This document discusses various methods of transistor biasing:
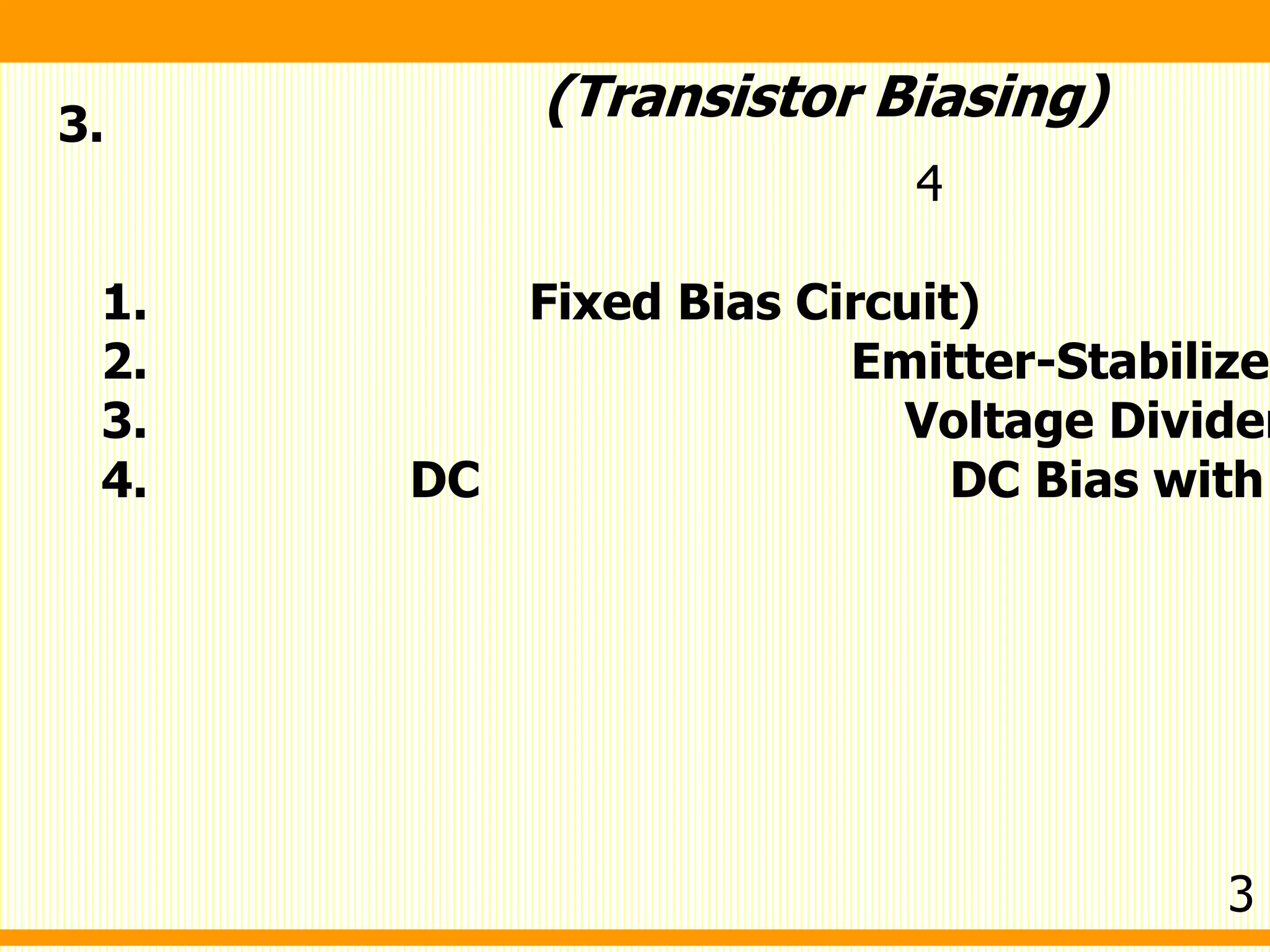
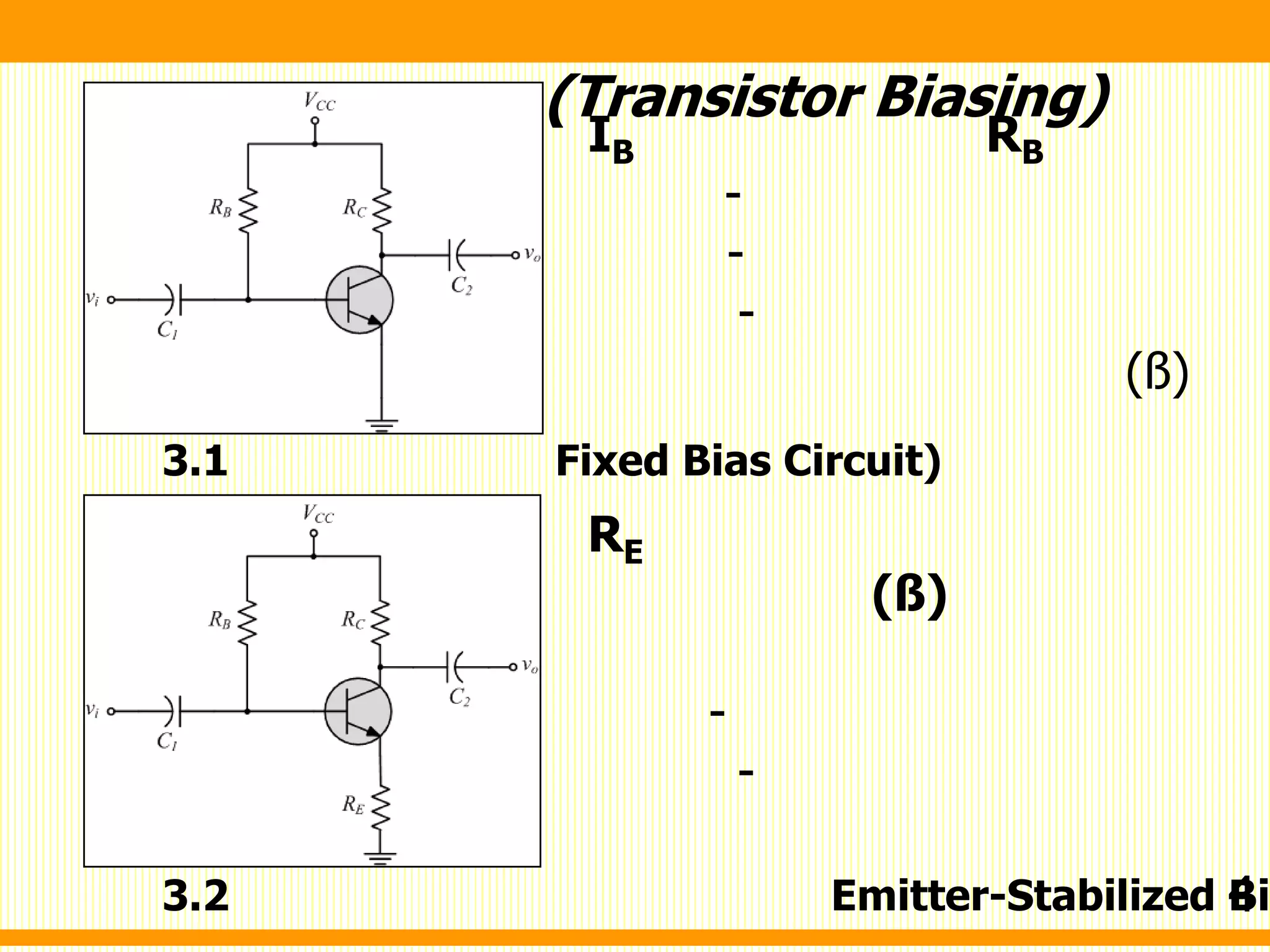
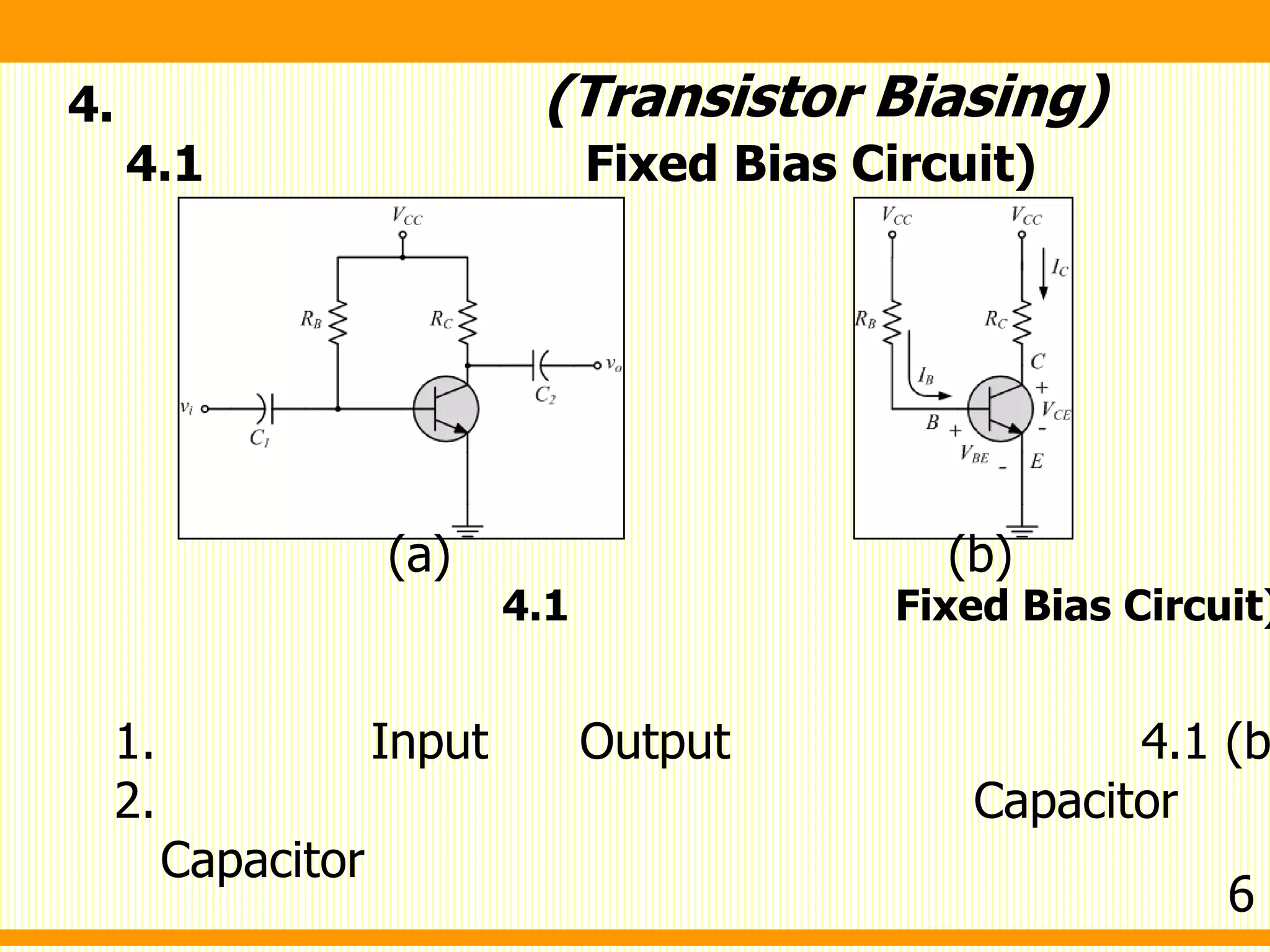
