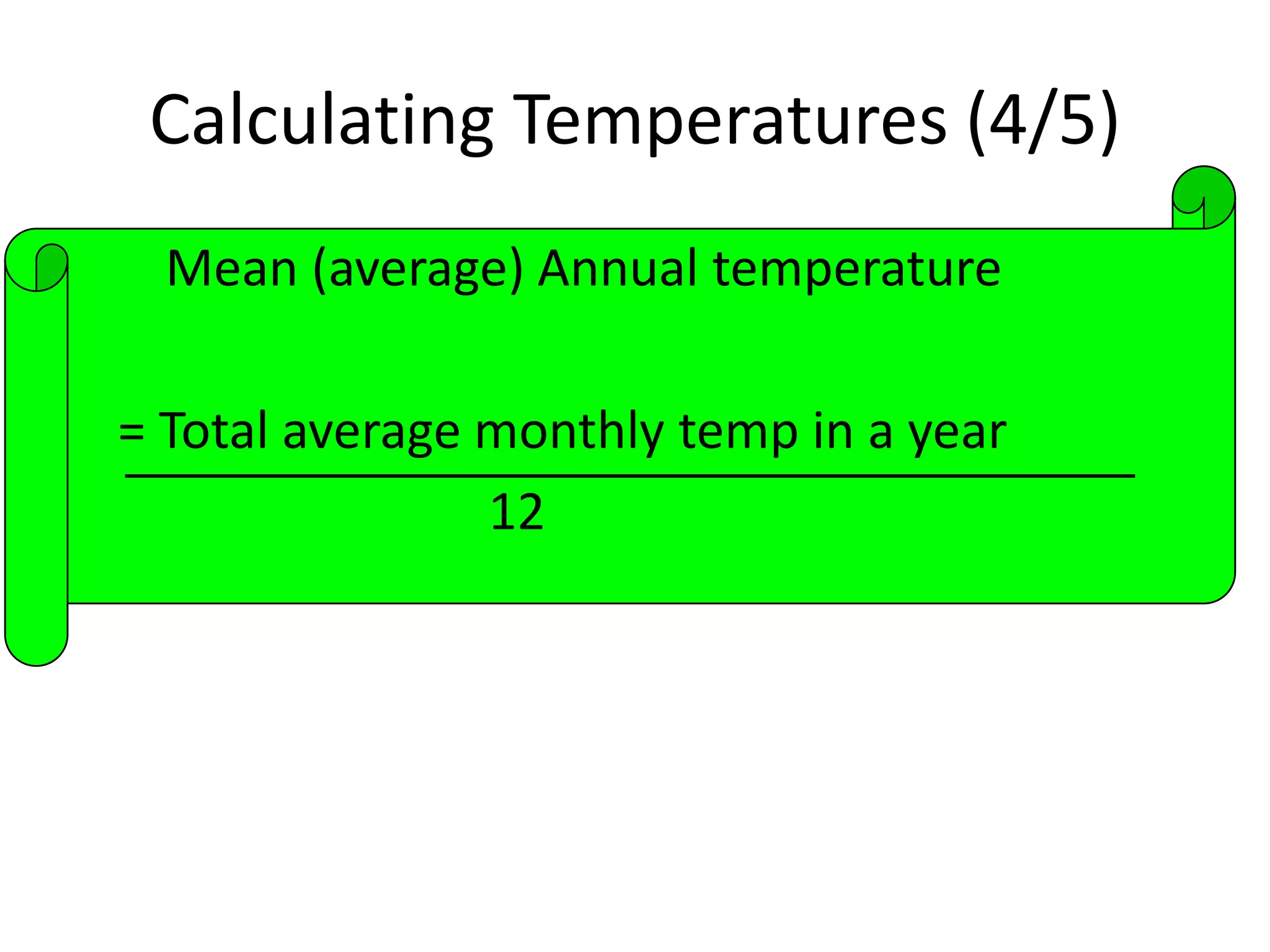
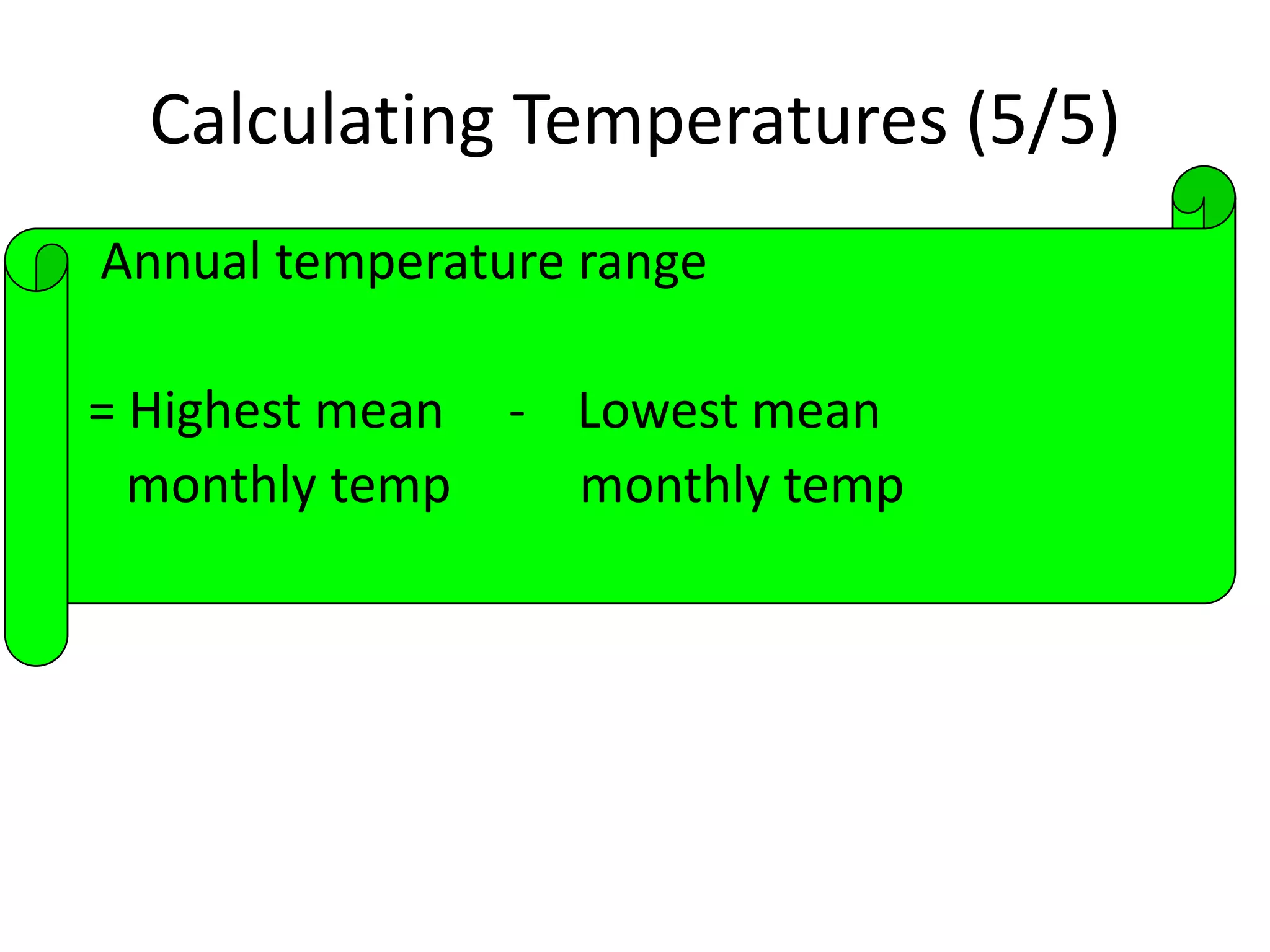
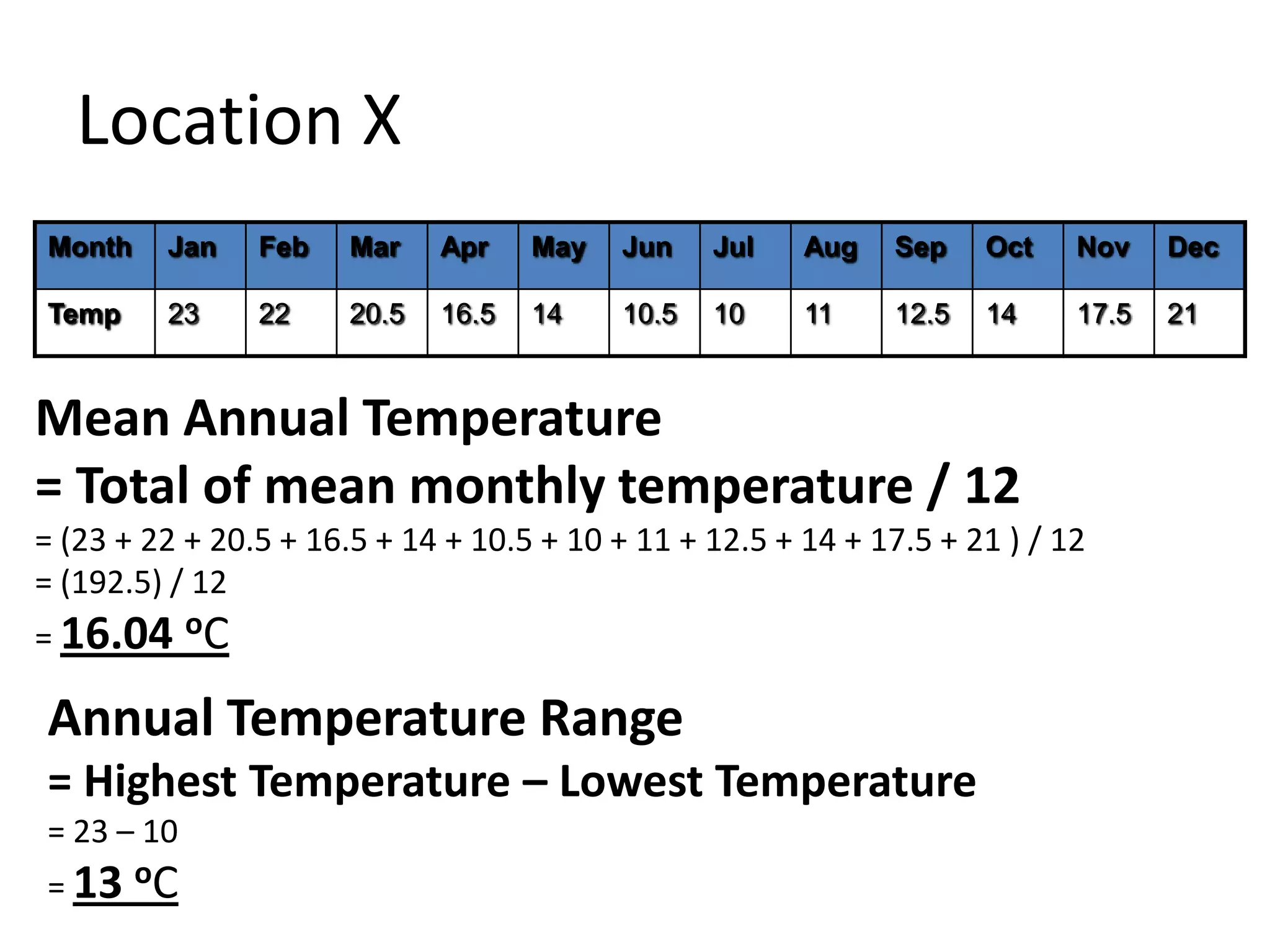
