Embed presentation

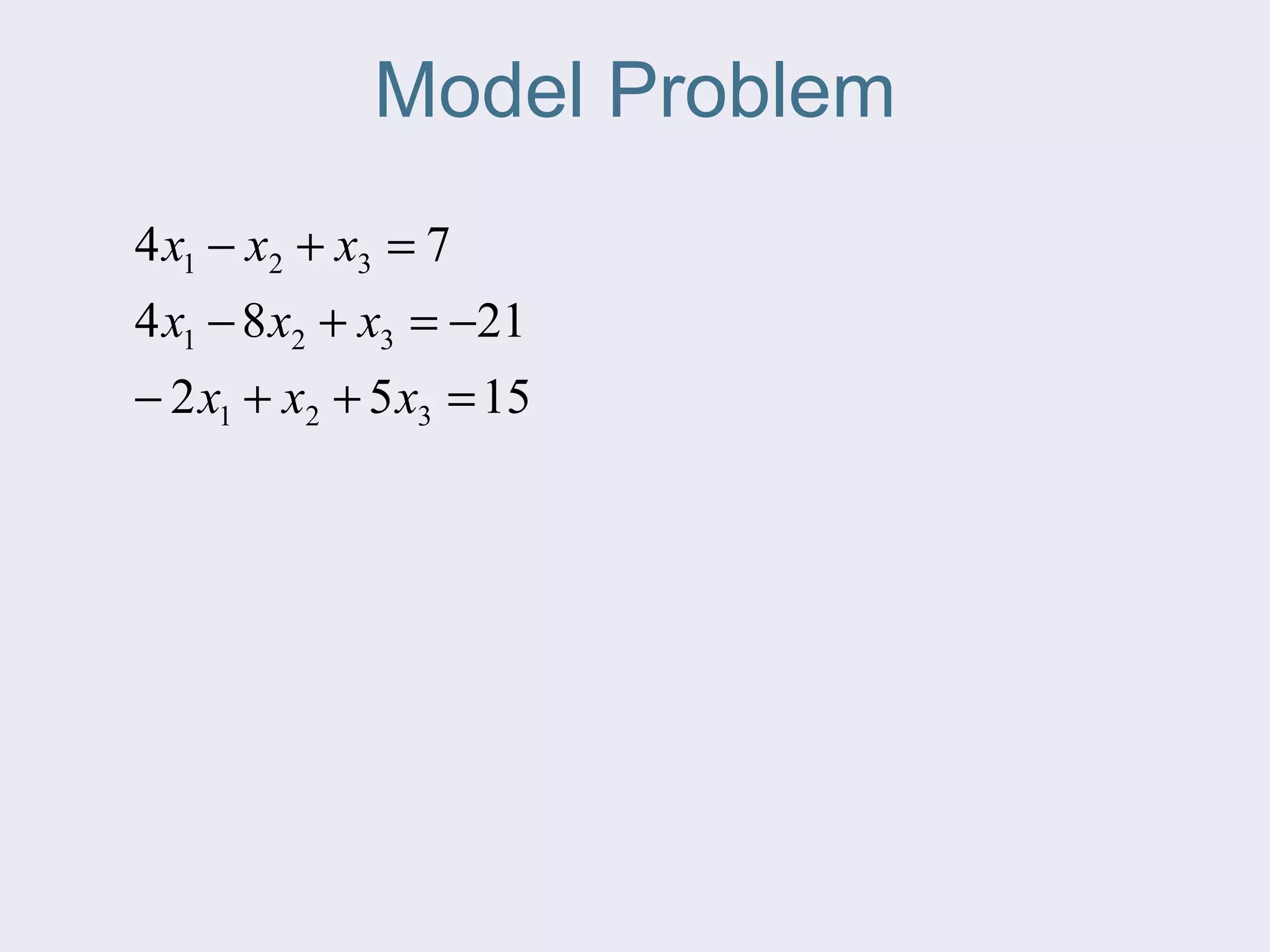
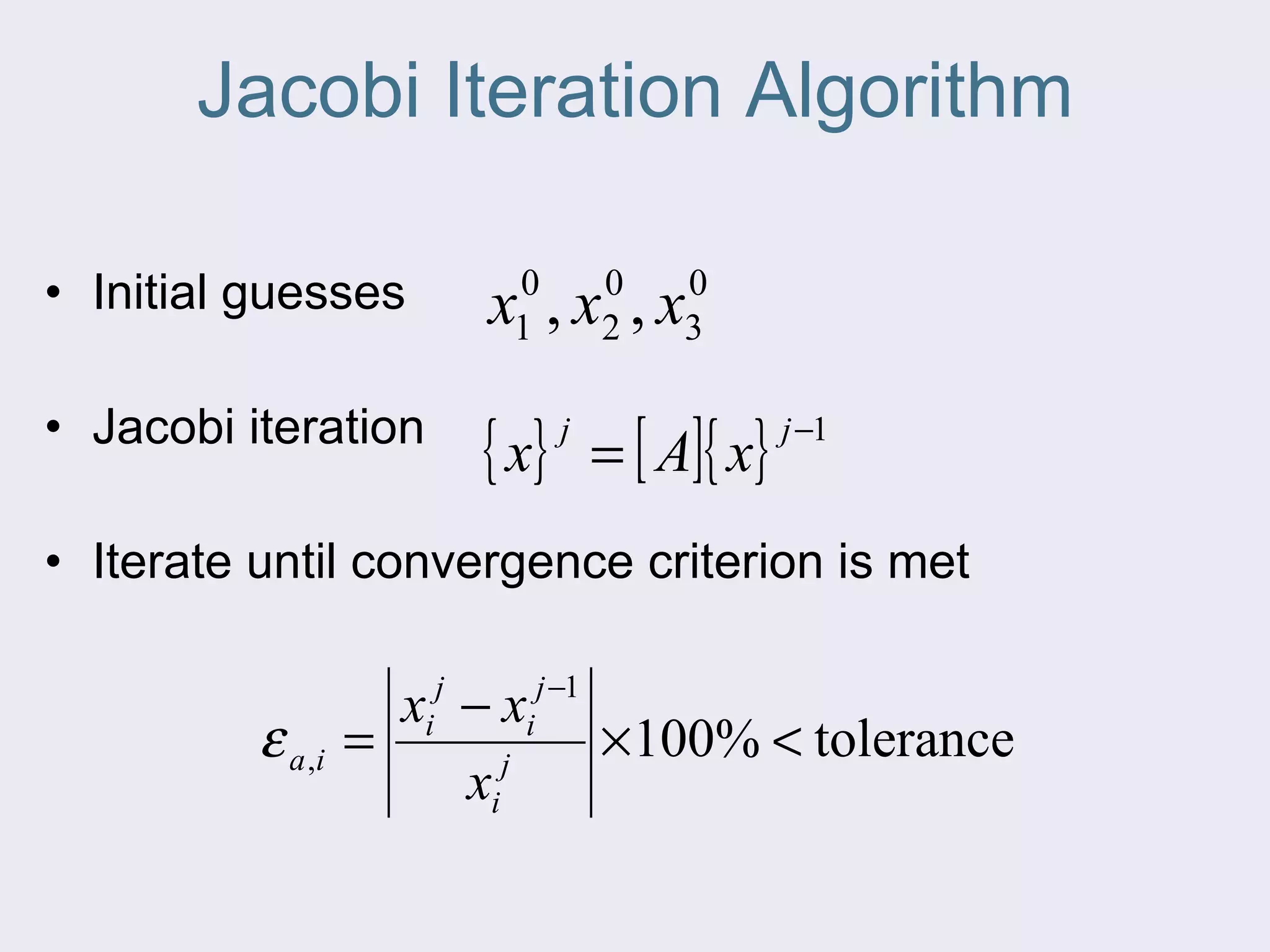