1. Fixed bias circuit - Applies a fixed voltage at the base through a resistor to establish a quiescent operating point.
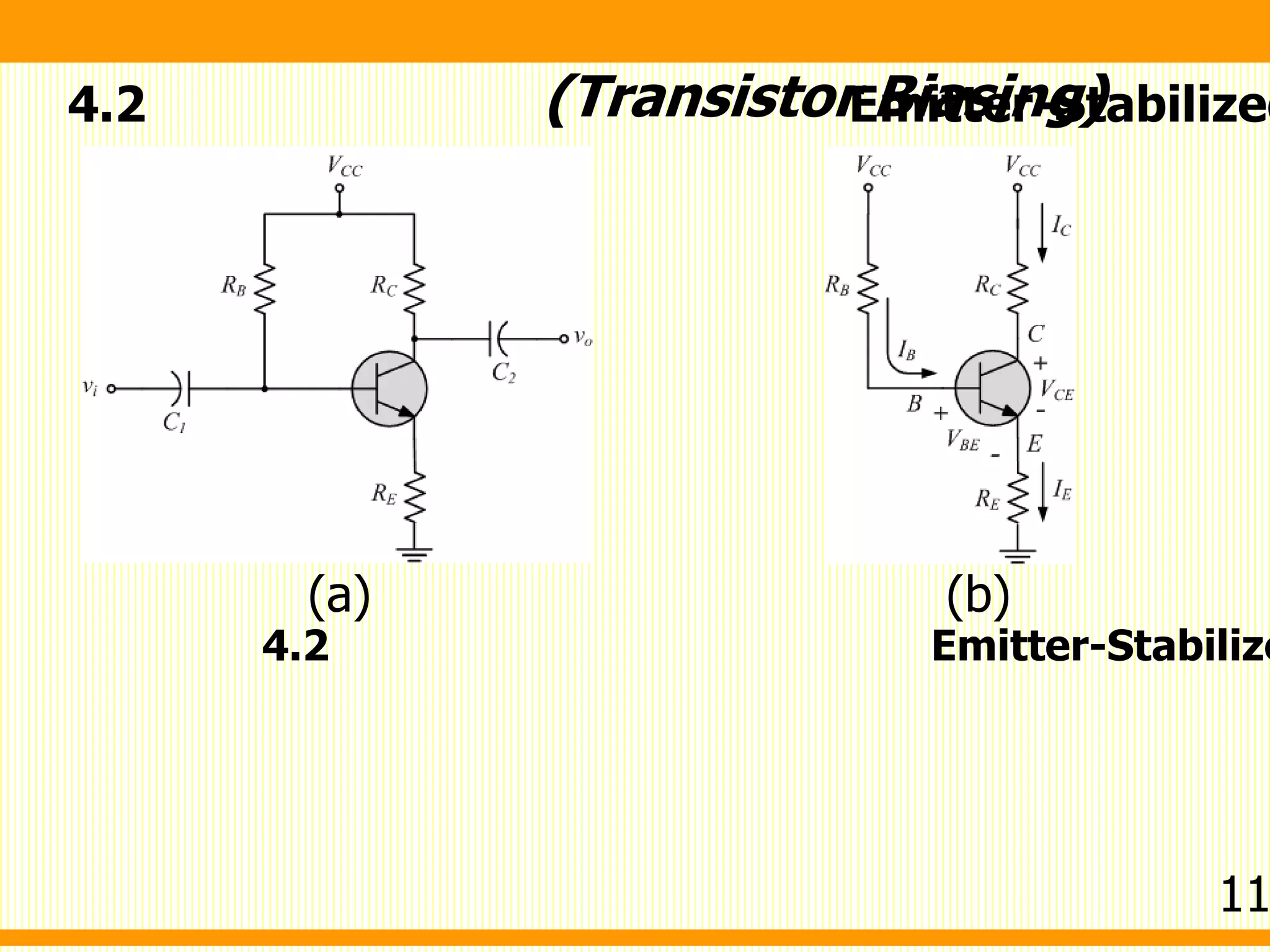
2. Emitter-stabilized bias - Uses feedback from the emitter leg to stabilize the operating point. A resistor between the emitter and ground provides feedback.