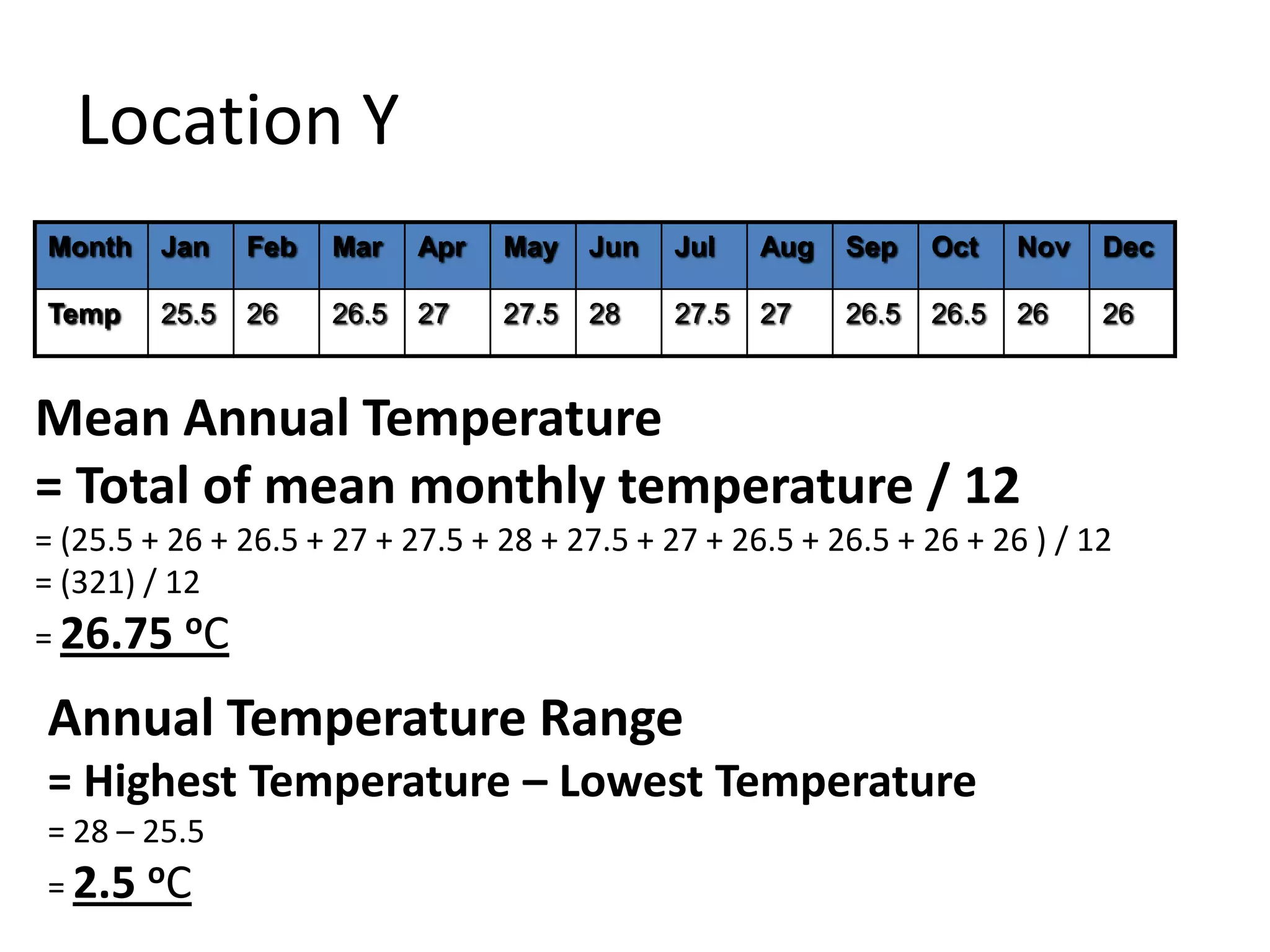
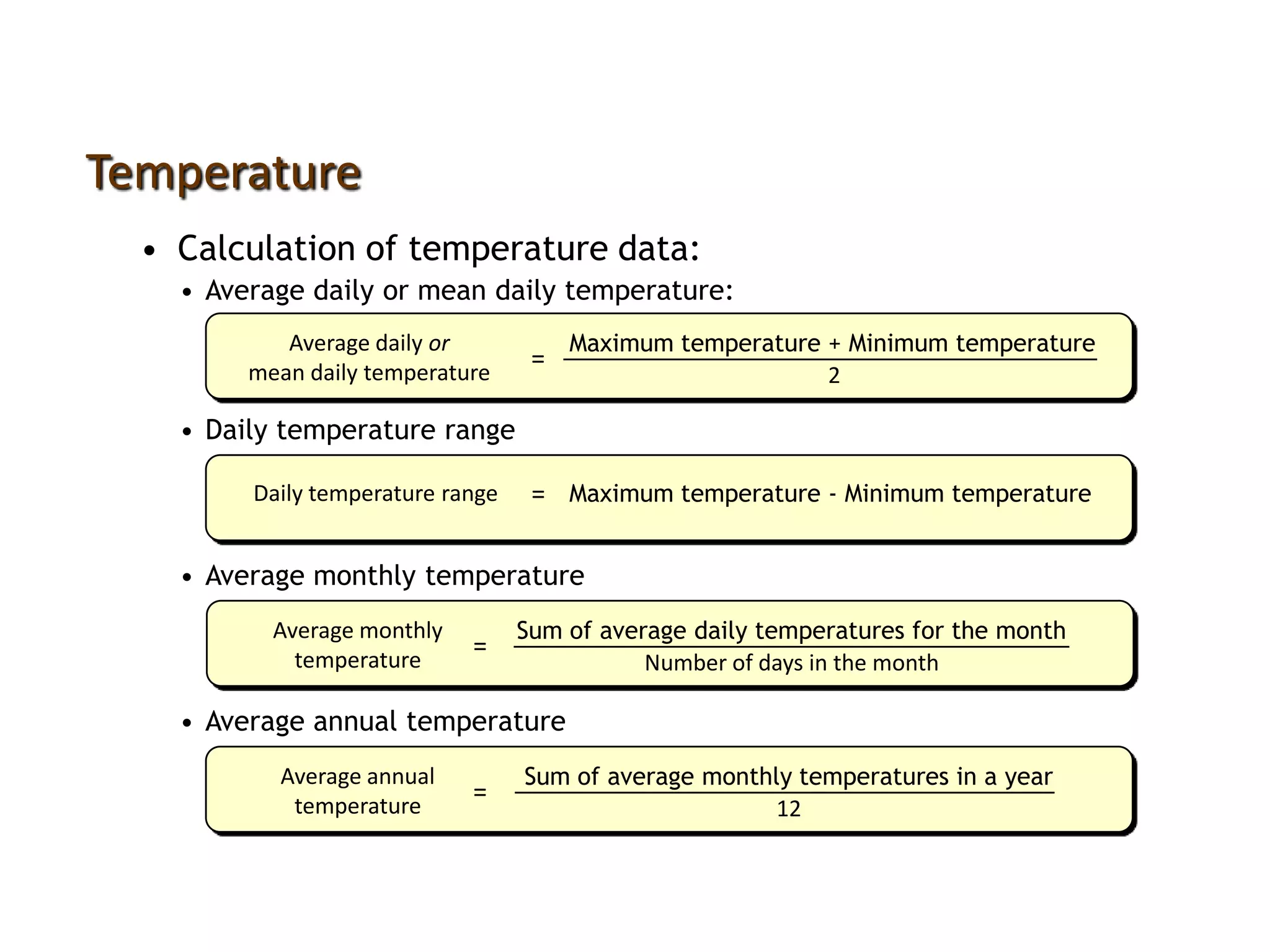
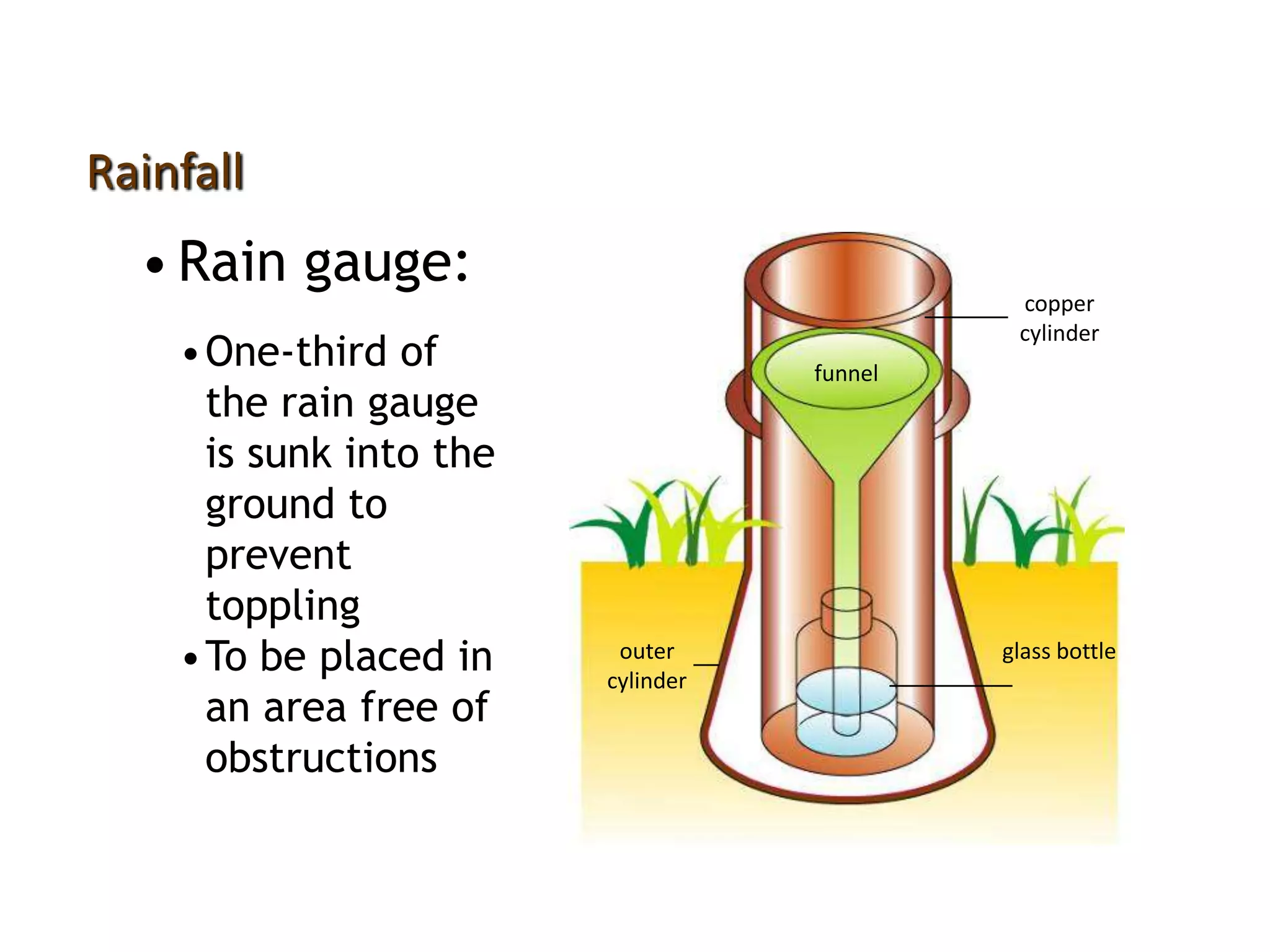