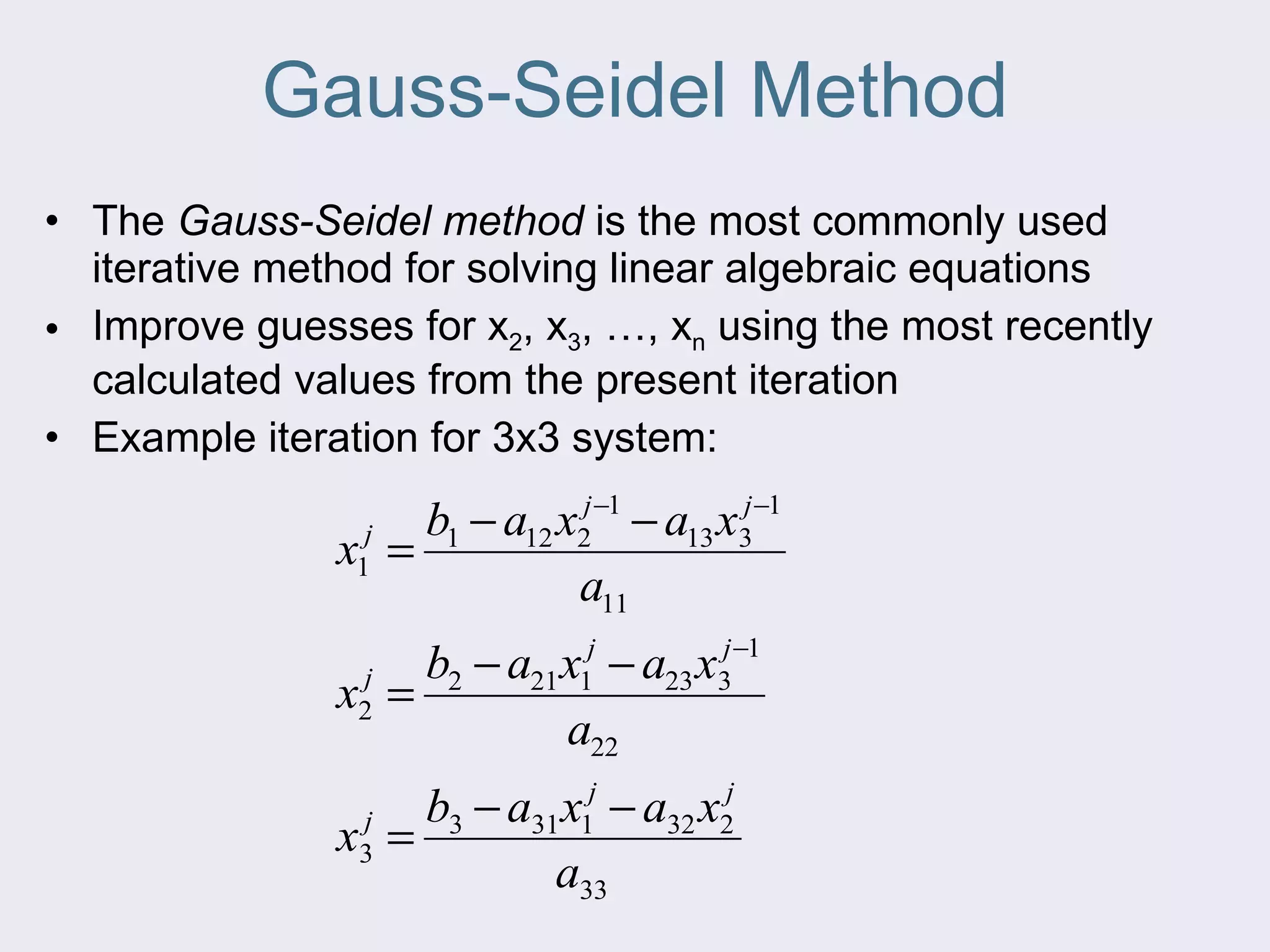
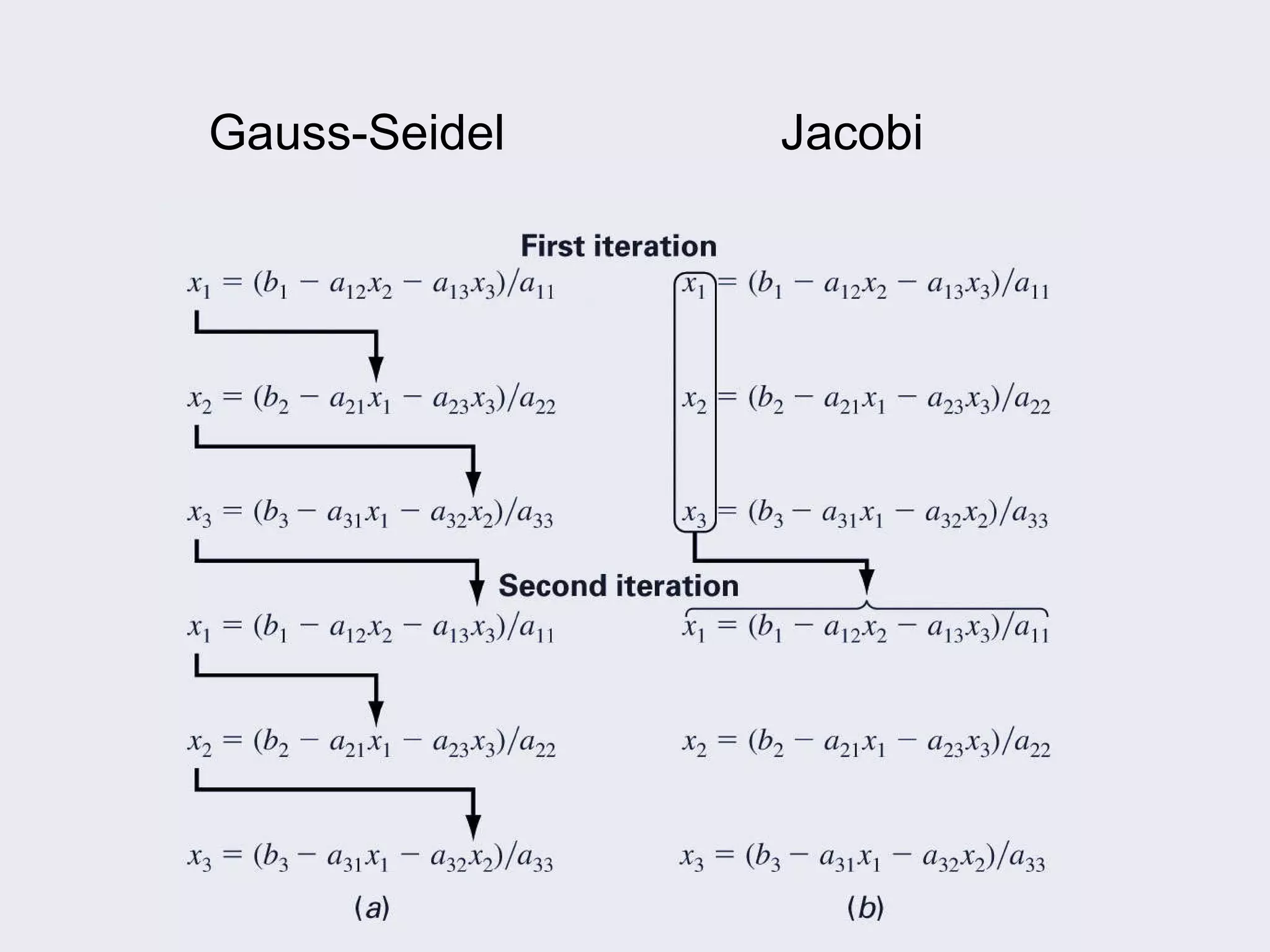
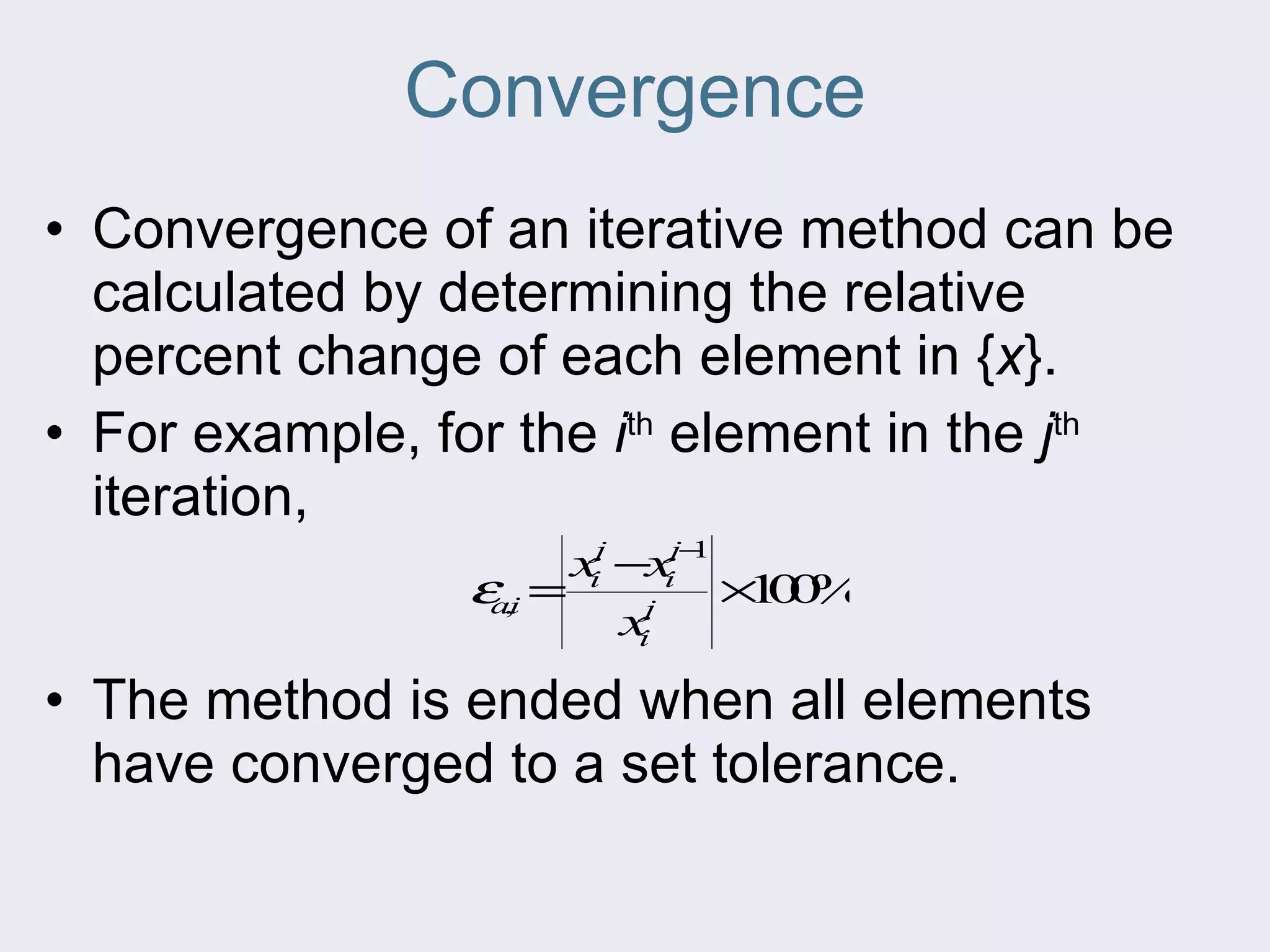