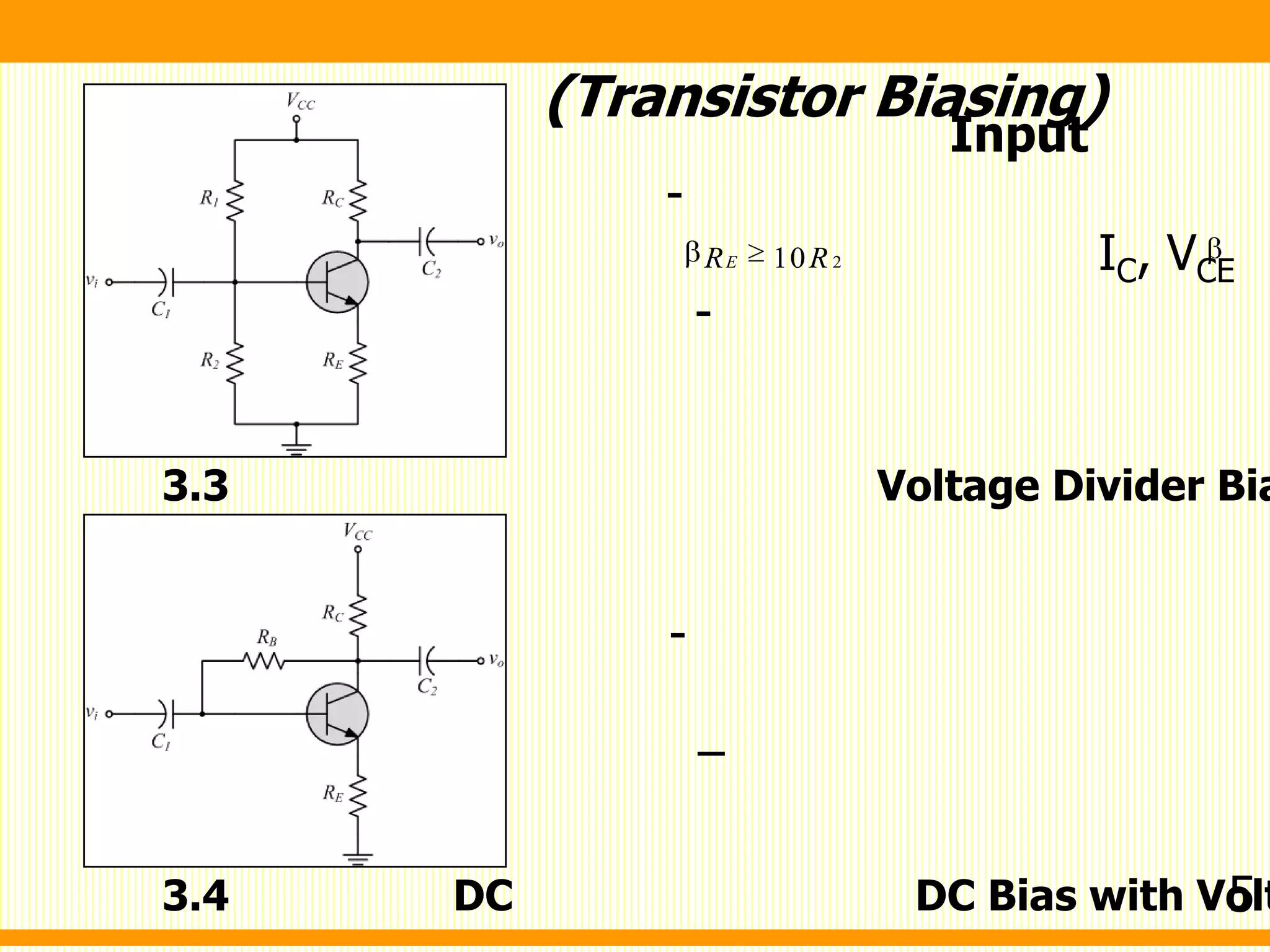
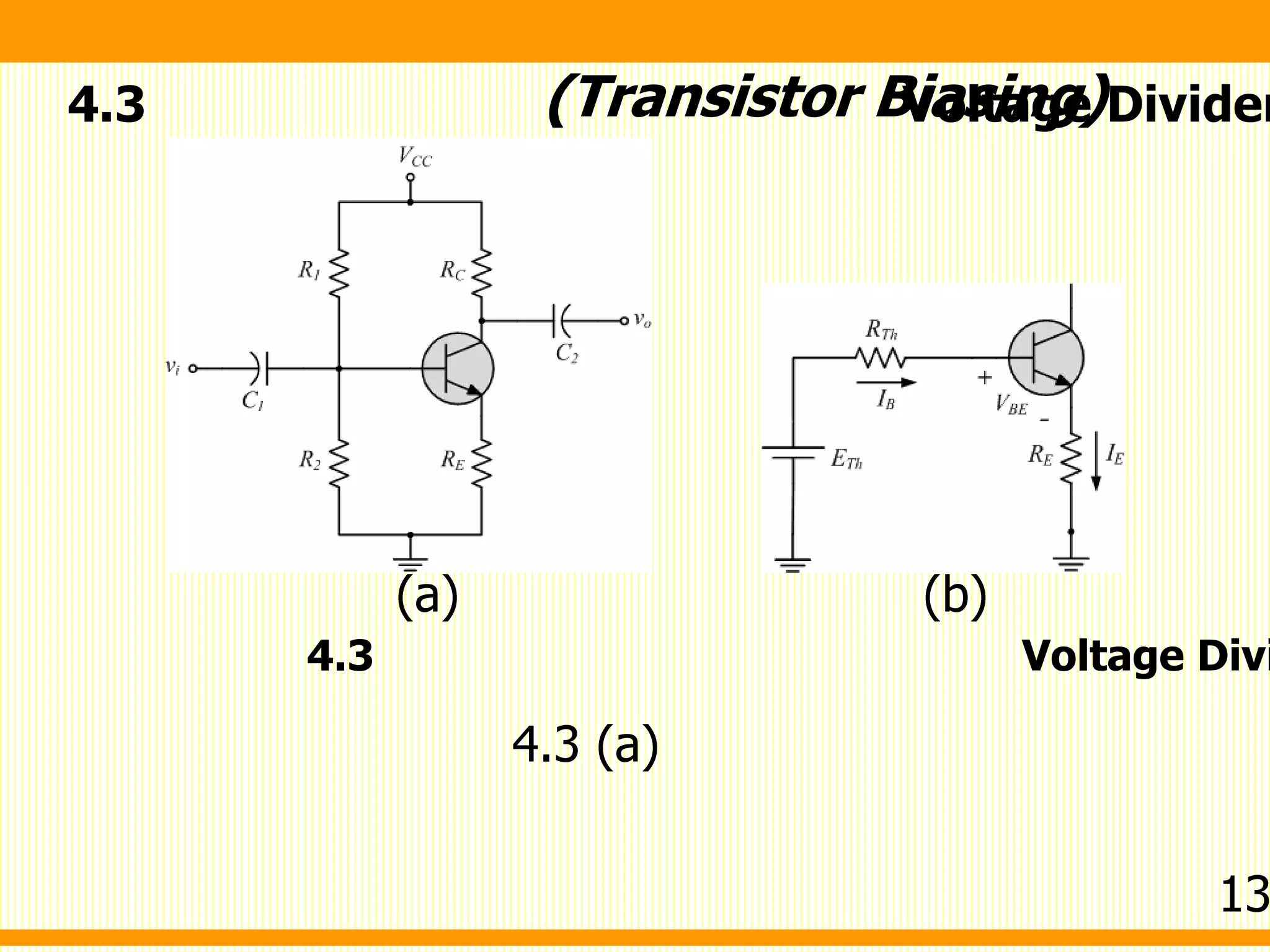
3. Voltage divider bias - Applies bias through a resistor voltage divider network between the power supply and ground, establishing the base voltage automatically as the transistor draws current.

![0
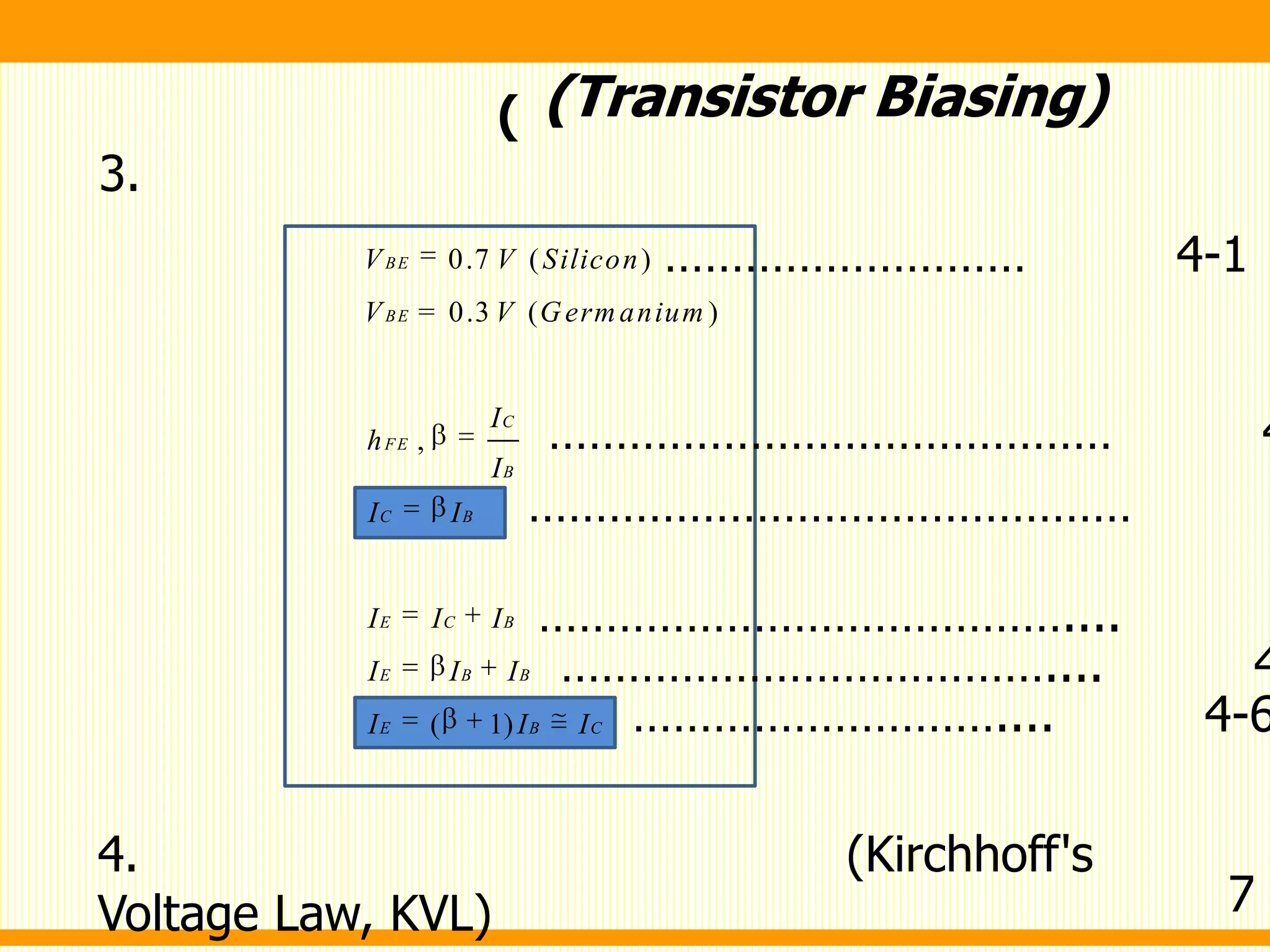
( 1)
( 1) 0
( 1)
[ ( 1) ]
-
( 1)
CC B B BE E E
E B
CC BE B B B E
CC BE B B B E
CC BE B B E
CC BE
B
B E