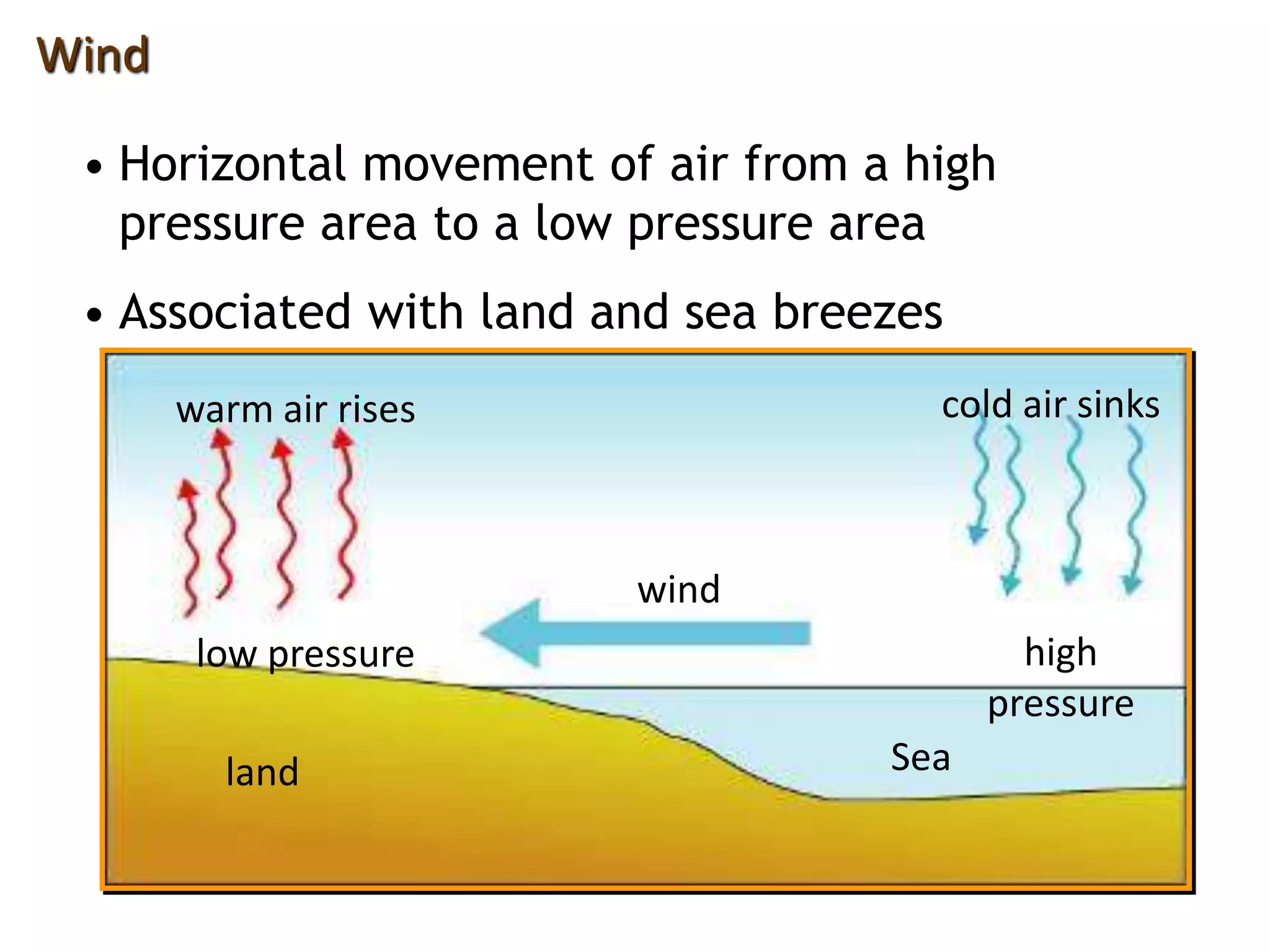
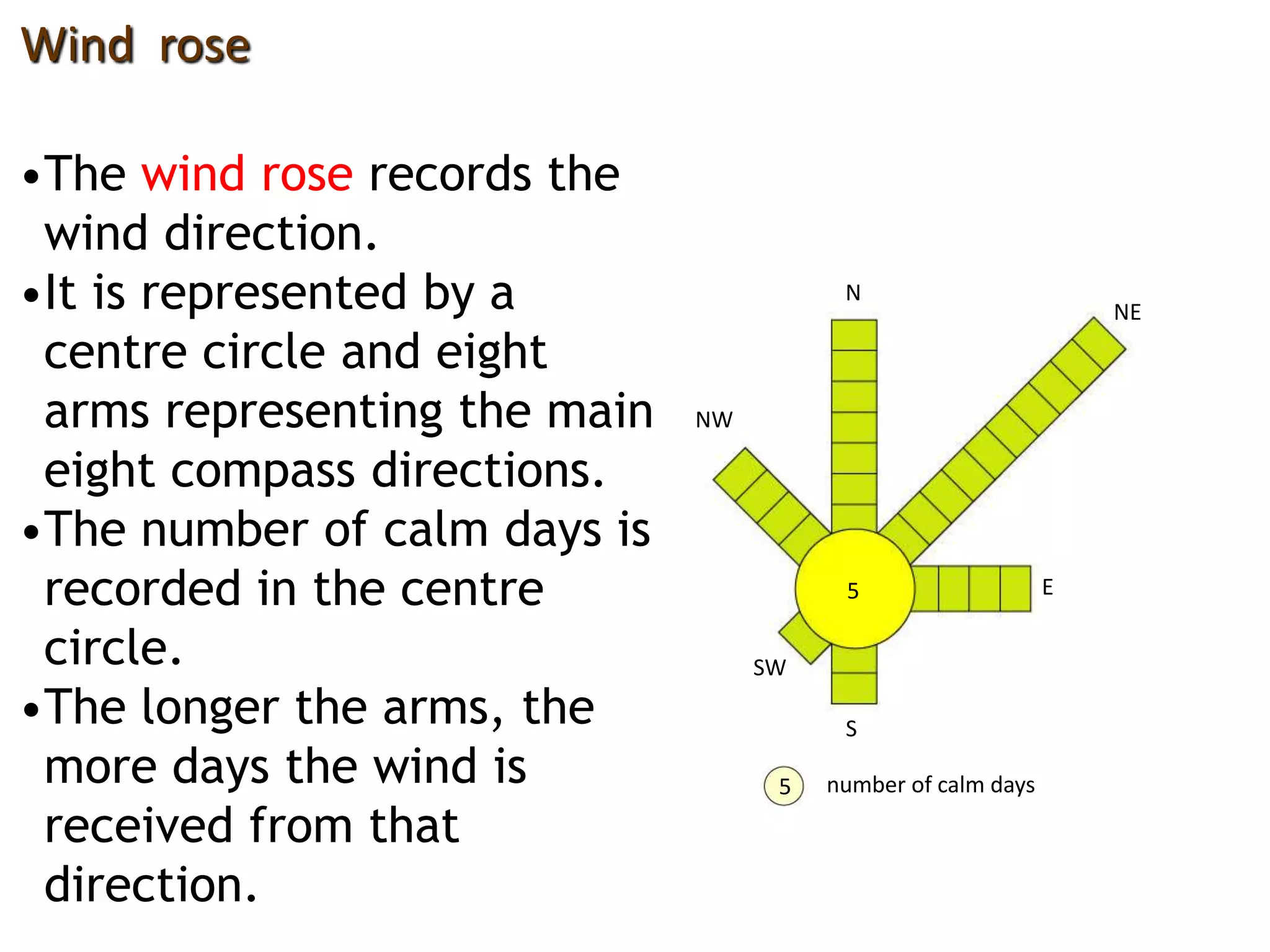
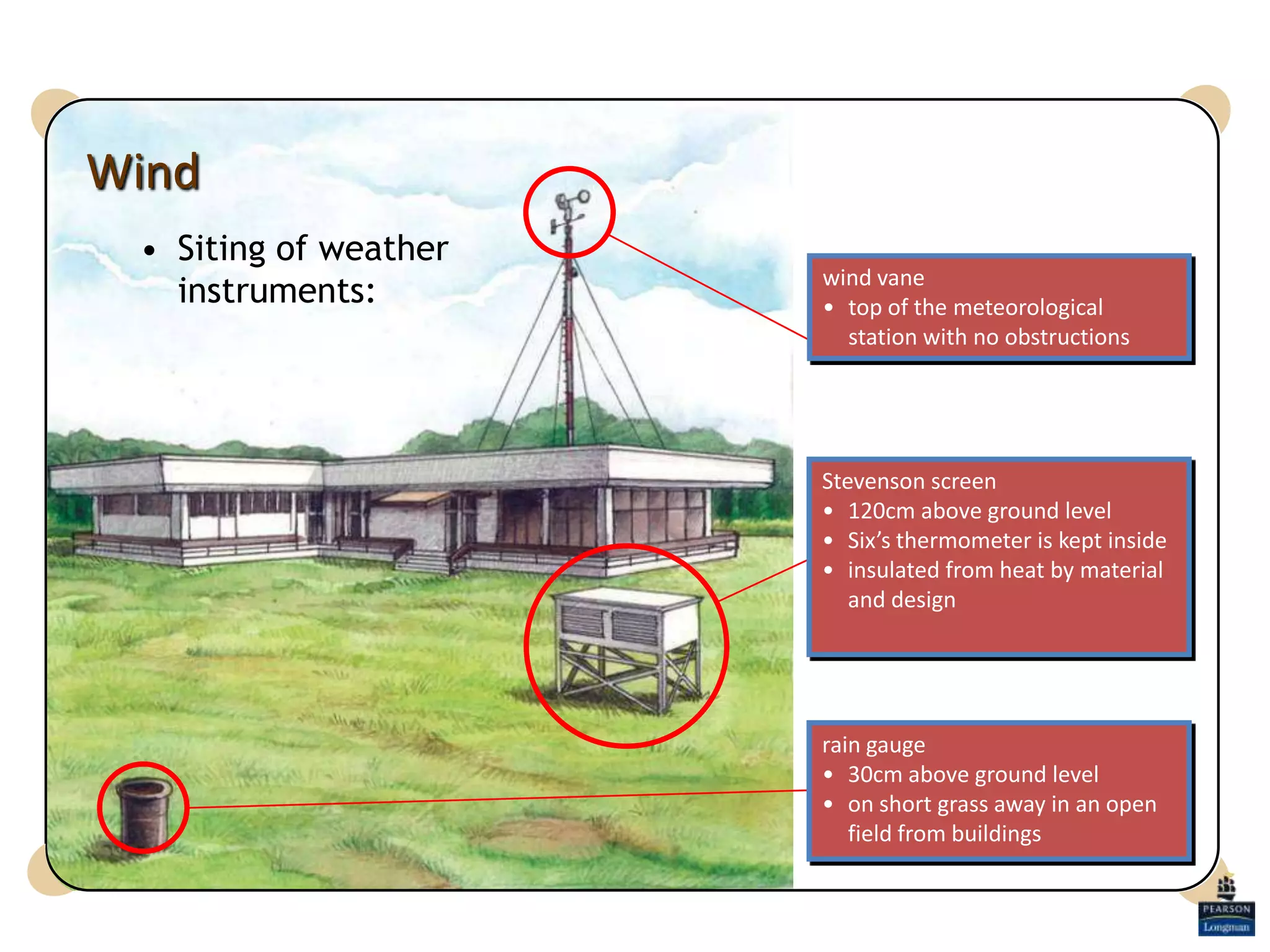