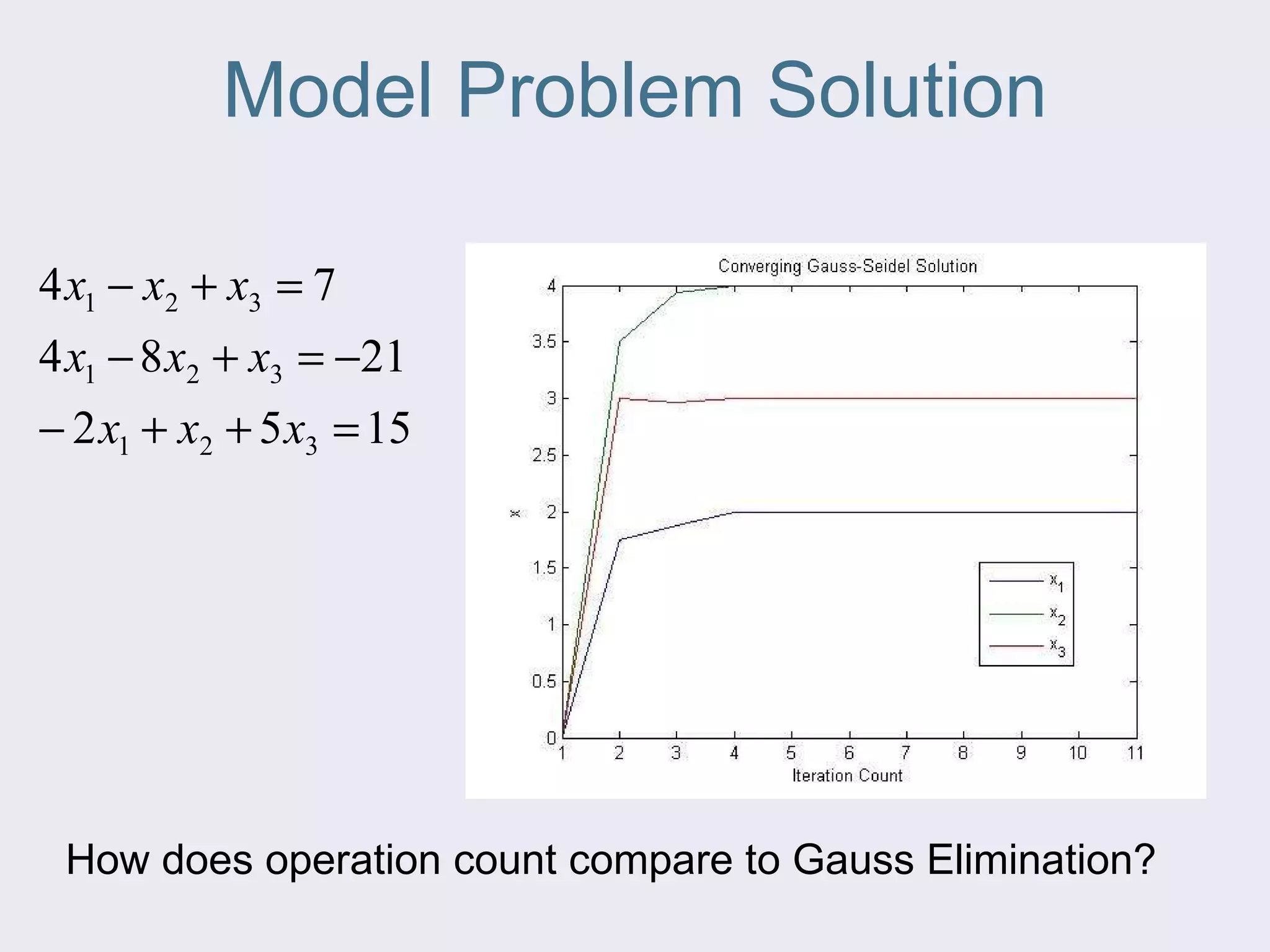
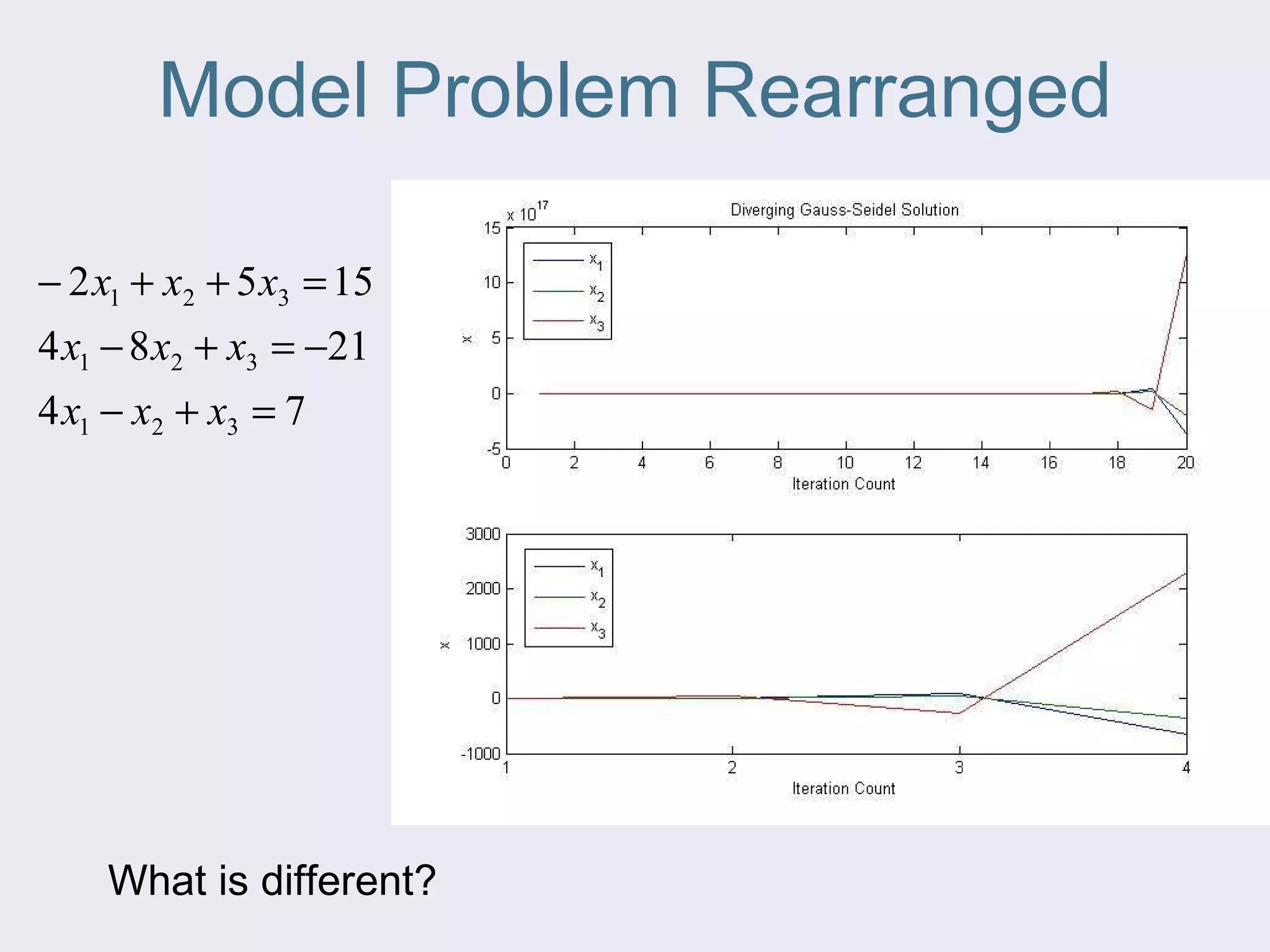