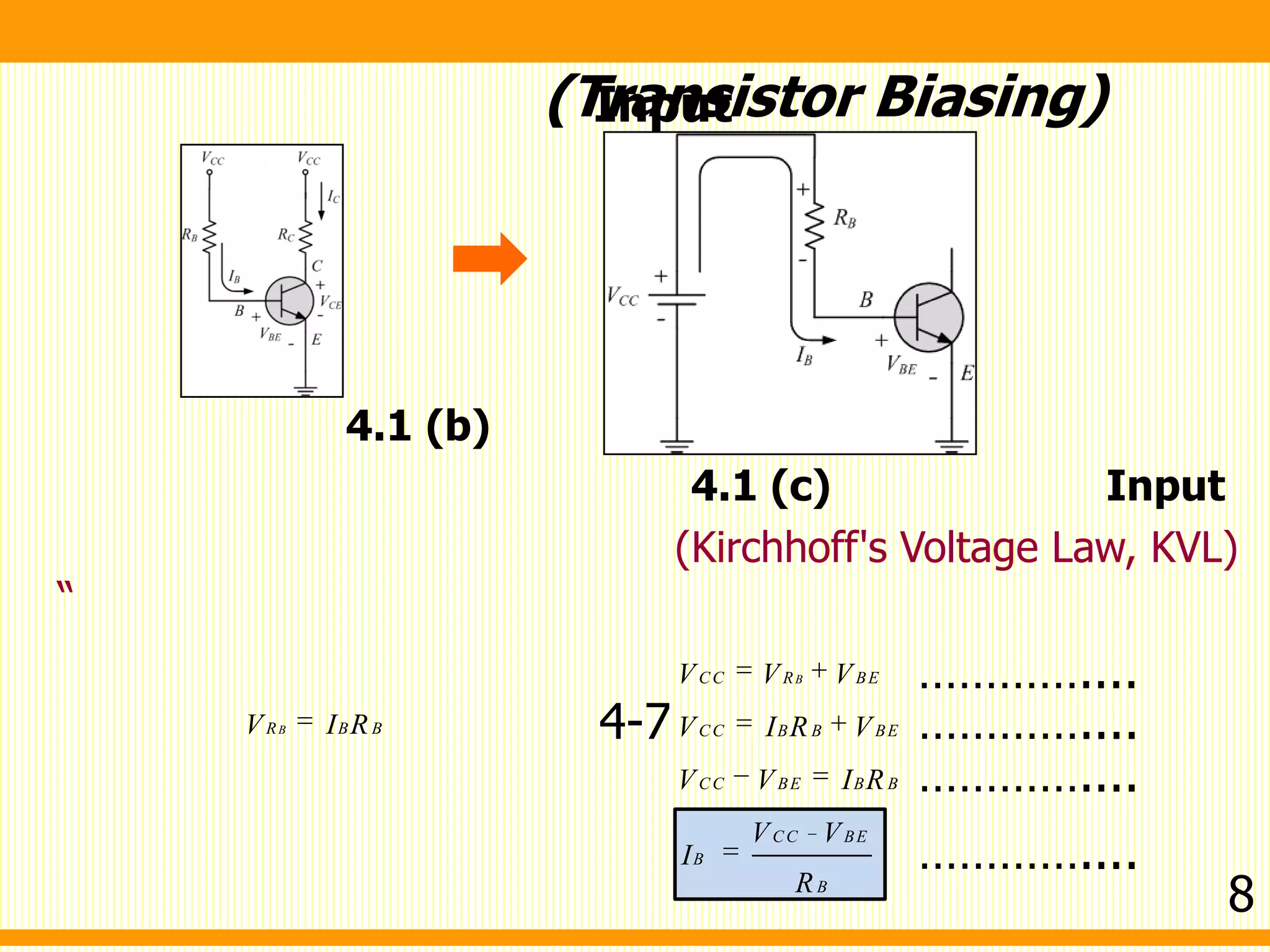
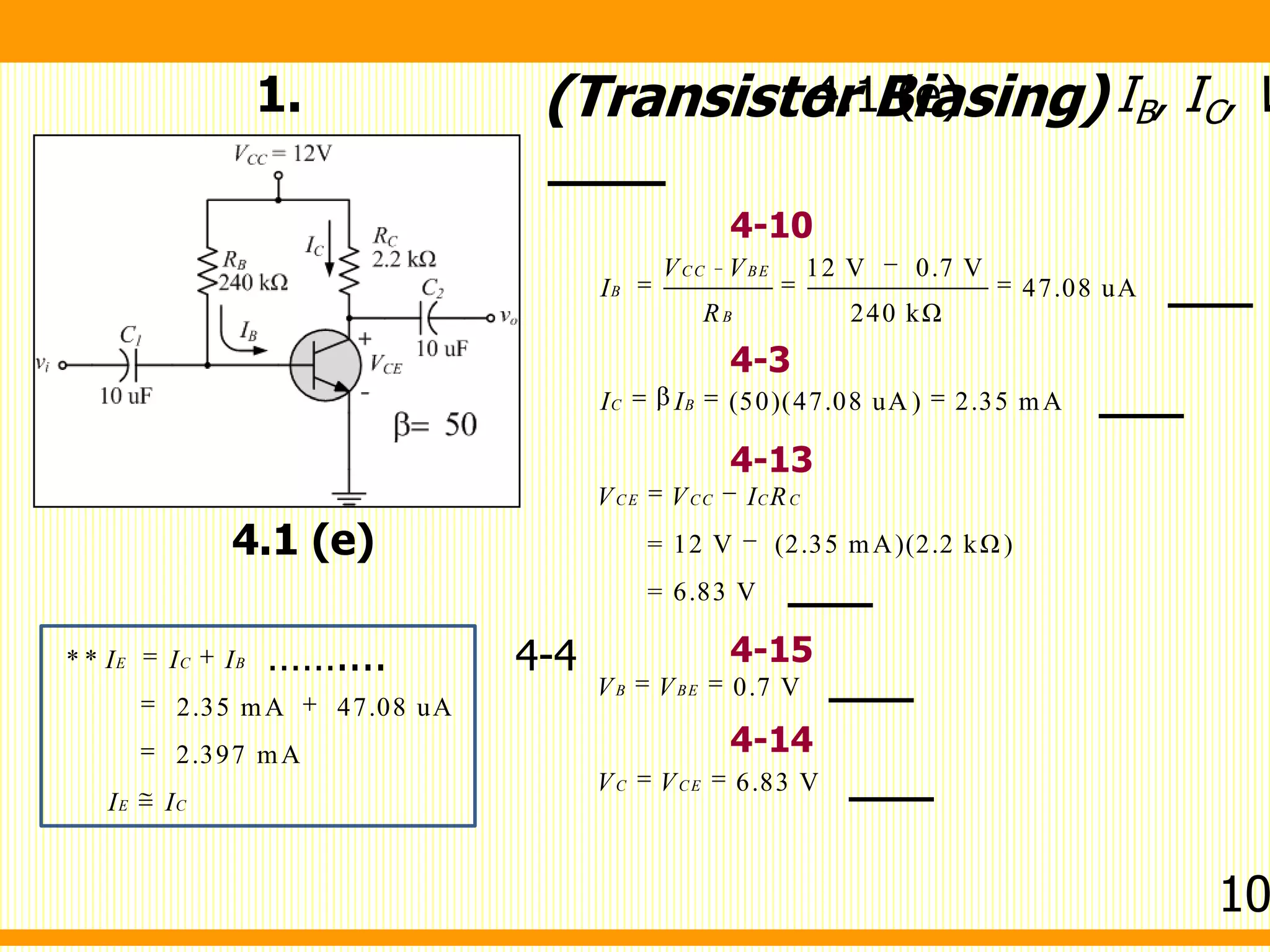
V I R V I R
I I
V V I R I R
V V I R I R
V V I R R
V V
I
R R
0
0
( ) 0
( )
CC C C CE E E
E C
CC C C CE C E
CC CE C C E
CE CC C C E
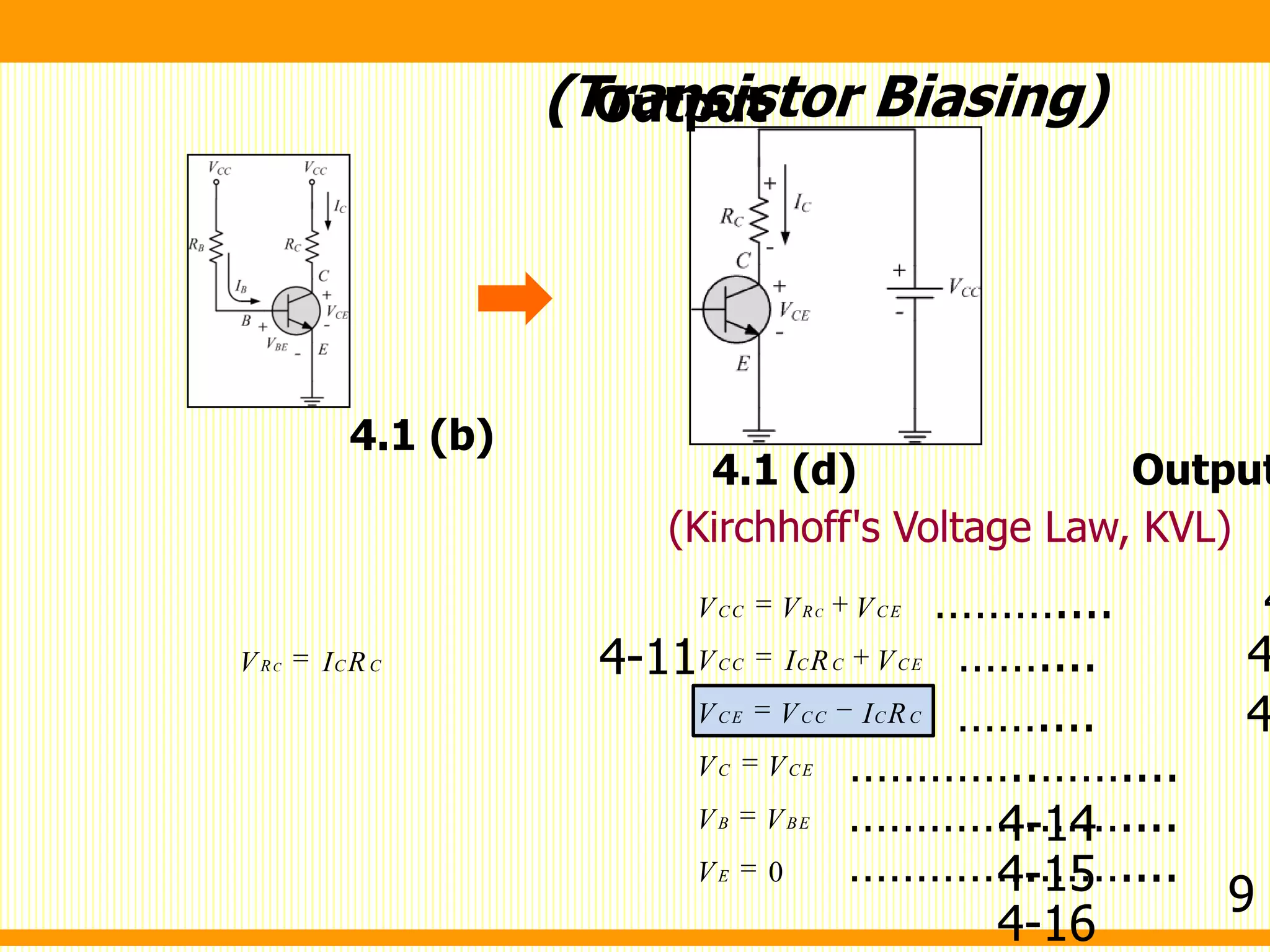
V I R V I R
I I
V I R V I R
V V I R R
V V I R R
(Transistor Biasing)
4.2 (c) Input 4.2 (d) O
…. 4-6 …. 4-6
…....
4-17
….
4-18