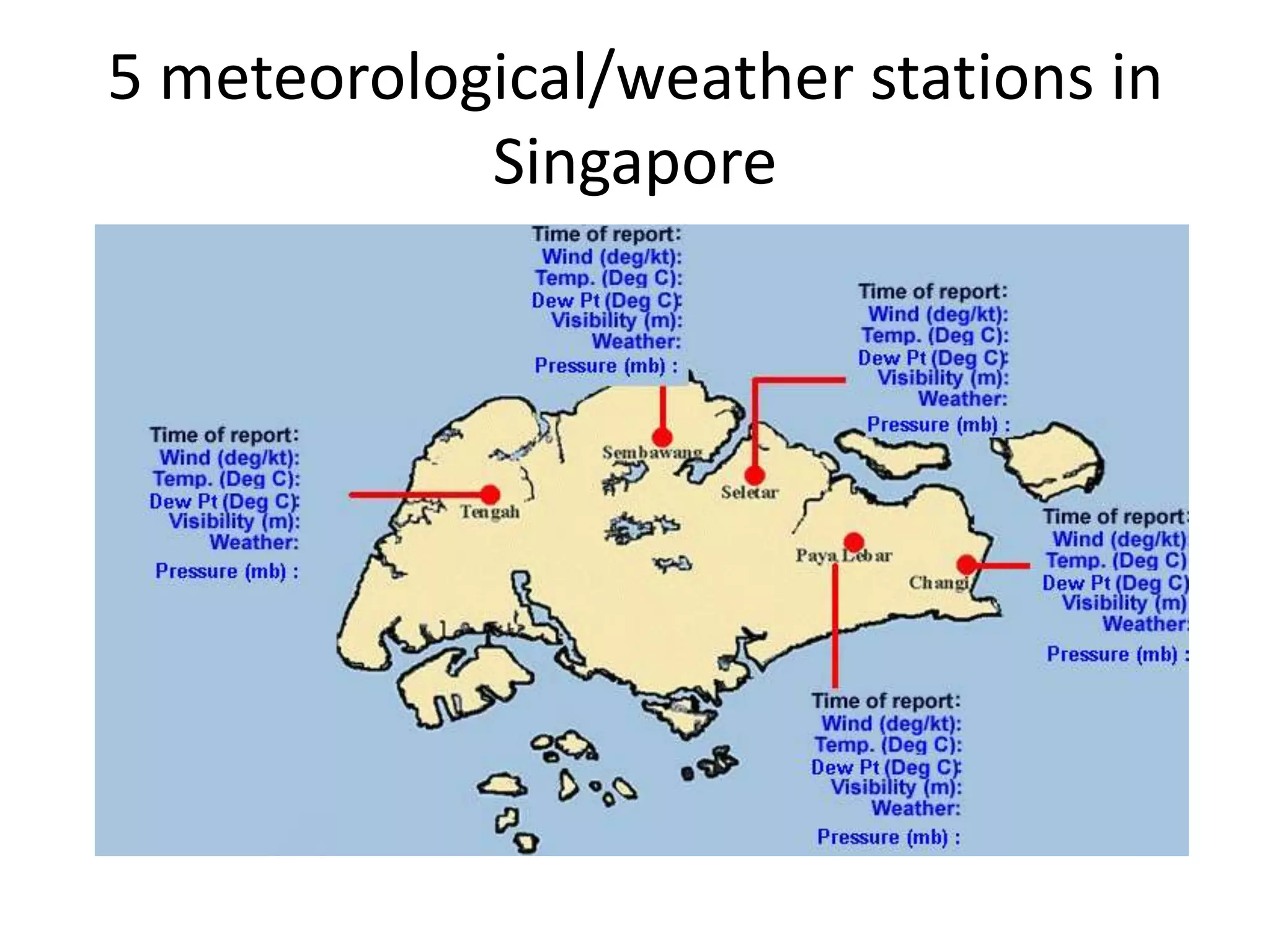
This document defines key weather elements and how they are measured. It describes weather as short-term atmospheric conditions while climate refers to long-term averages. Common instruments are discussed like the six's thermometer for temperature inside a Stevenson screen, the rain gauge for rainfall, and the wind vane and wind rose for wind direction and patterns. Formulas are provided for calculating daily, monthly, and annual averages of temperature and rainfall from collected data. Proper siting of instruments is also outlined.