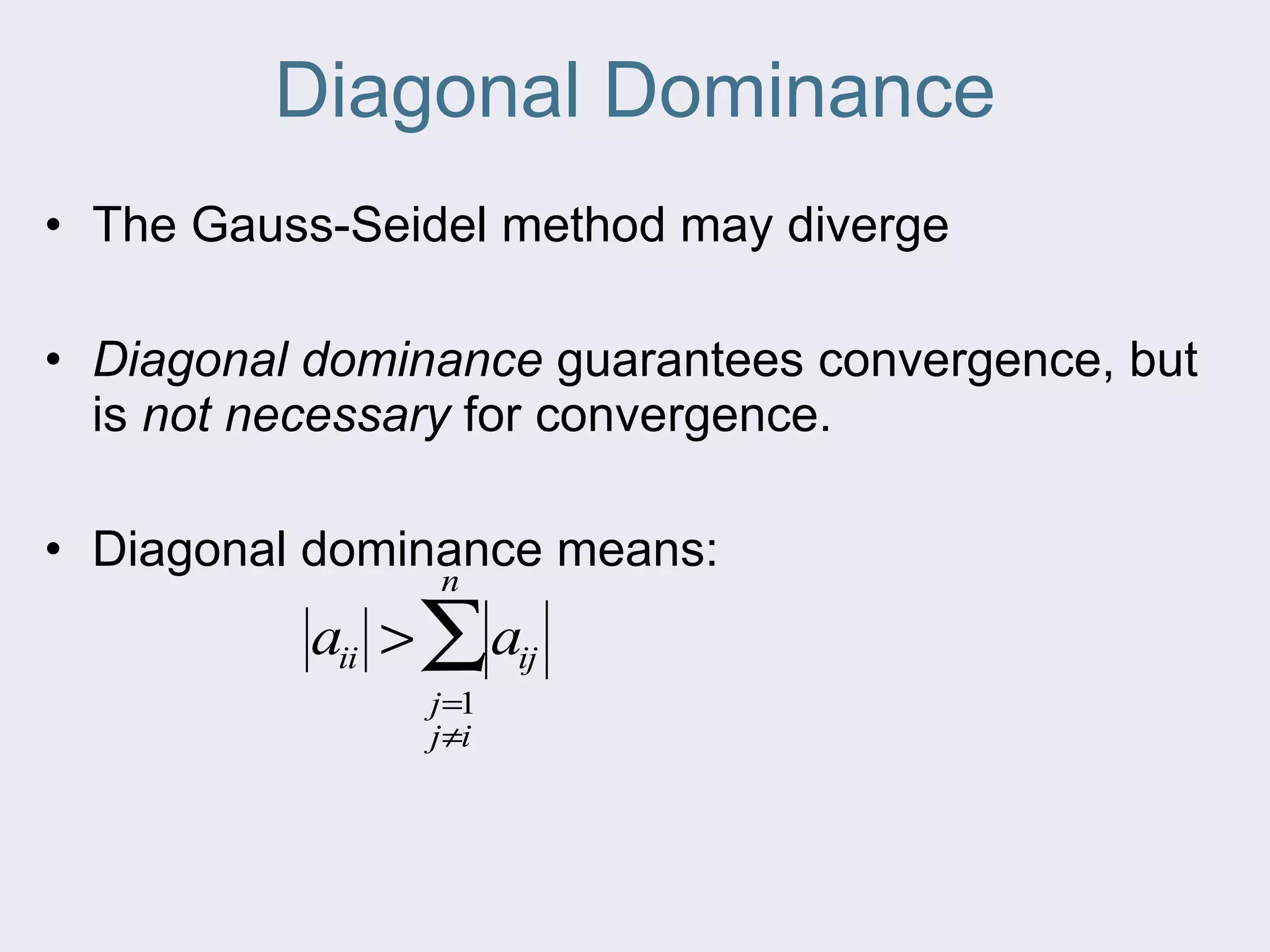
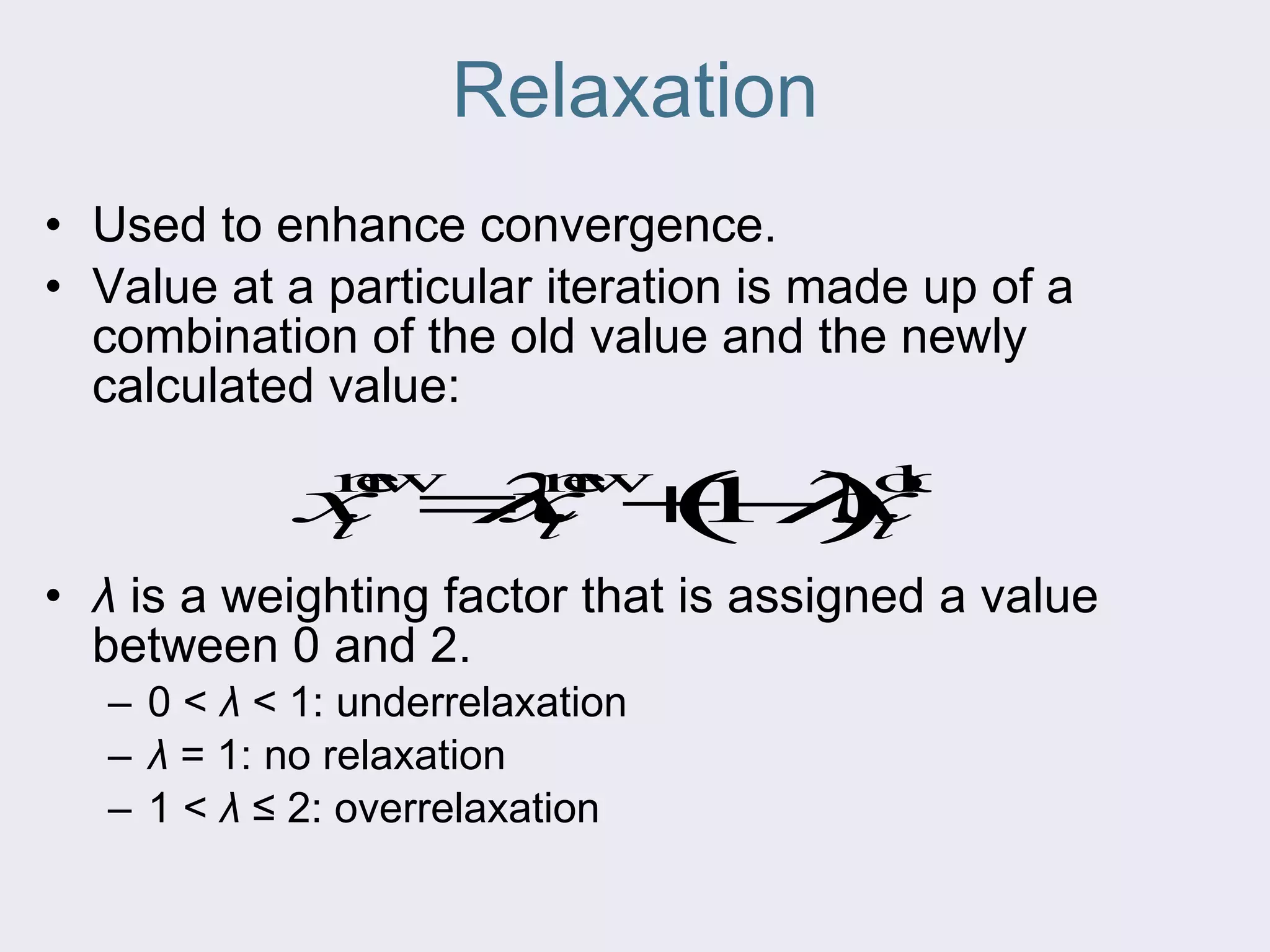
The document discusses several iterative methods for solving systems of equations, including Jacobi iteration, Gauss-Seidel method, and relaxation methods. The Gauss-Seidel method is commonly used and improves guesses for unknowns using values from the current iteration. Convergence is determined by calculating the relative percent change between iterations. Relaxation methods can enhance convergence by taking a weighted average of old and new values at each iteration.