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transistorbiascircuit-130928041929-phpapp01/75/Transistor-bias-circuit-14-2048.jpg)
![1 2ThR R R
1 2
2
1 2
2
1 2
1 2
1
2
2
( )
[ ]
CC R R
CC
CC
Th R
CC
Th
V V V IR IR
V I R R
V
I
R R
E V IR
V
E R
R R
(Transistor Biasing)
4.3 (c) 4.3 (d)
4.3 (e) VR2
…..…..….
4-19
...…..….
4-20
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transistorbiascircuit-130928041929-phpapp01/75/Transistor-bias-circuit-16-2048.jpg)
![0
( 1)
( 1) 0
( 1)
[ ( 1) ]
-
( 1)
Th B Th BE E E
E B
Th BE B Th B E
Th BE B Th B E
Th BE B Th E
Th BE
B
Th E
E I R V I R
I I
E V I R I R
E V I R I R
E V I R R
E V
I
R R
(Transistor Biasing)
4.3 (f) ...…..….
4-21
Output
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transistorbiascircuit-130928041929-phpapp01/75/Transistor-bias-circuit-17-2048.jpg)
![' 0
'
' ,
0
0
= ( )
[ ( )]
CC C C B B BE E E
C B C
C C E C
CC C C B B BE C E
C B
CC B C B B BE B E
CC BE B C B B B E
B C B E
CC BE B B C E
V I R I R V I R
I I I
I I I I
V I R I R V I R
I I
V I R I R V I R
V V I R I R I R
I R R R
V V I R R R
I
-
( )
CC BE
B
B C E
V V
R R R
(Transistor Biasing)4.4 DC DC Bias
with Voltage Feedback)
4.4 DC
...…..….
4-22
(a)
(b)
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transistorbiascircuit-130928041929-phpapp01/75/Transistor-bias-circuit-18-2048.jpg)